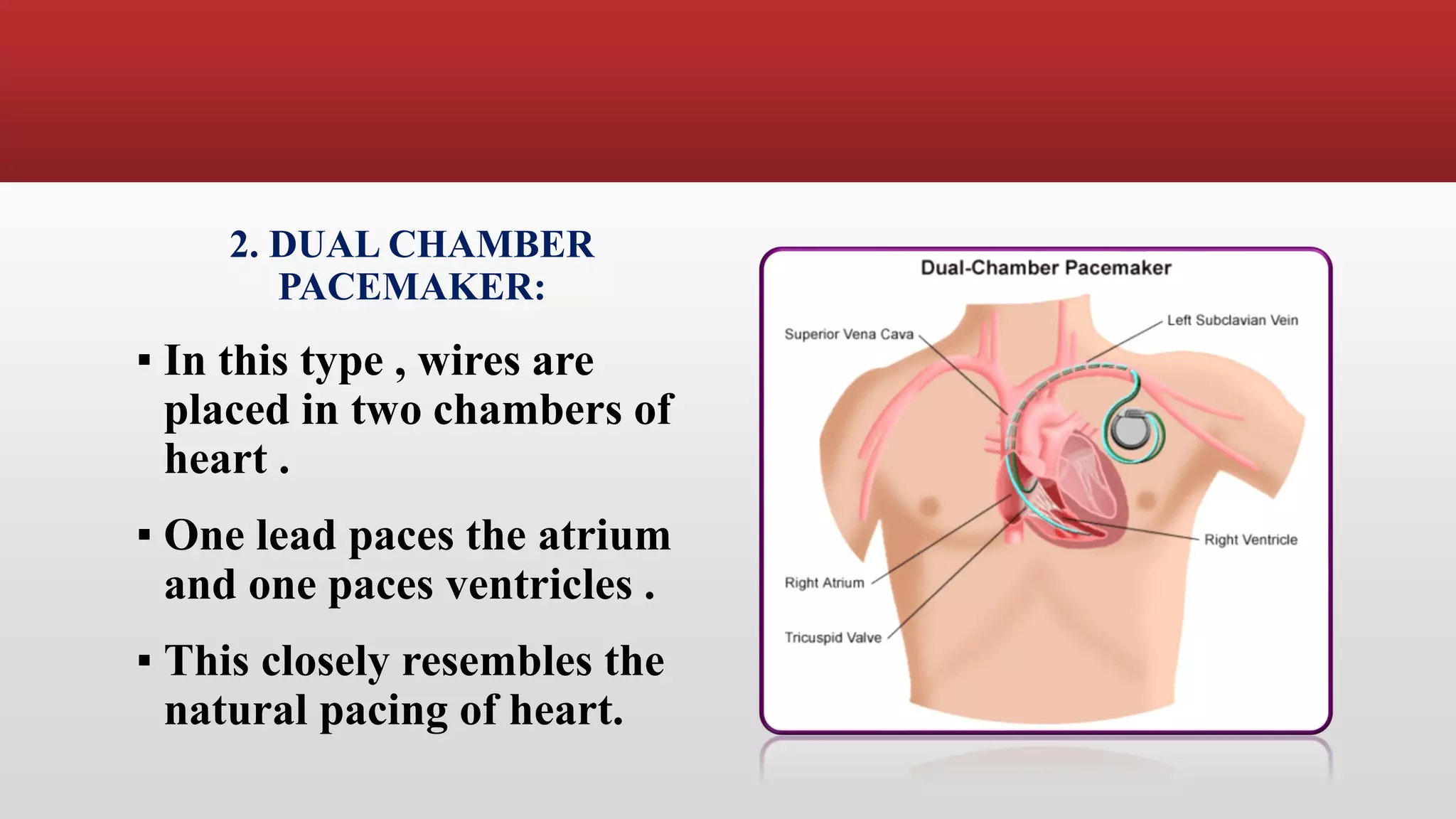
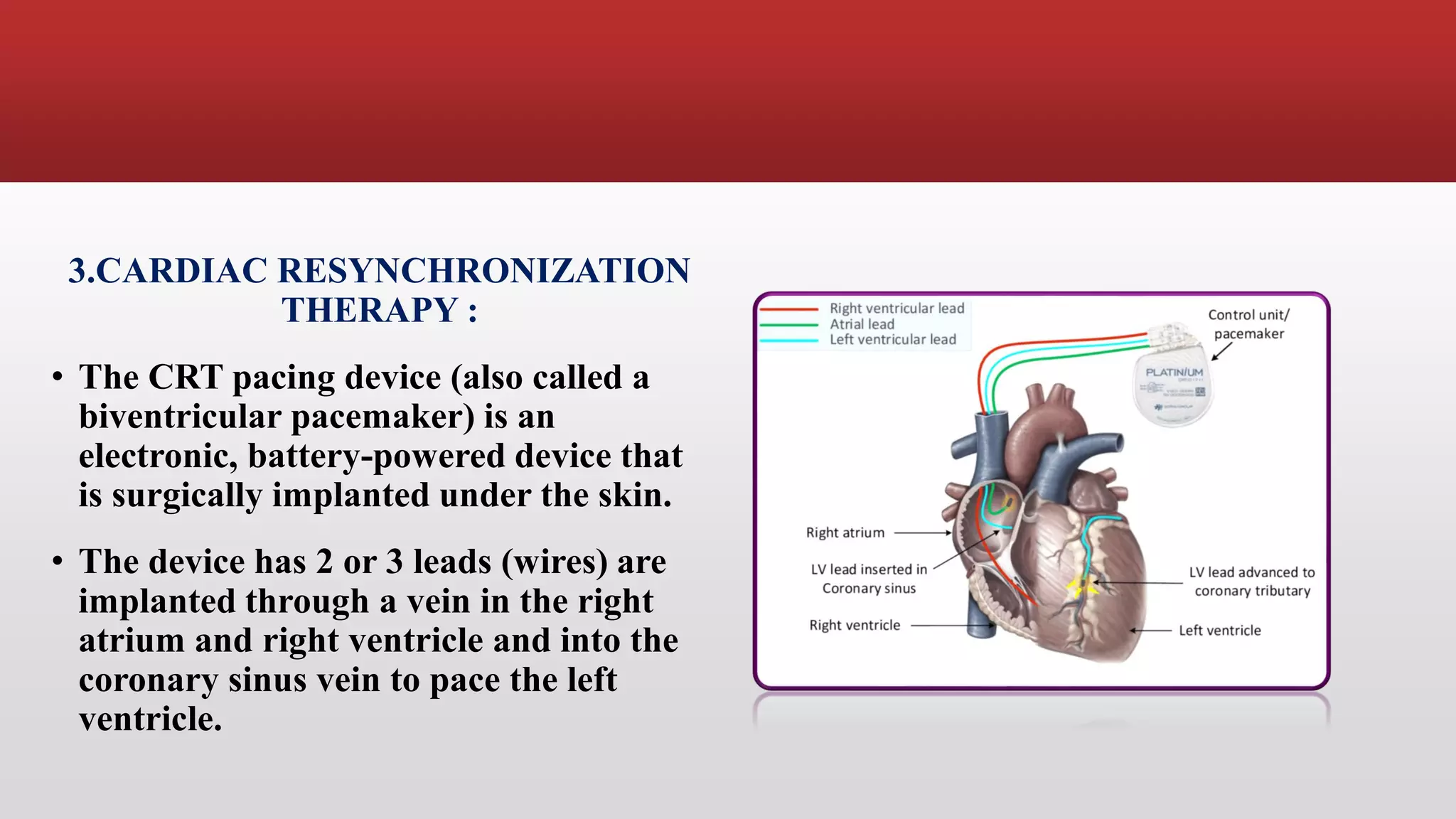
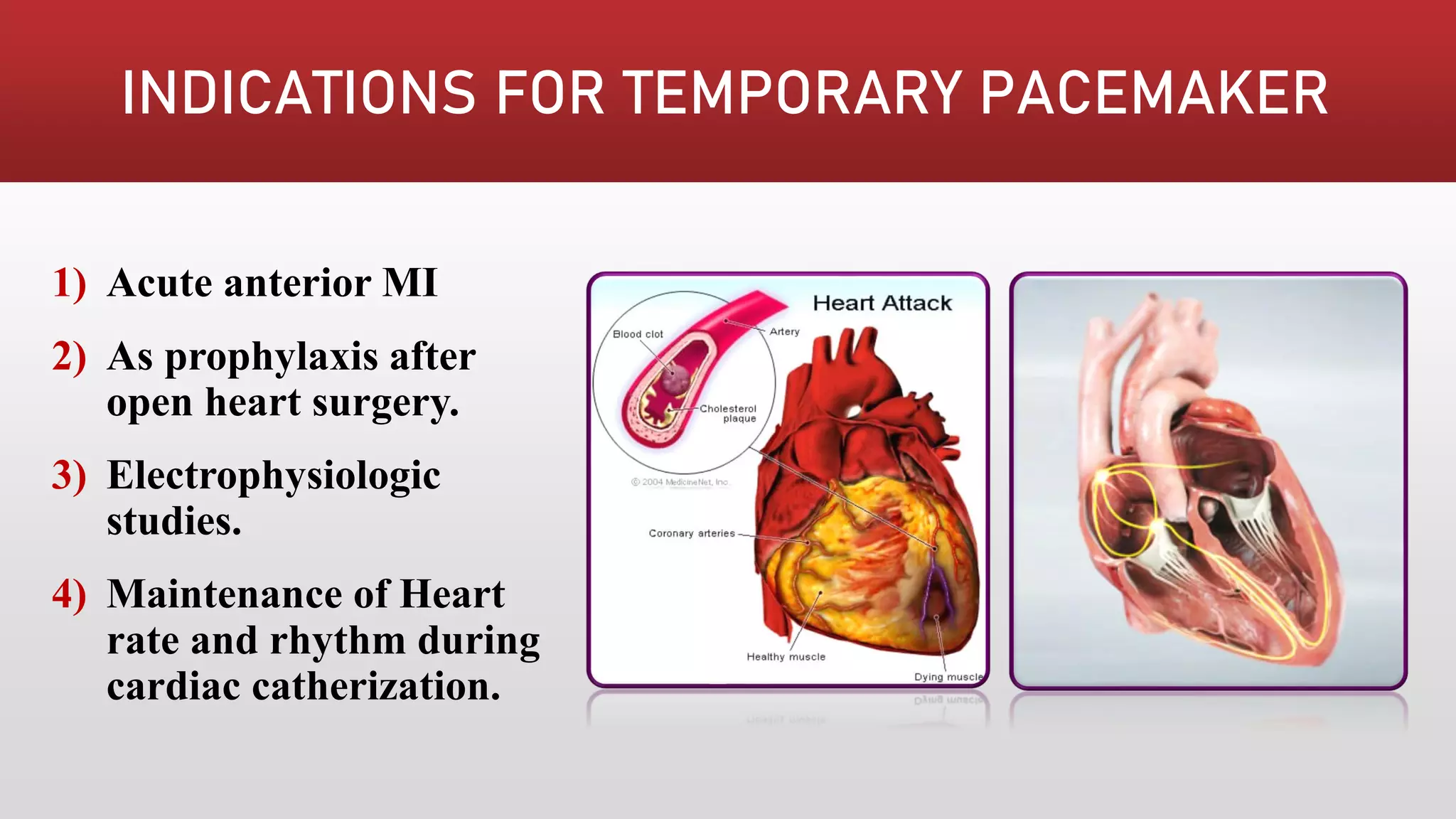
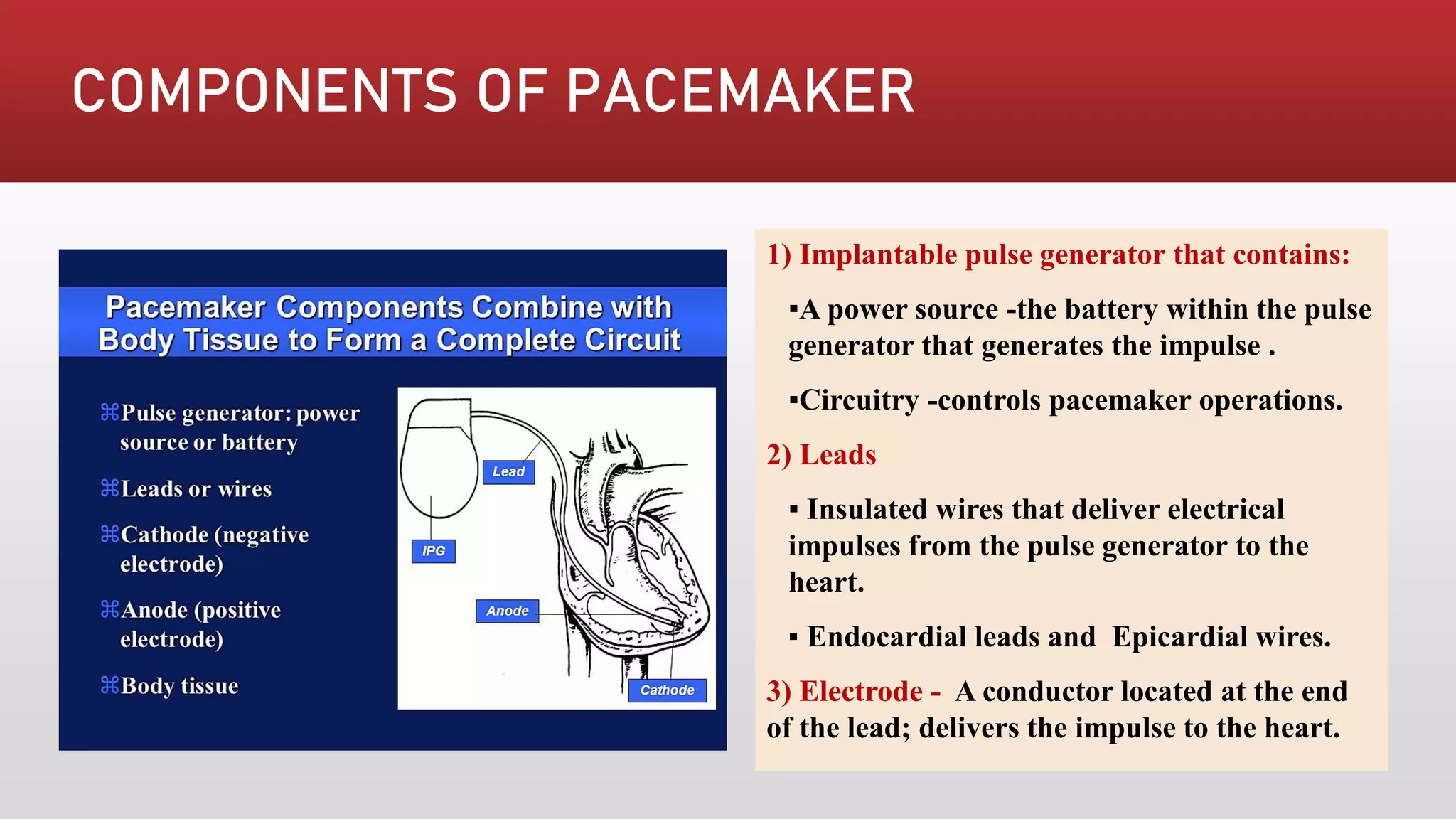
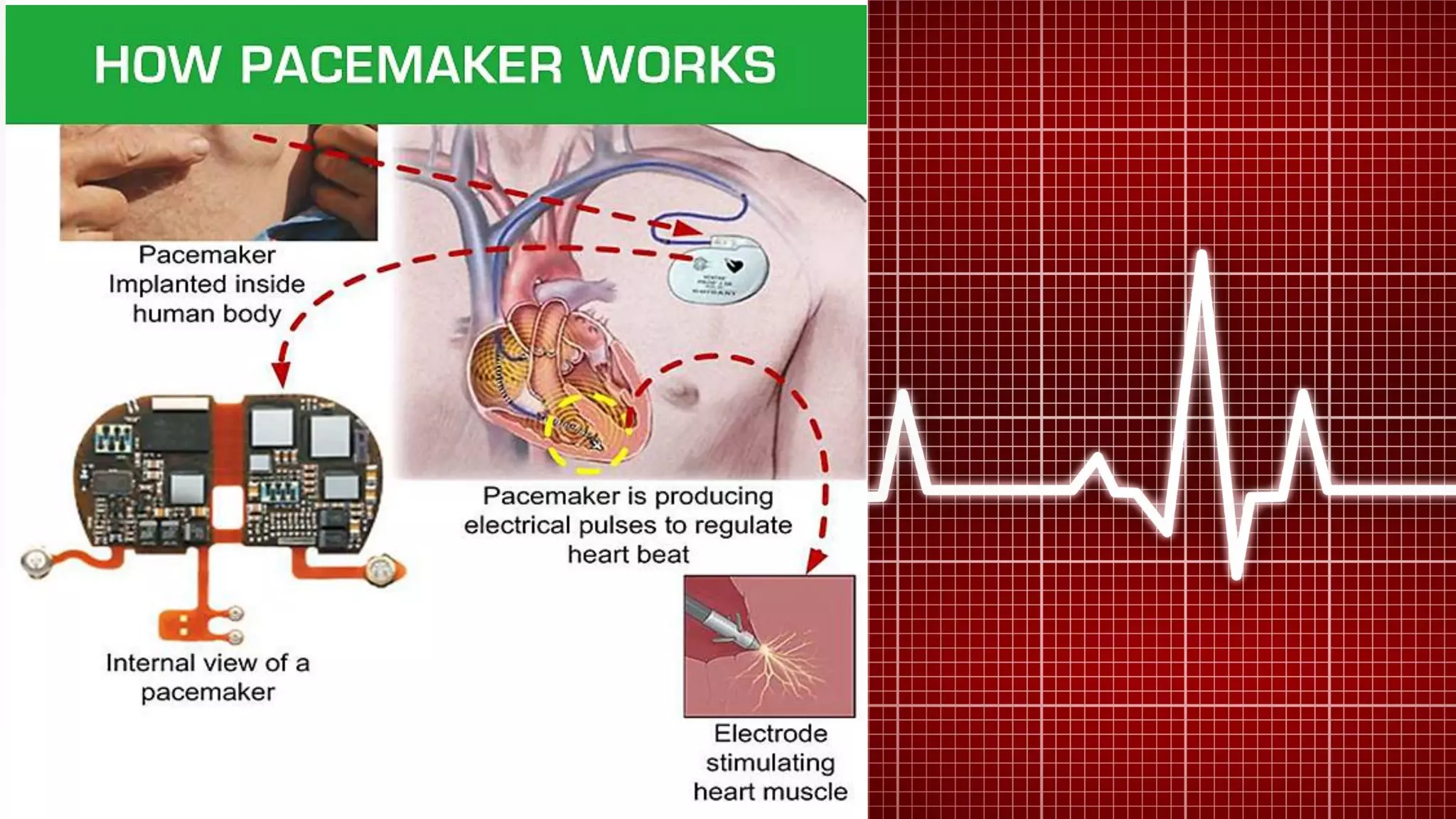
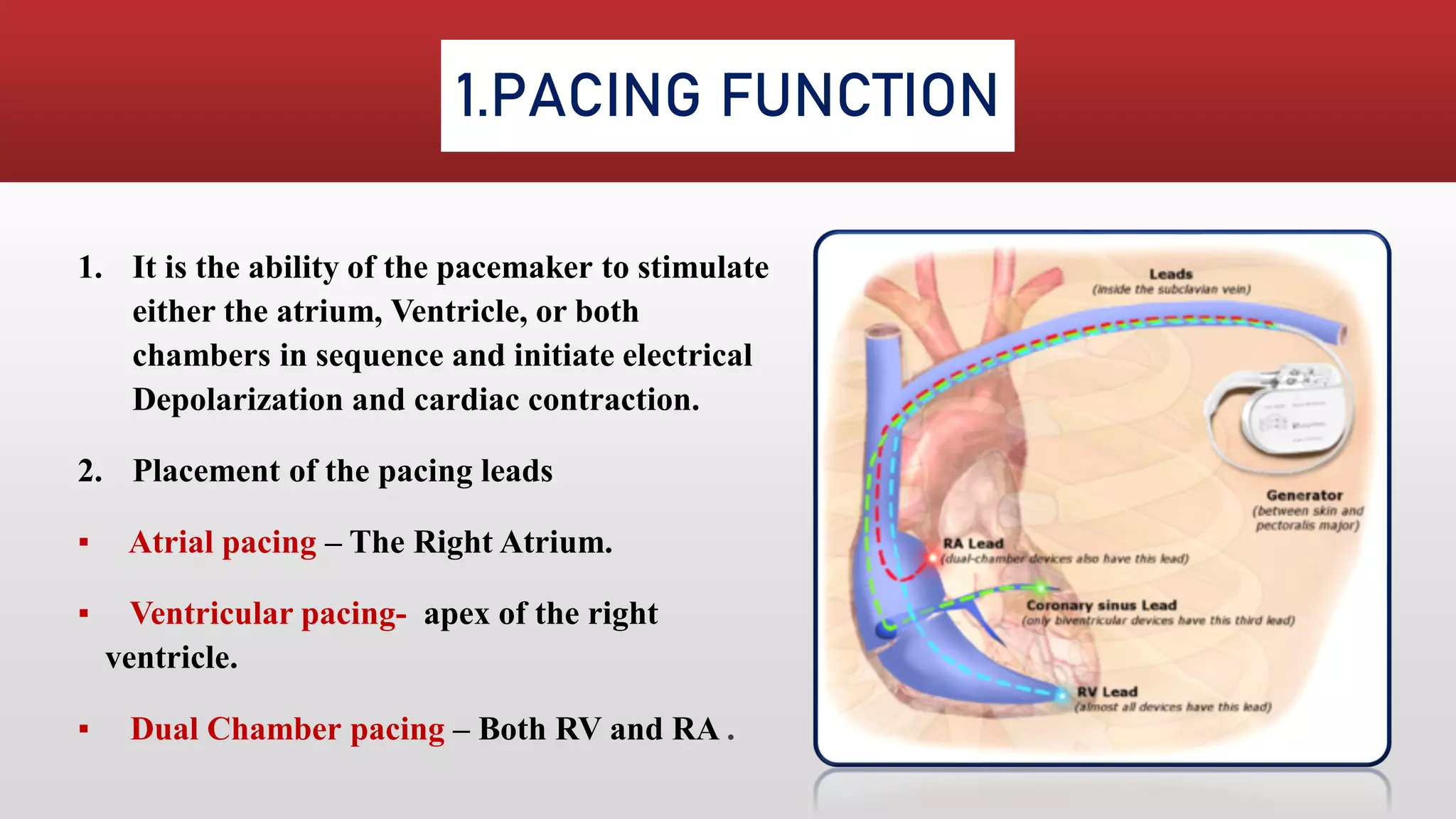
Pacemakers are electronic devices that are implanted to initiate heartbeat when the heart's intrinsic electrical system cannot generate an adequate rate. They consist of a pulse generator, leads, and electrodes. Pacemakers have evolved significantly from early external and bulky models to current miniaturized implantable devices with enhanced functions. Nursing care involves assessing for pacemaker function and complications as well as educating patients.




















![3. CAPTURE FUNCTION
The ability of the pacemaker to generate
a response from the heart [contraction]
after electrical stimulation is referred as
capture.
▪ Electrical capture : Indicated by P or
QRS following and corresponding to a
pacemaker spike.
▪ Mechanical capture: Palpable pulse
corresponding to the electrical event.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pacemaker-200716083909/75/PACEMAKER-26-2048.jpg)