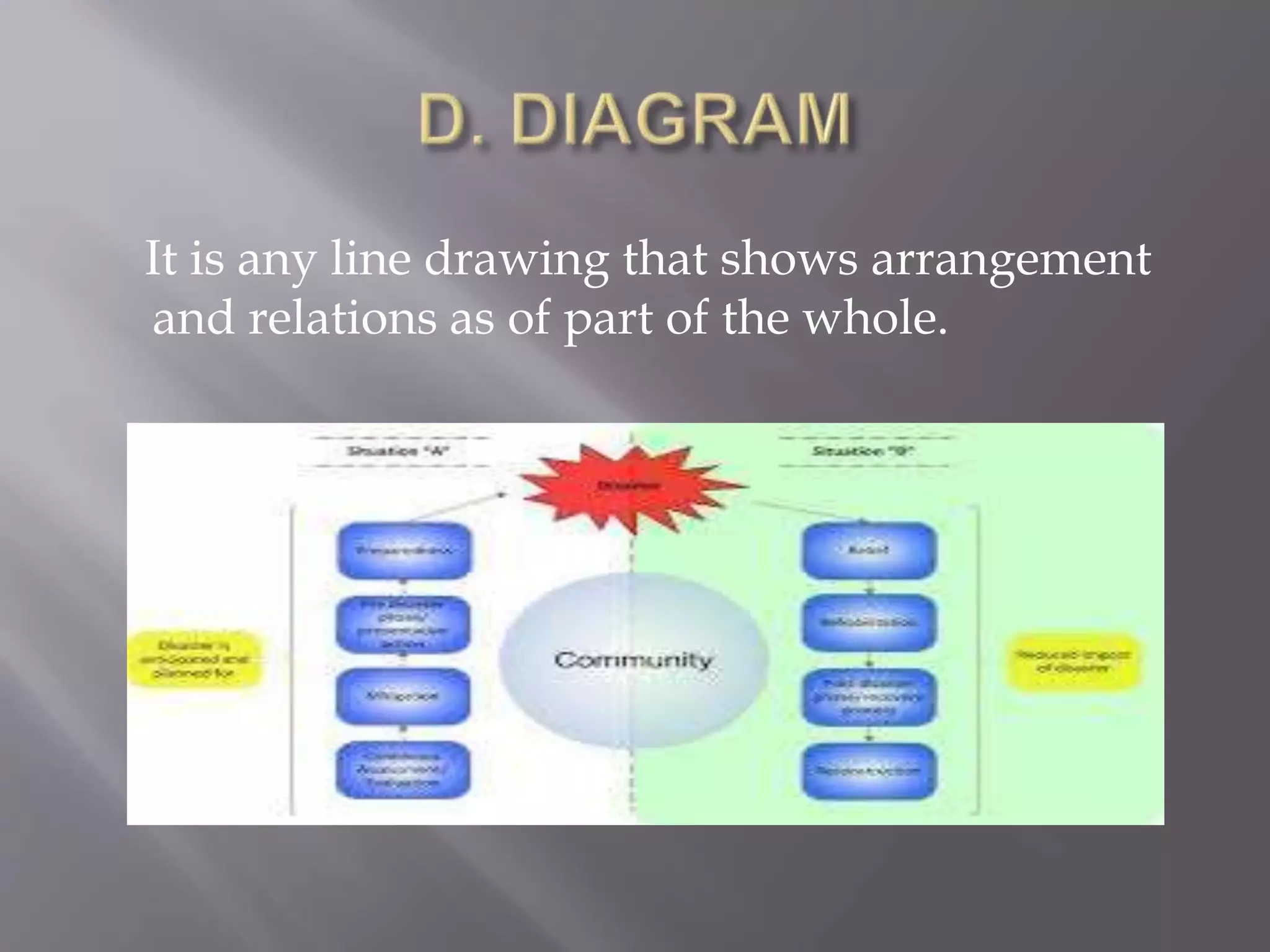
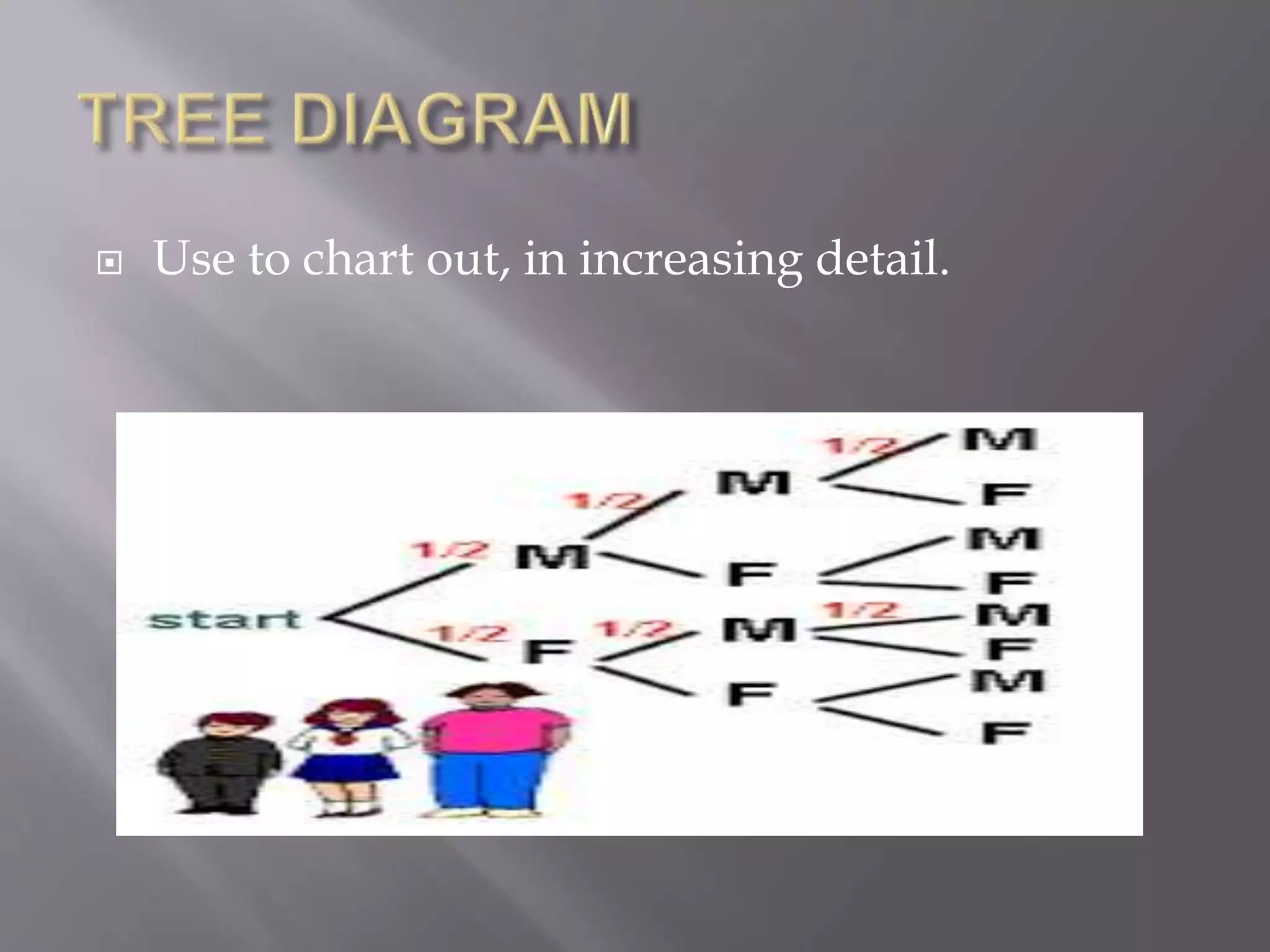
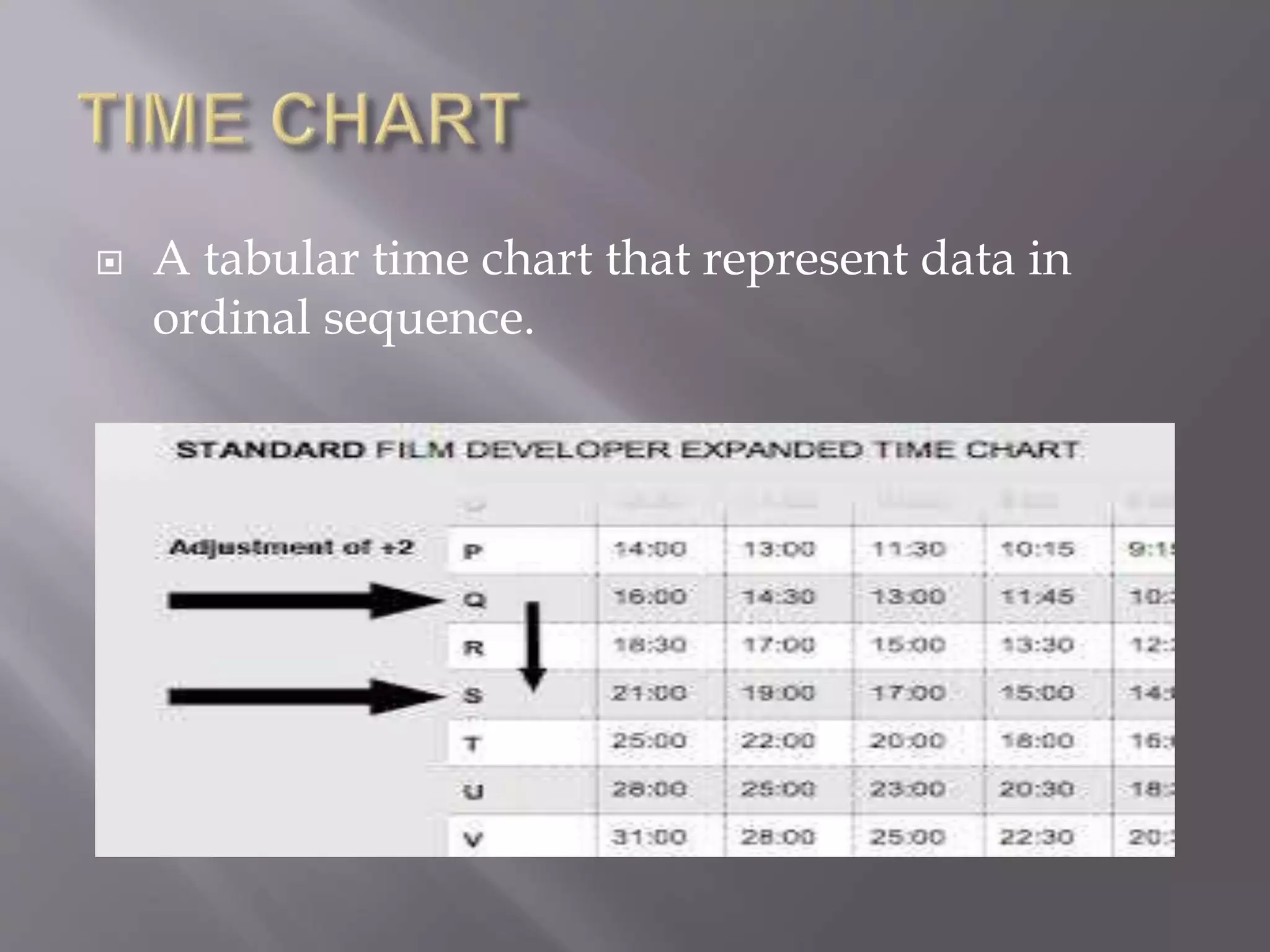
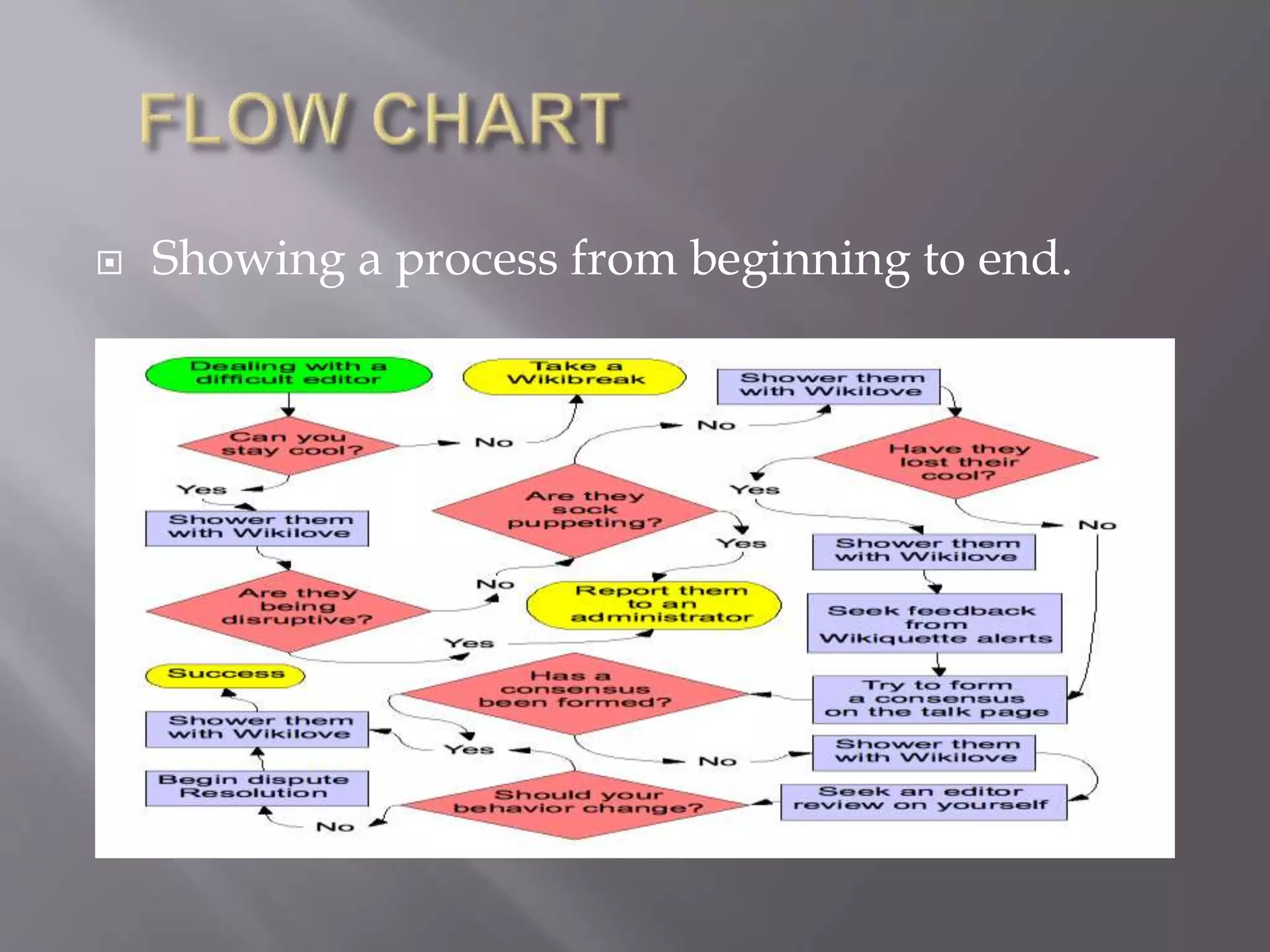
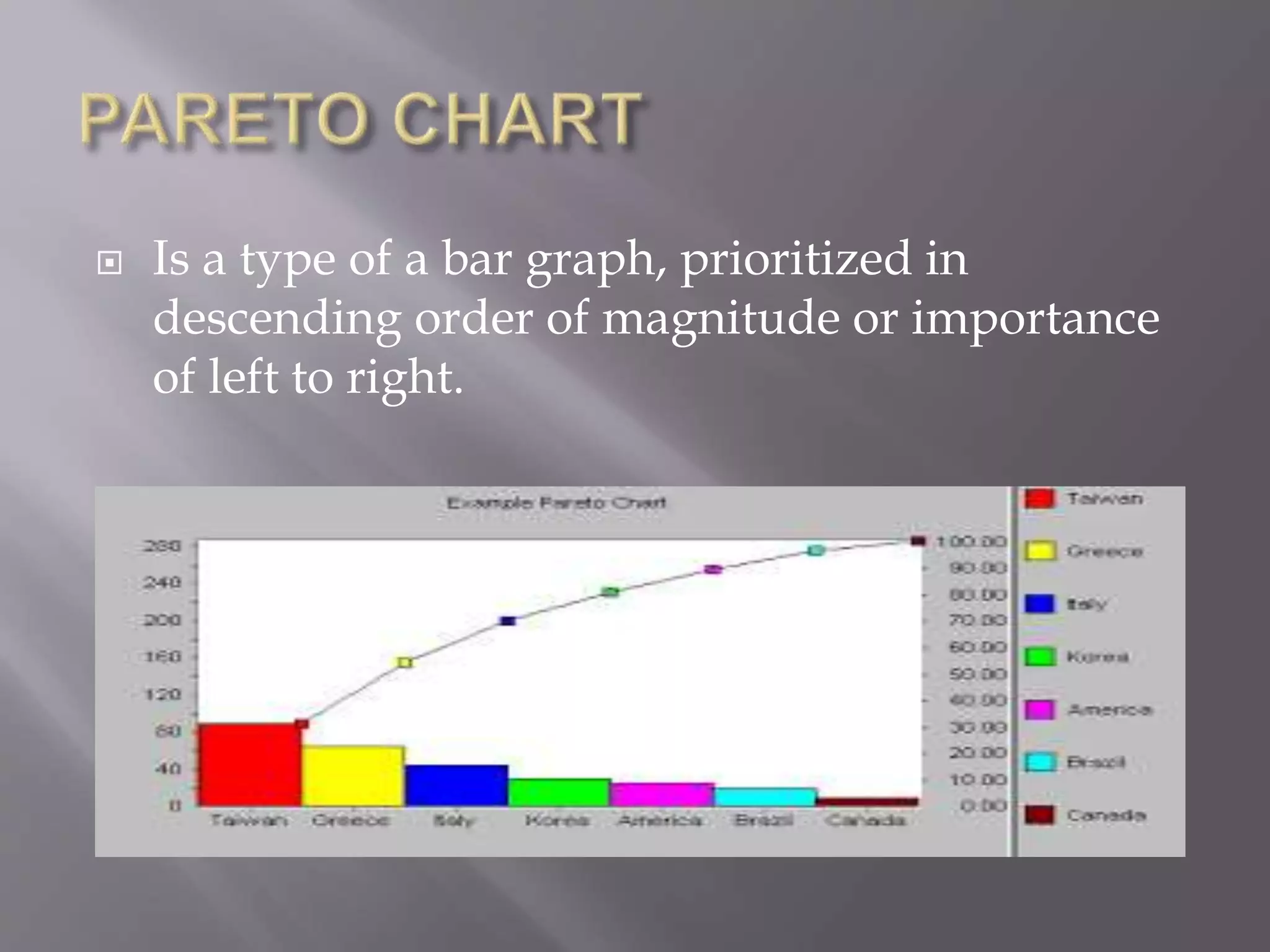
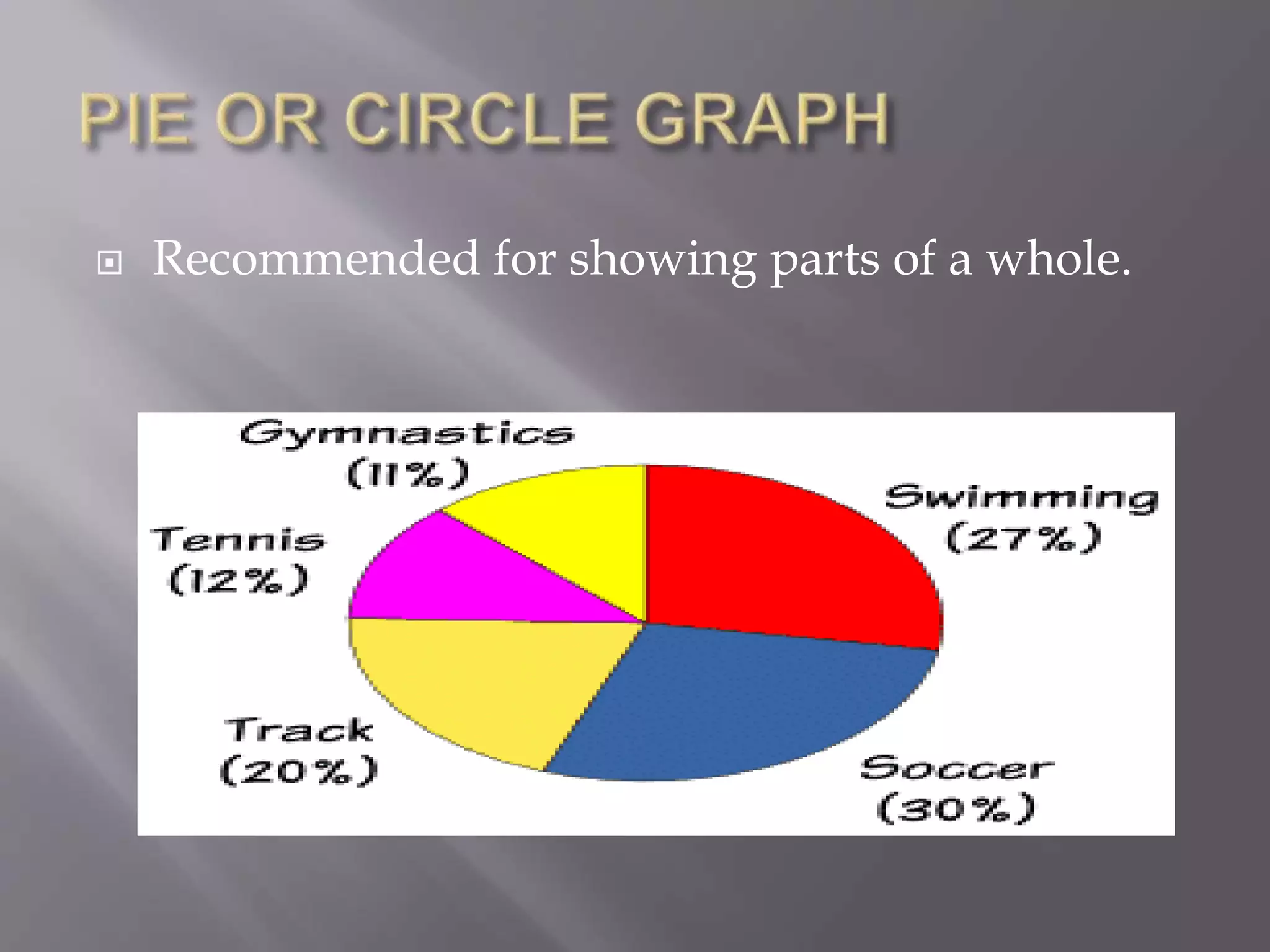
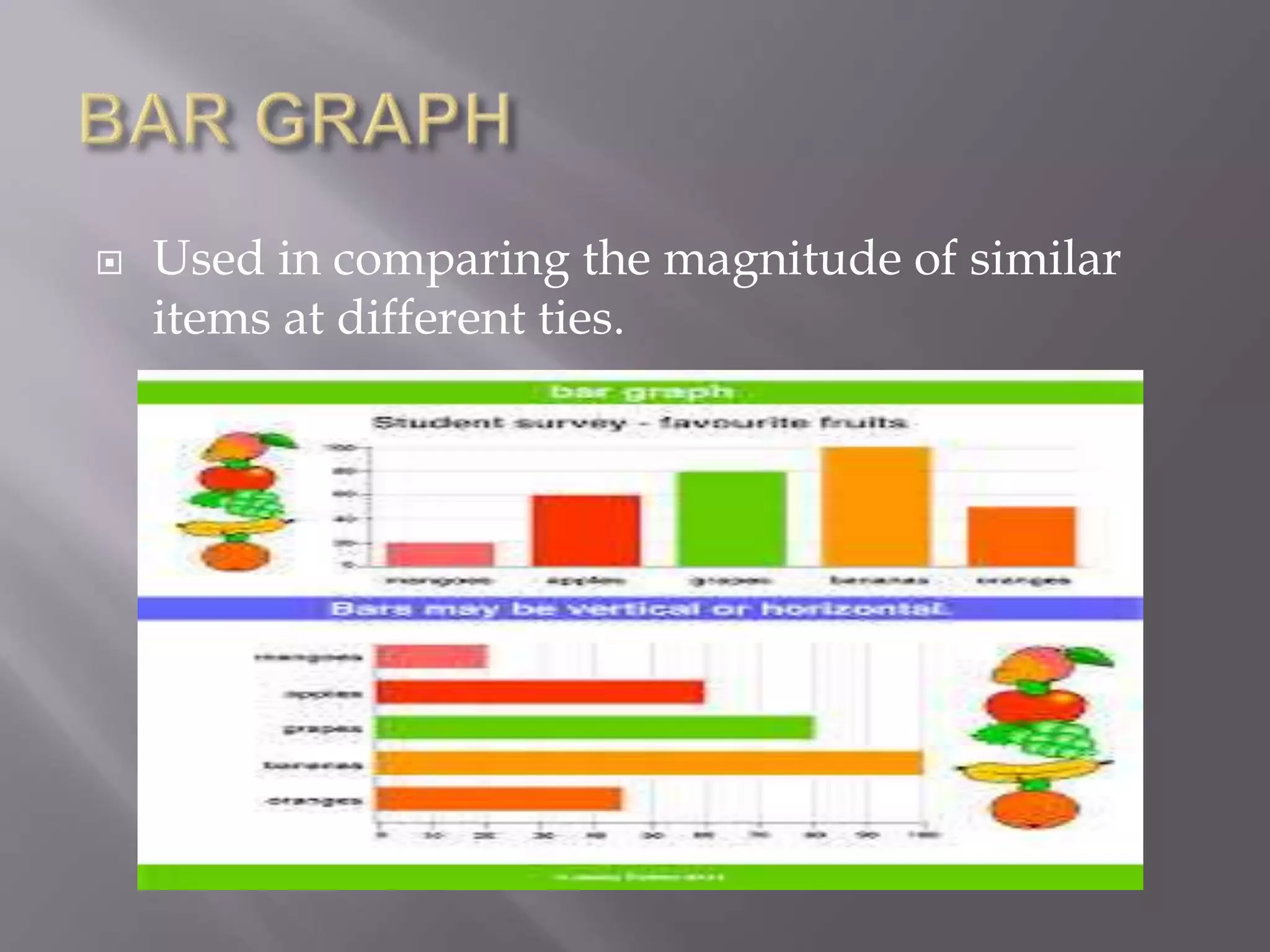
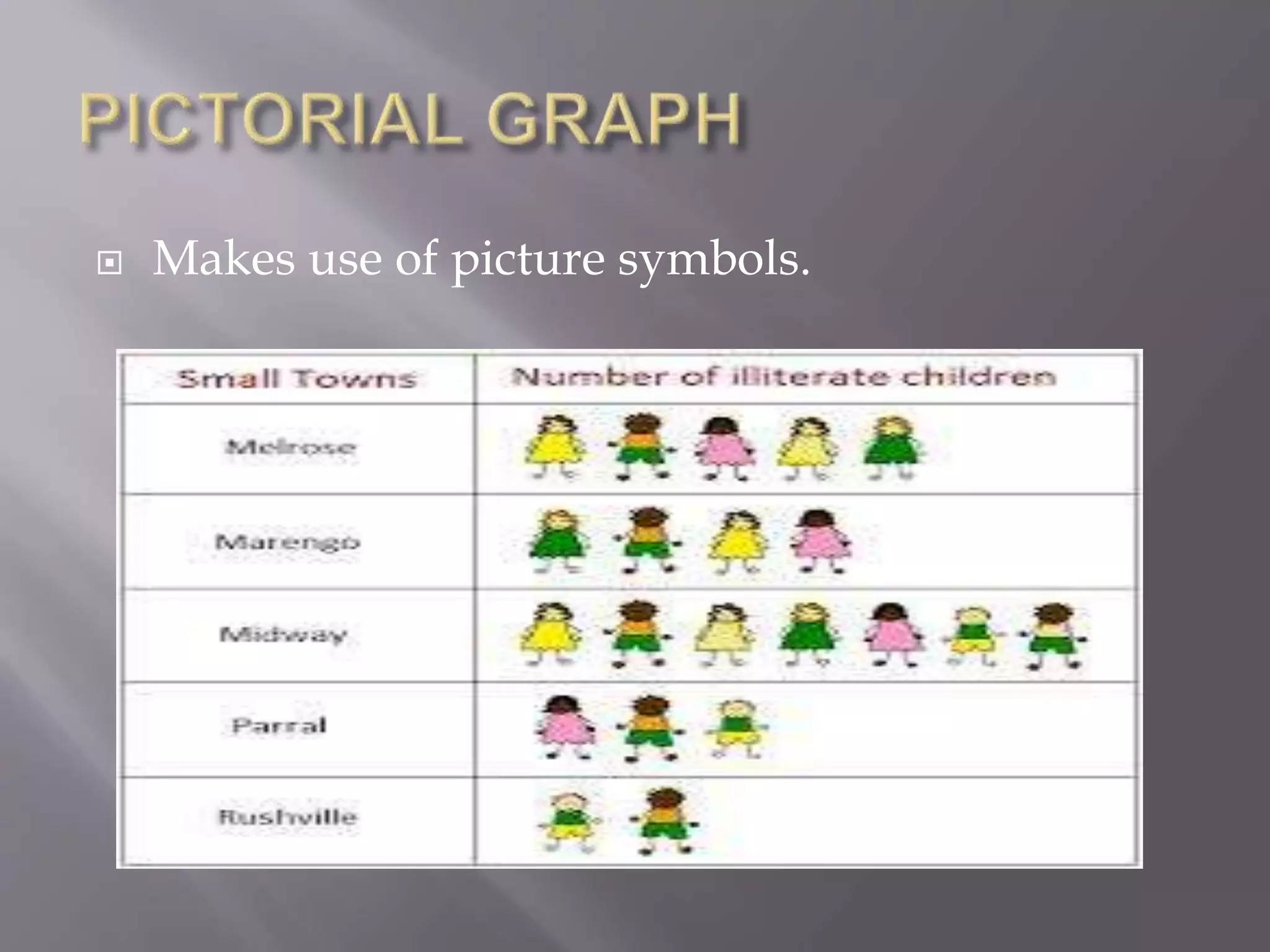
This document discusses various types of visual aids that can be used when teaching, including drawings, cartoons, diagrams, charts, graphs, and maps. It provides examples of different kinds of diagrams like affinity diagrams, fishbone diagrams, flow charts, organizational charts, and more. It also discusses different types of graphs like pie graphs, bar graphs, and pictorial graphs. Finally, it mentions different kinds of maps such as physical maps, relief maps, and political maps. The overall document serves as a reference for different visual representation tools that can be used to enhance teaching.