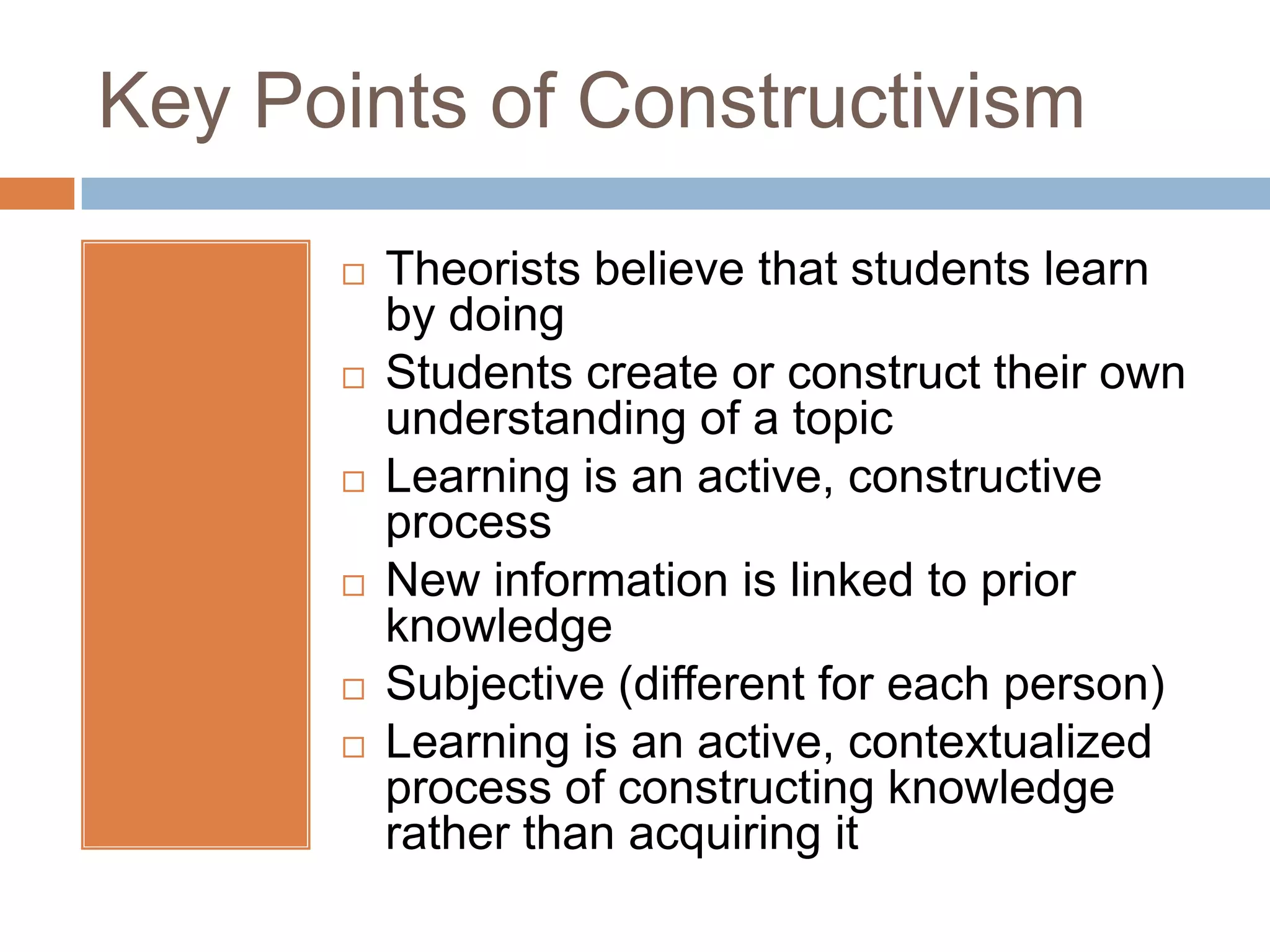
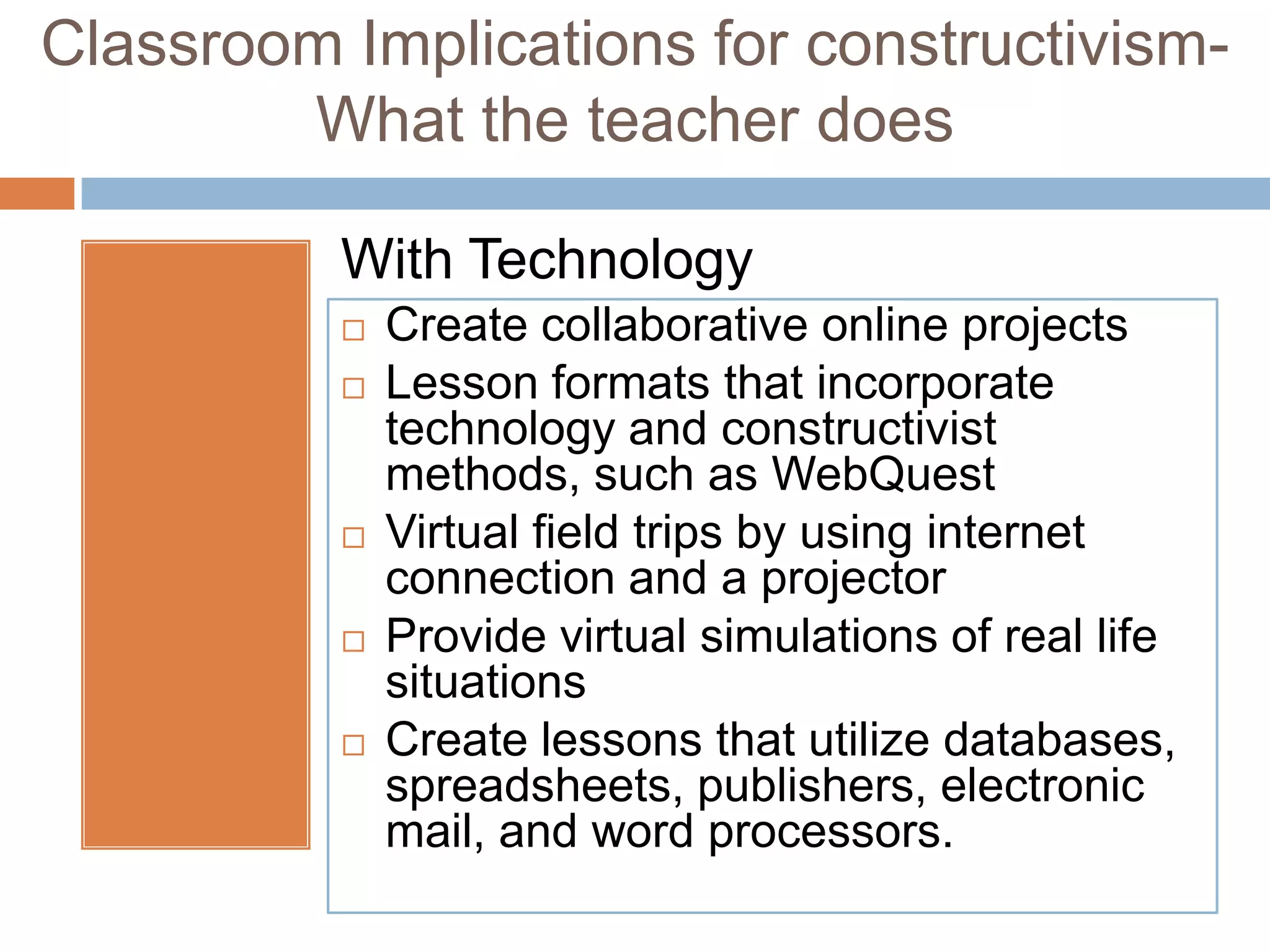
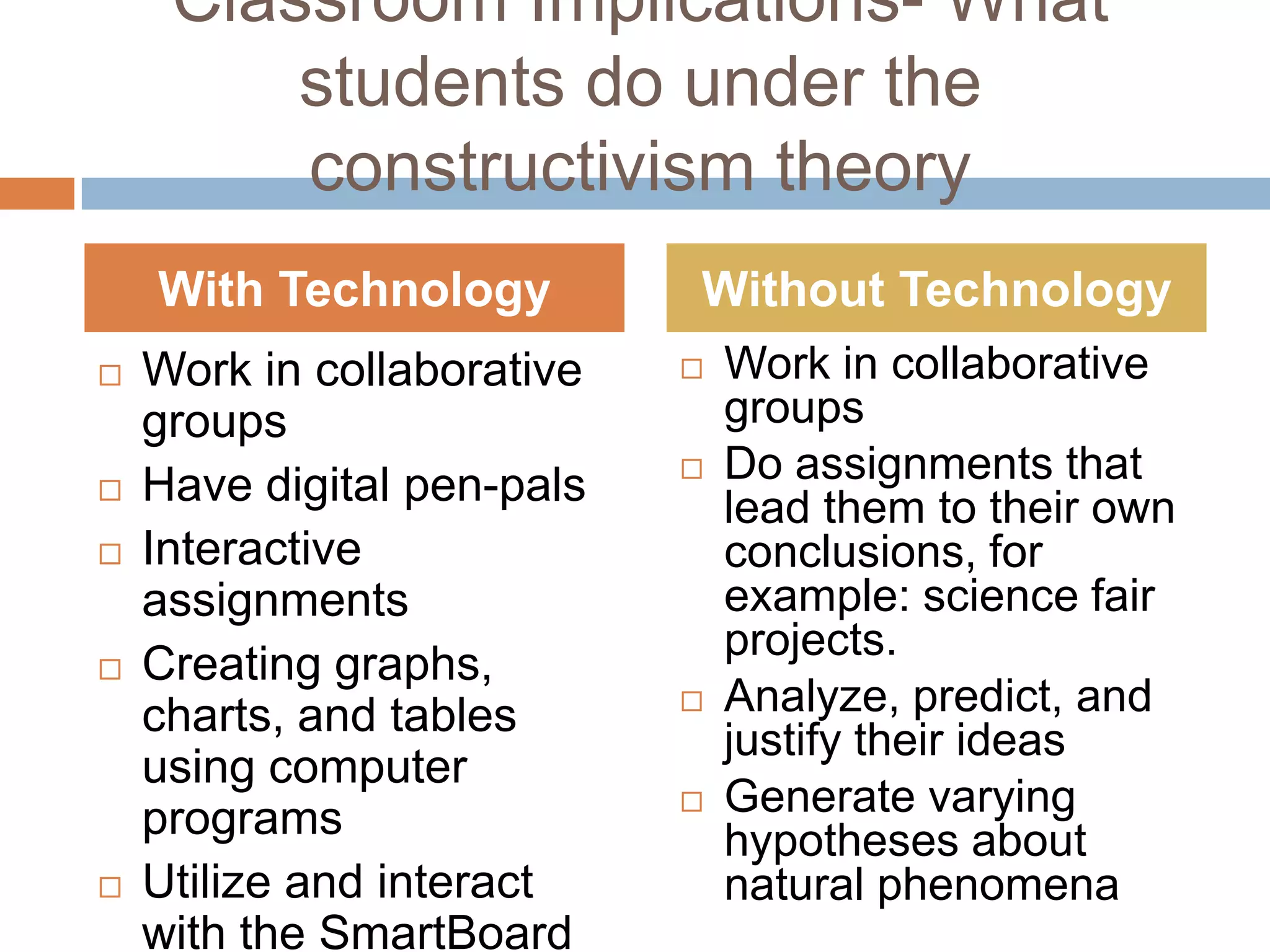
This document summarizes the constructivist learning theory and its key figures. It discusses Jean Piaget's cognitive stages, Jerome Bruner's view of participatory learning, and Lev Vygotsky's social cognition theory including the zone of proximal development. The document outlines constructivism's view that learning is an active process where students construct their own understanding through experience. It provides implications for constructivist classrooms, including collaborative work, hands-on activities, and facilitating student-led discussions and conclusions with or without technology.






![References
Shelly, G.B. & Gunter, G.A. & Gunter, R.E. (2012). Teachers
Discovering Computers; Integrating Technology In a
Connected World. Massachusetts: Cengage Learning.
(2007.) Index of Learning Theories and Models. Retrieved
from: www.learning-theories.com.
[Untitled photograph of children working in groups] Retrieved
April 11, 2013:
http://becs126.edublogs.org/files/2009/04/classroomphoto.jp
g
[Untitled photograph of Lev Vygotsky] Retrieved April 11,
2013: http://www.goodtherapy.org/famous-psychologists/lev-
vygotsky.html
[Untitled photograph of Jean Piaget] Retrieved April 11, 2013:
http://nursingcrib.com/wp-content/uploads/jean-
piaget1.png?9d7bd4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techproject-130411191002-phpapp01/75/Tech-project-10-2048.jpg)