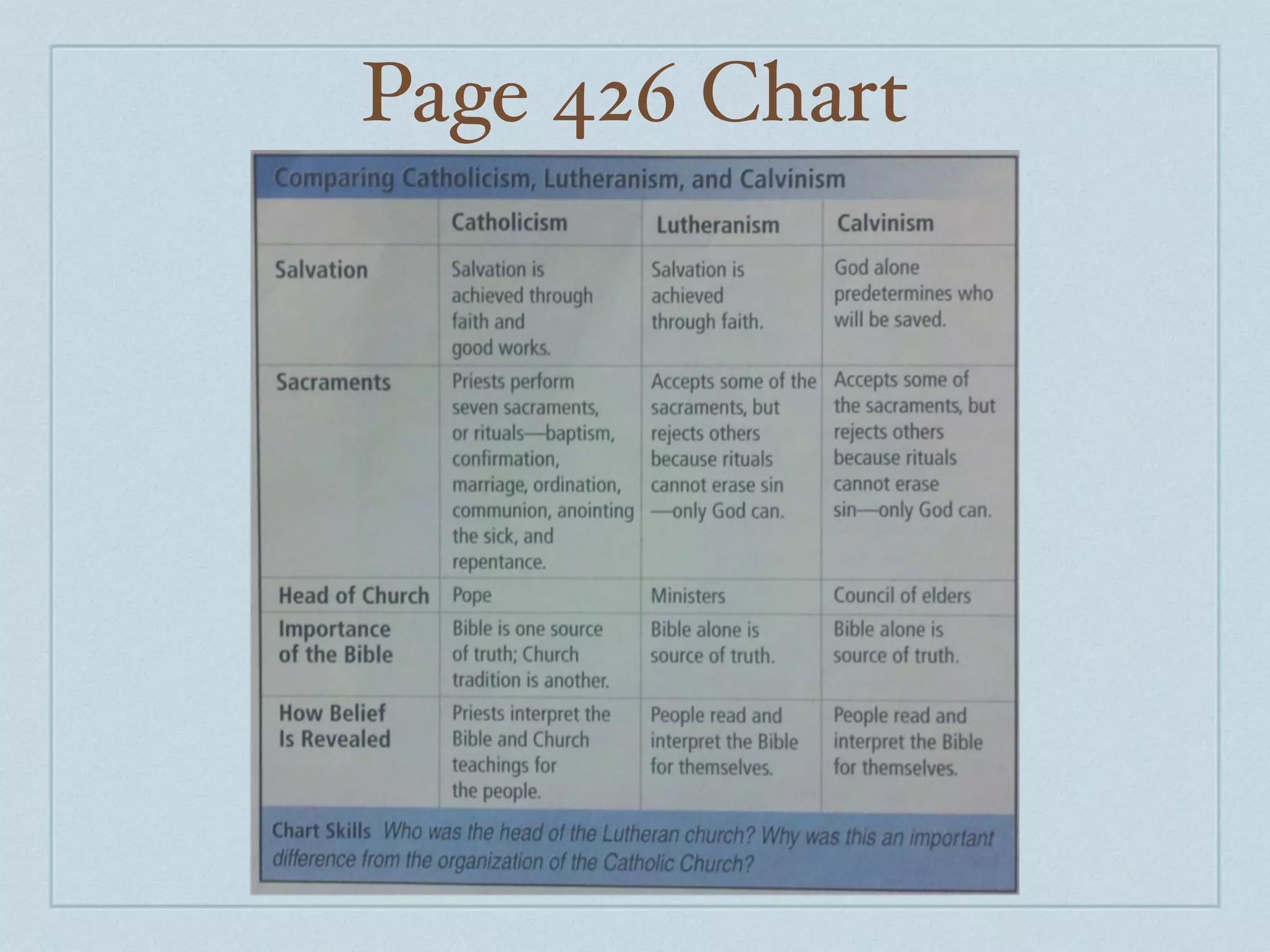
The document summarizes some of the key factors that led to the Protestant Reformation in Europe, including issues with the Catholic Church that caused unrest, such as selling indulgences and living lavish lifestyles. It describes how Martin Luther drafted the 95 Theses challenging indulgences and certain Church authorities, which spread widely through printing and stirred debate. While Luther was eventually excommunicated, his ideas gained many followers and split from the Catholic Church to form Protestantism, spreading reforms across Germany and Switzerland under Luther and Calvin respectively.