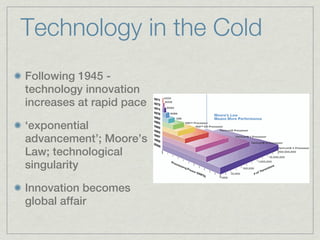
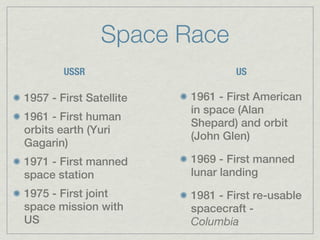
Here is a possible journal entry response:
While rocket technology was initially developed during World War II as weapons, its lasting legacy has been to enable the exploration of outer space. Rockets provided the means for both the US and USSR to engage in the Space Race and achieve many firsts, such as Sputnik, the first satellite, and the Apollo moon landings. Rockets allowed humans to break free of Earth's atmosphere and glimpse the wonders of the cosmos. Though ICBMs maintained rocketry's military uses during the Cold War, nations also harnessed rockets' power to launch satellites, space stations, and probes to distant planets. Rockets lifted the veil on the unknown, capturing humanity's imagination and inspiring future scientists and expl