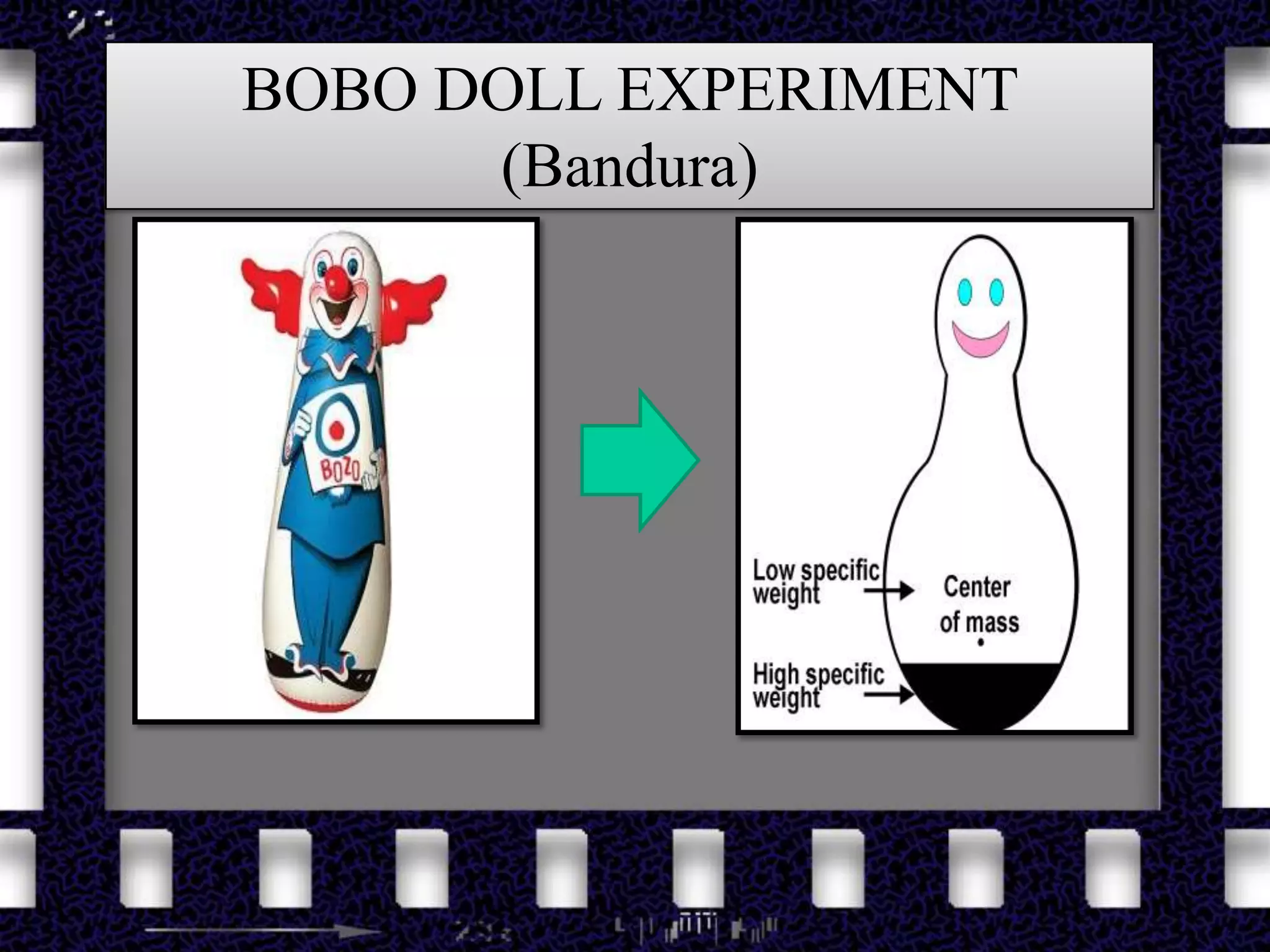
Social learning theory, also known as observational learning, emphasizes that learning occurs through observation of others. The theory proposes that people can learn new behaviors both by watching others perform behaviors and through the associated outcomes of those behaviors, without their own direct experiences. There are four main concepts of social learning theory: attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation. Teachers can apply social learning theory in the classroom by having students observe and model behaviors, such as using adjectives in a descriptive writing lesson.