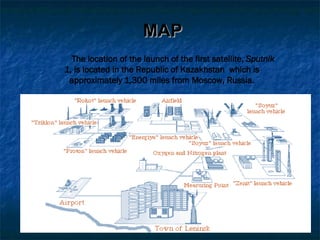
The document summarizes the key events of the Space Race between the United States and Soviet Union during the Cold War. It began in 1957 when the Soviet Union launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite, demonstrating their technological capabilities. Both nations worked to launch animals and humans into space, with Yuri Gagarin becoming the first person in space in 1961. The US achieved several milestones as well, with Neil Armstrong landing on the moon in 1969, representing an American victory in the Space Race.