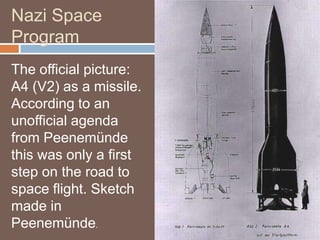
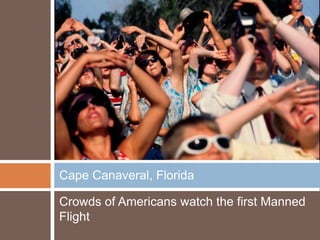
The document outlines the historical development of the space race during the Cold War, highlighting the contributions of German scientists to both the US and USSR's space programs. Key events include the launch of the Soviet's Sputnik satellites, which catalyzed the US space program, and the eventual moon landing by Apollo 11 in 1969. It also touches on espionage efforts in space and suggests that the space race served as a symbolic competition between the superpowers, culminating in collaborative moments like the handshake in orbit between American and Soviet astronauts.