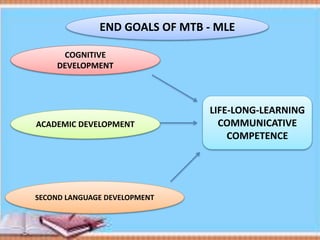
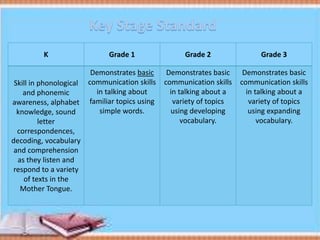
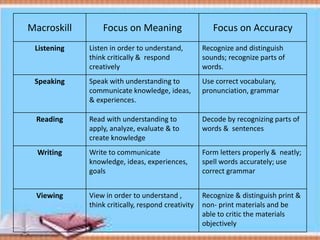
The document discusses Mother Tongue-Based Multilingual Education (MTB-MLE) in the Philippines. It notes that under DepEd guidelines, there are 19 major local languages used as the medium of instruction from kindergarten to grade 3. 12 languages are currently used in MTB-MLE programs, with 7 additional languages added in 2013-2014. The goals of MTB-MLE include developing students' second language abilities, academic skills, cognitive development, and lifelong learning through the use of the mother tongue as the primary language of instruction.