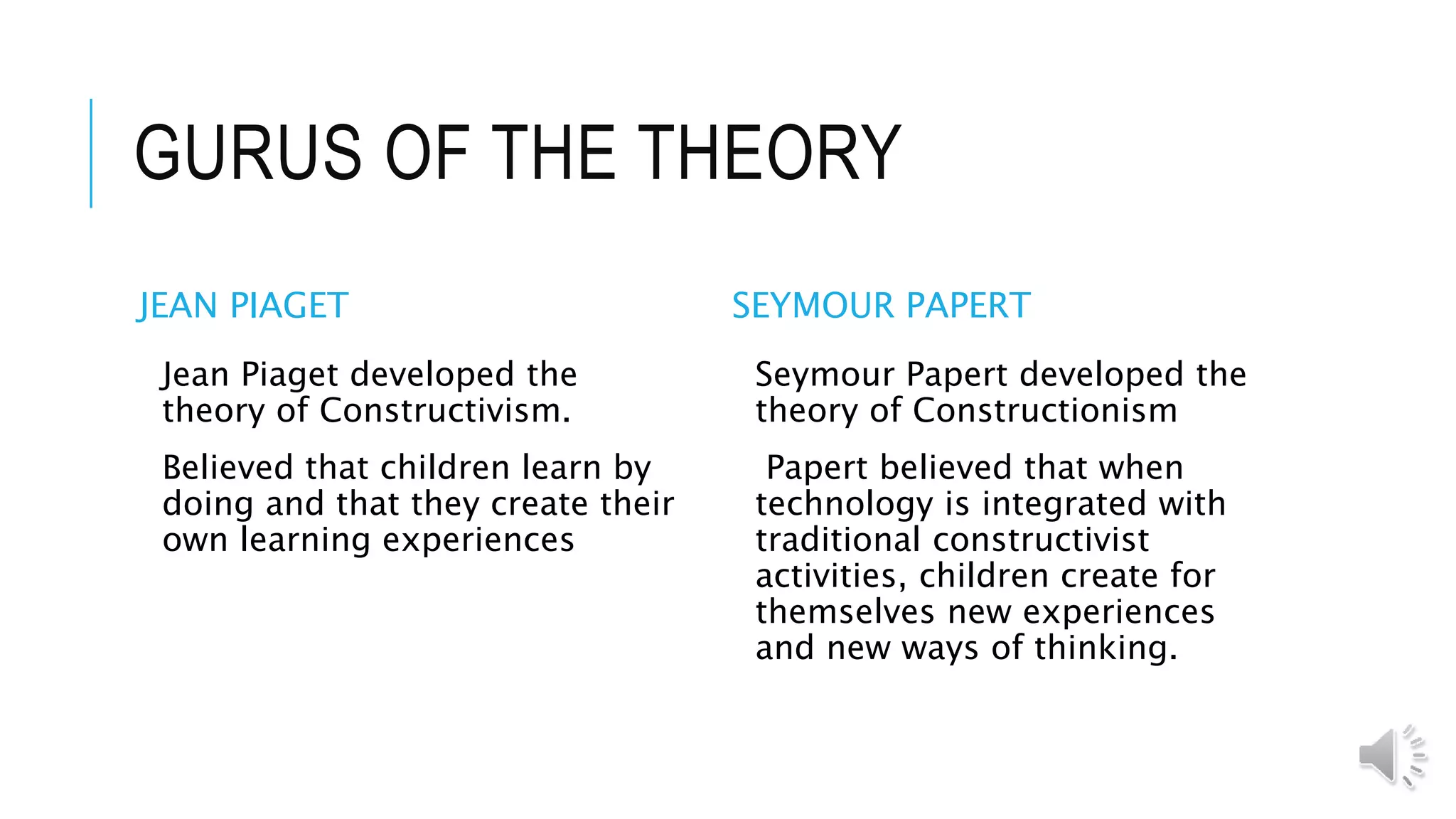
Constructionism is a learning theory that states knowledge is built best through making tangible and shareable things. It supports learner-centered education and often involves technology. The theory was developed by Jean Piaget, who believed learning occurs through doing, and Seymour Papert, who felt integrating technology with constructivist activities creates new experiences and ways of thinking for children. The four basic concepts are: learning by designing projects meaningful to oneself and community; using technology as a learning tool; encountering powerful ideas; and developing safe, responsible technology use.