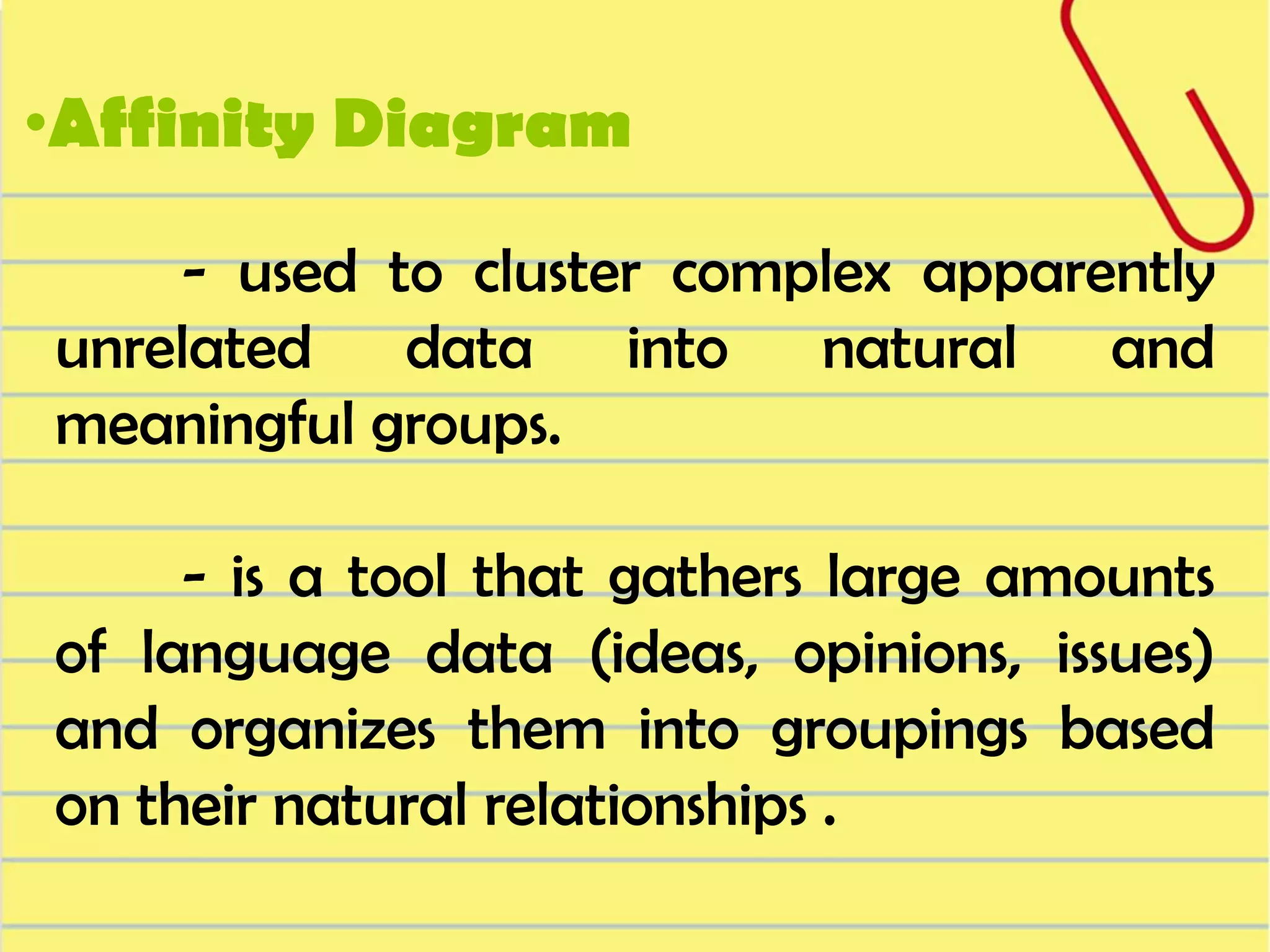
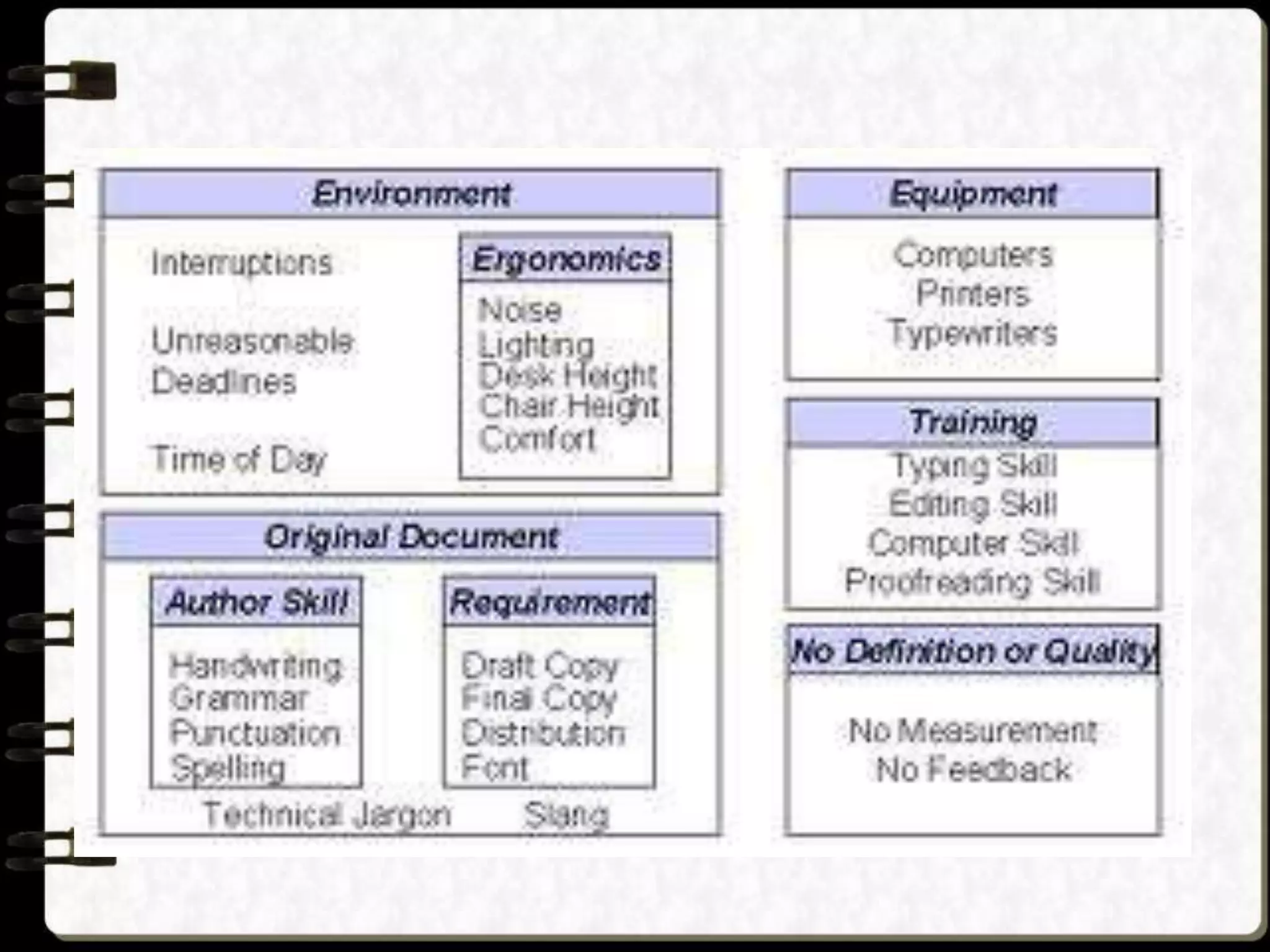
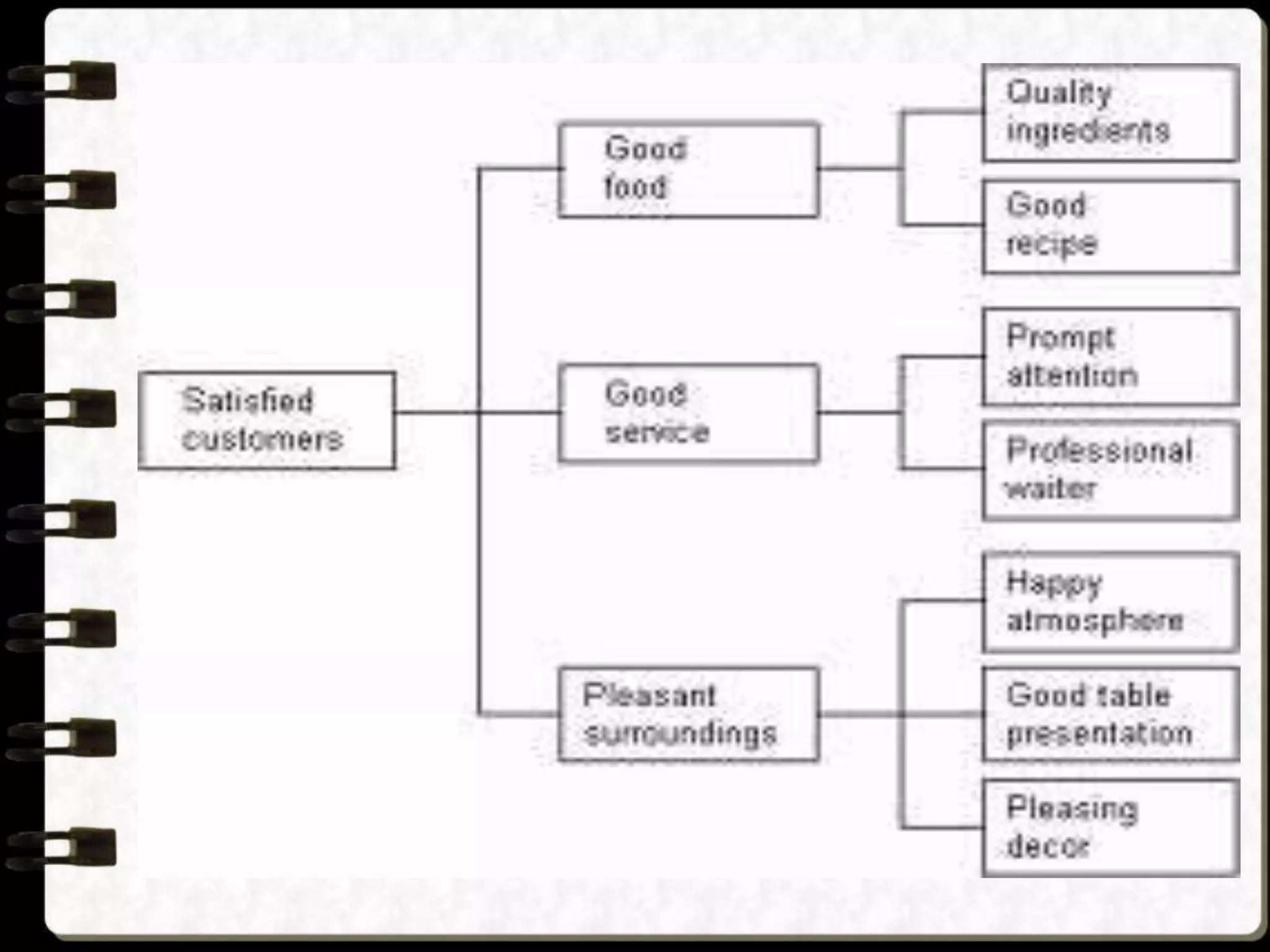
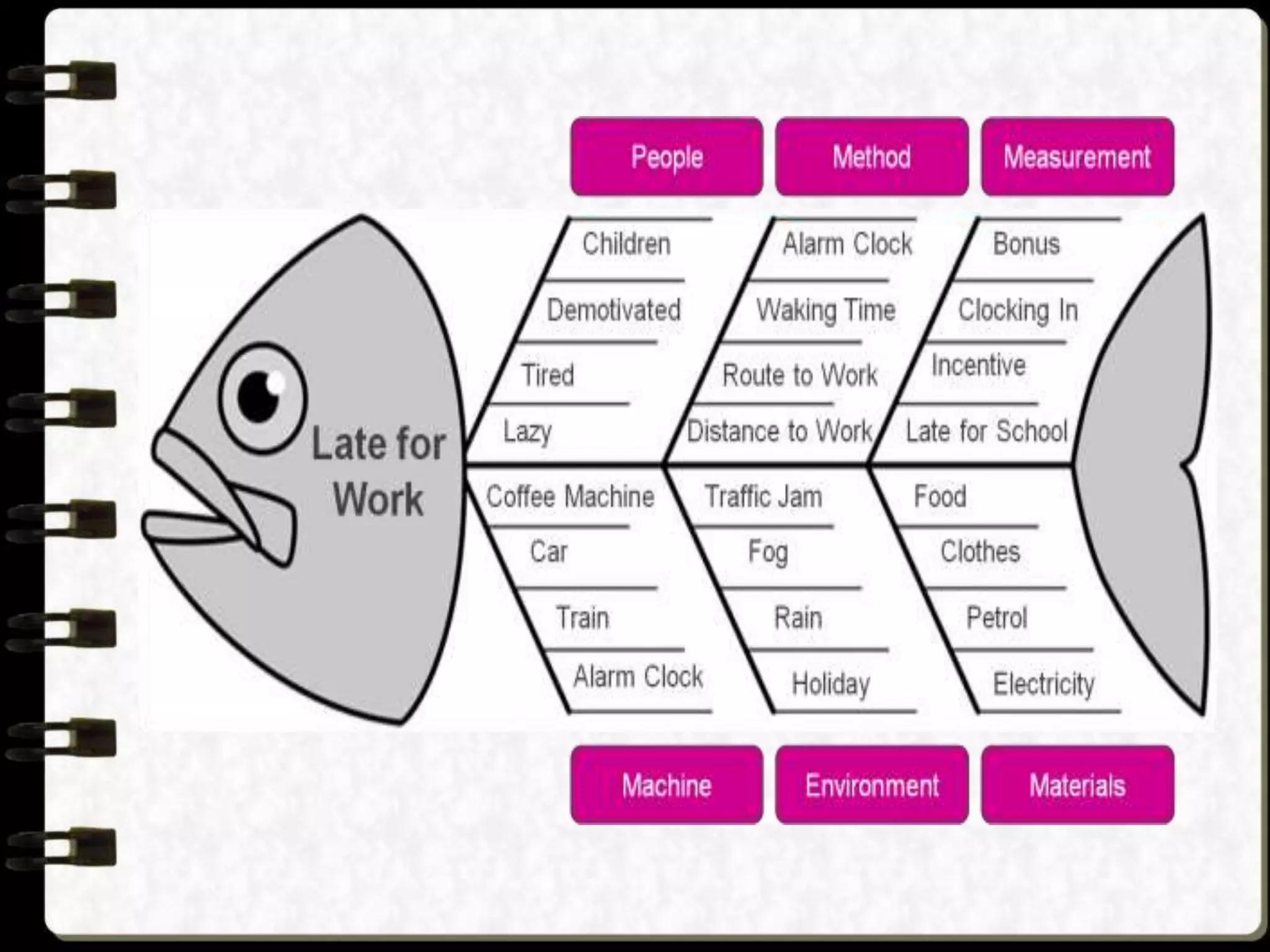
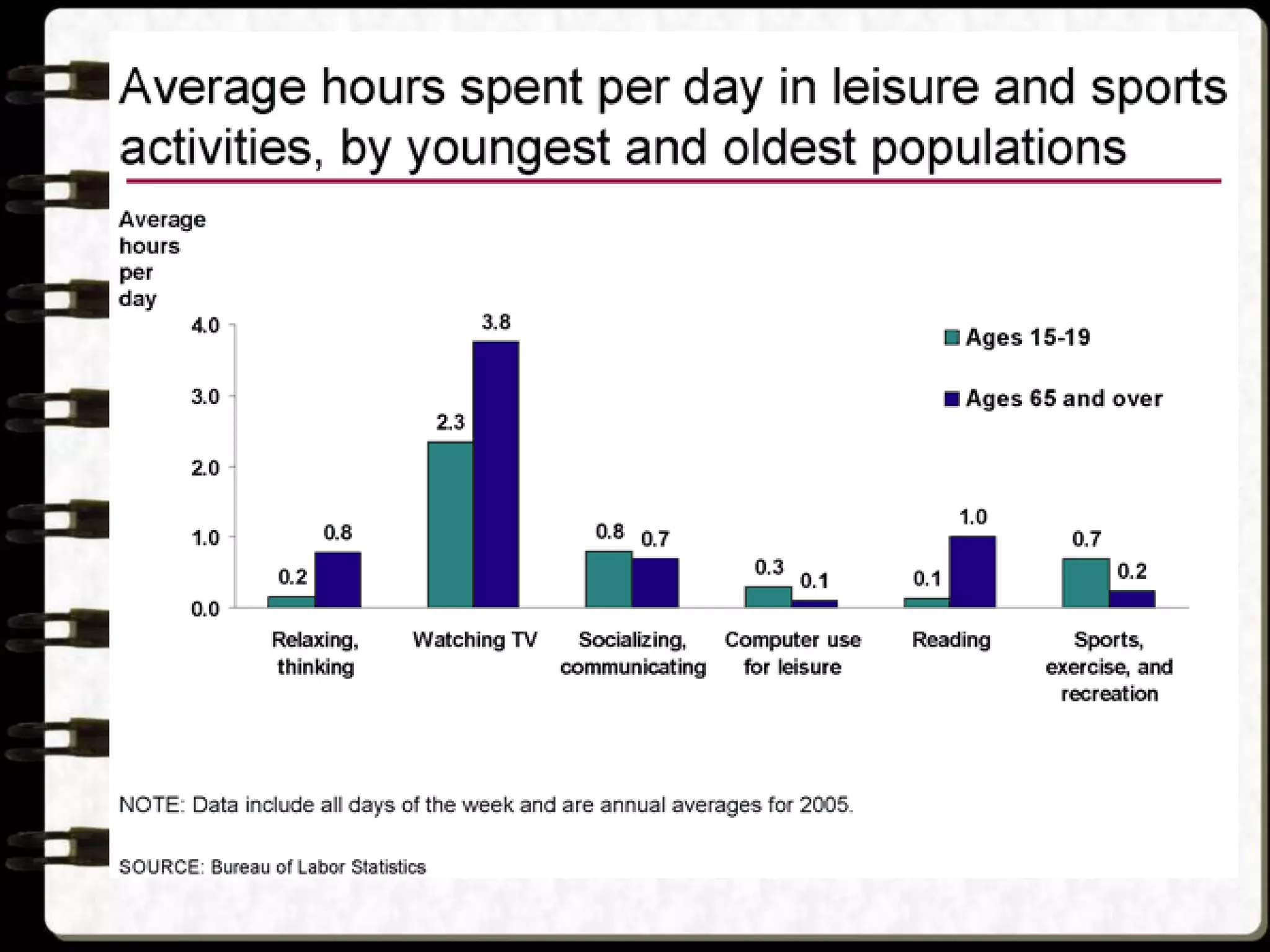
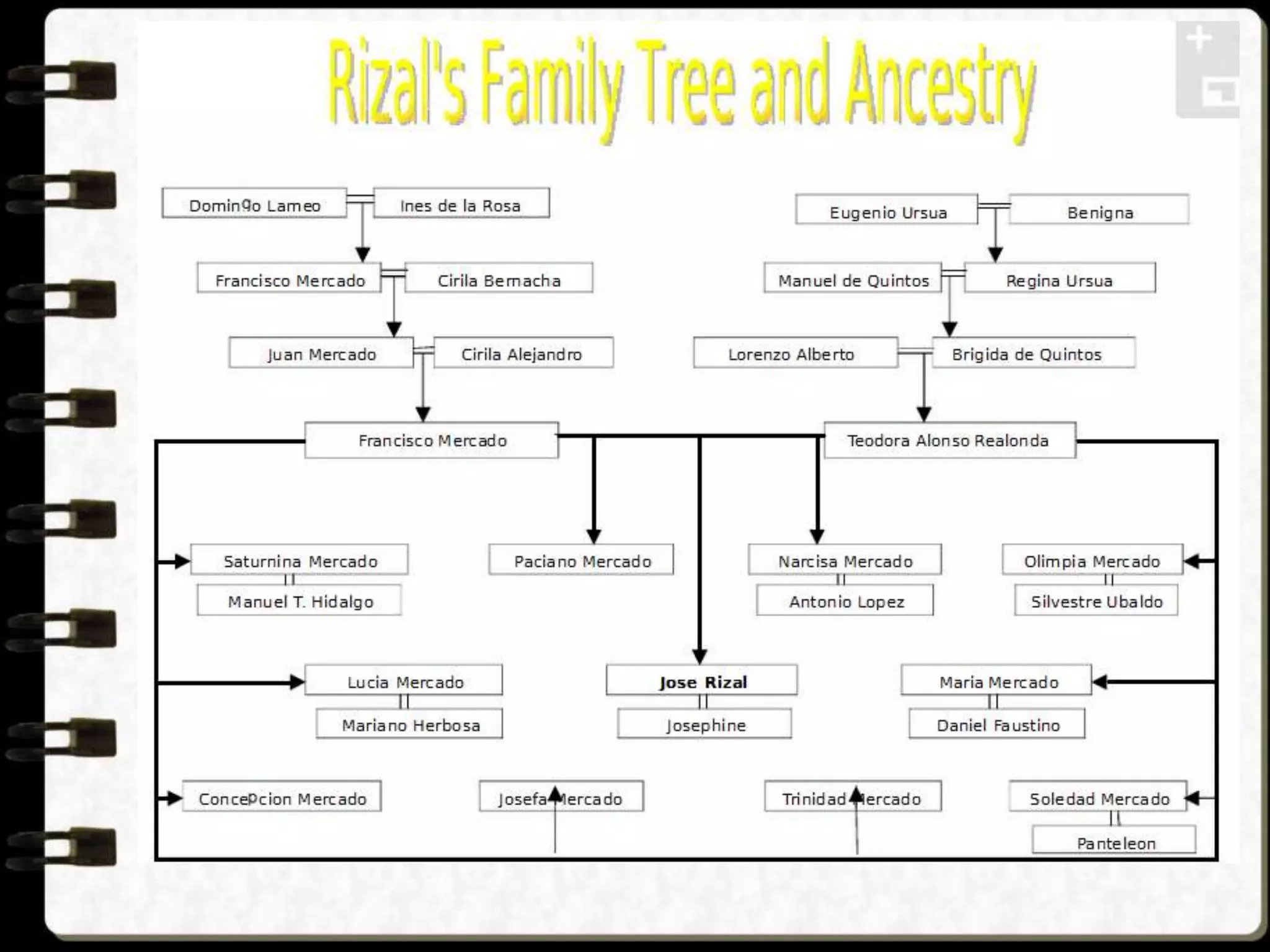
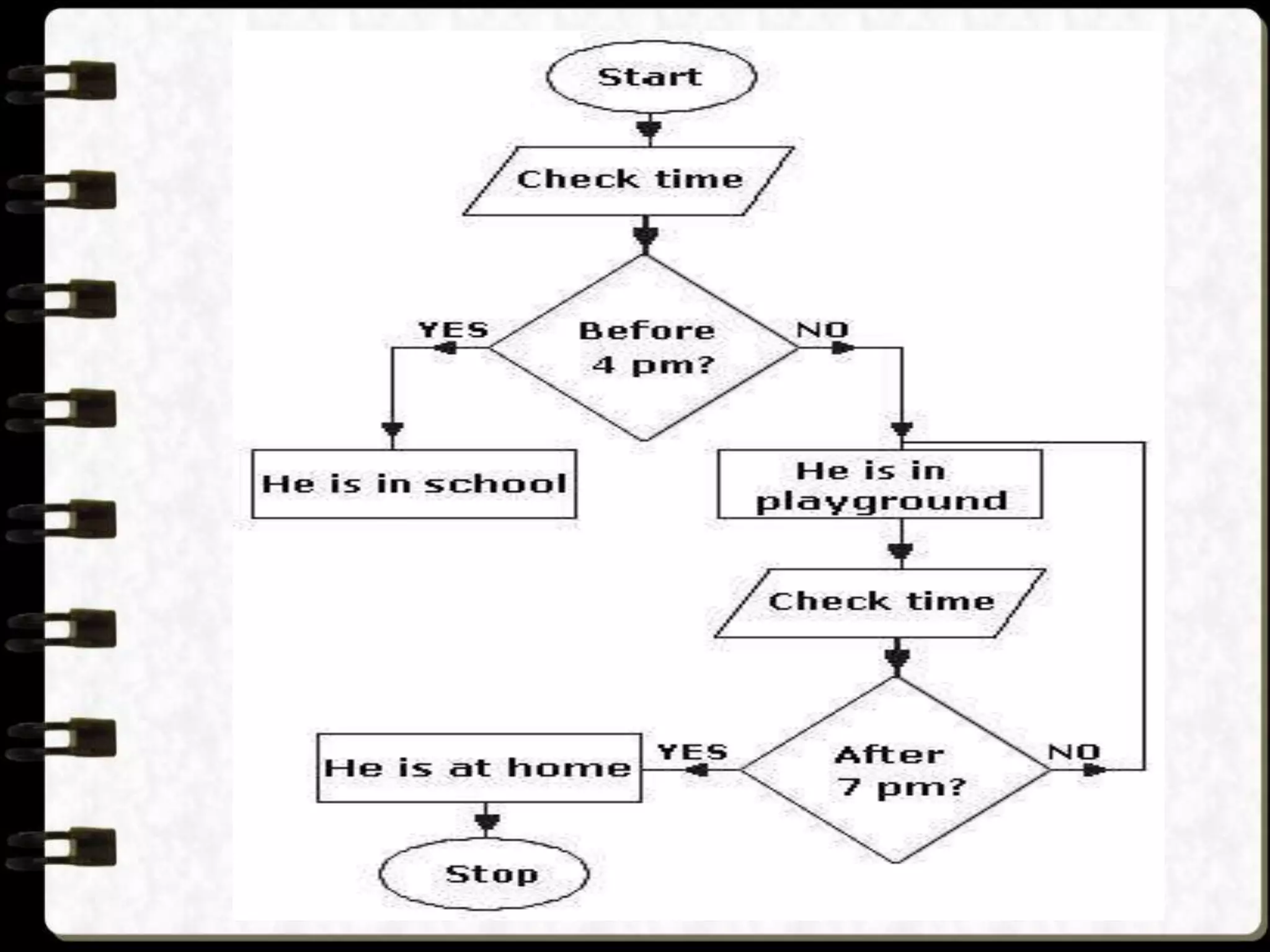
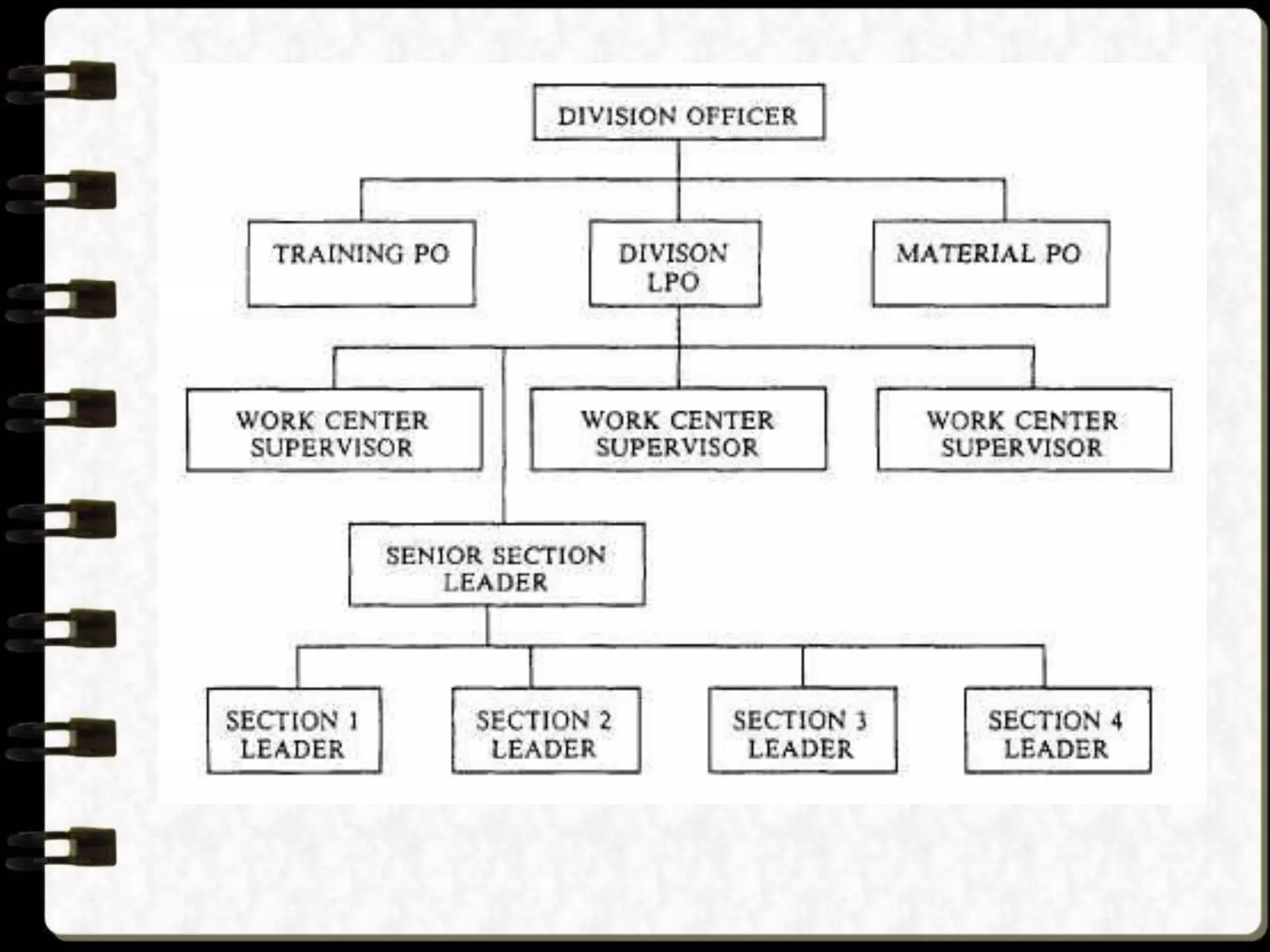
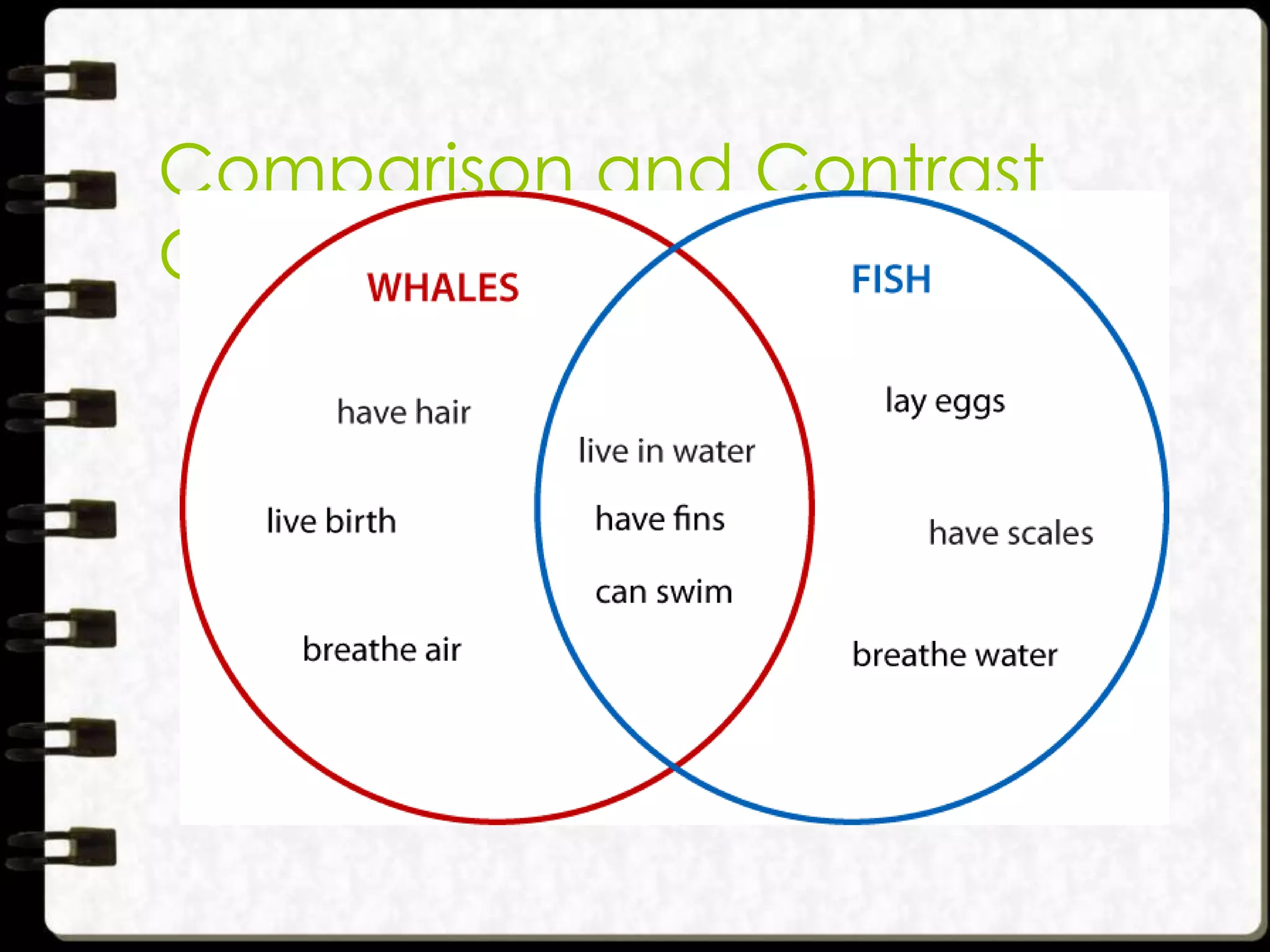
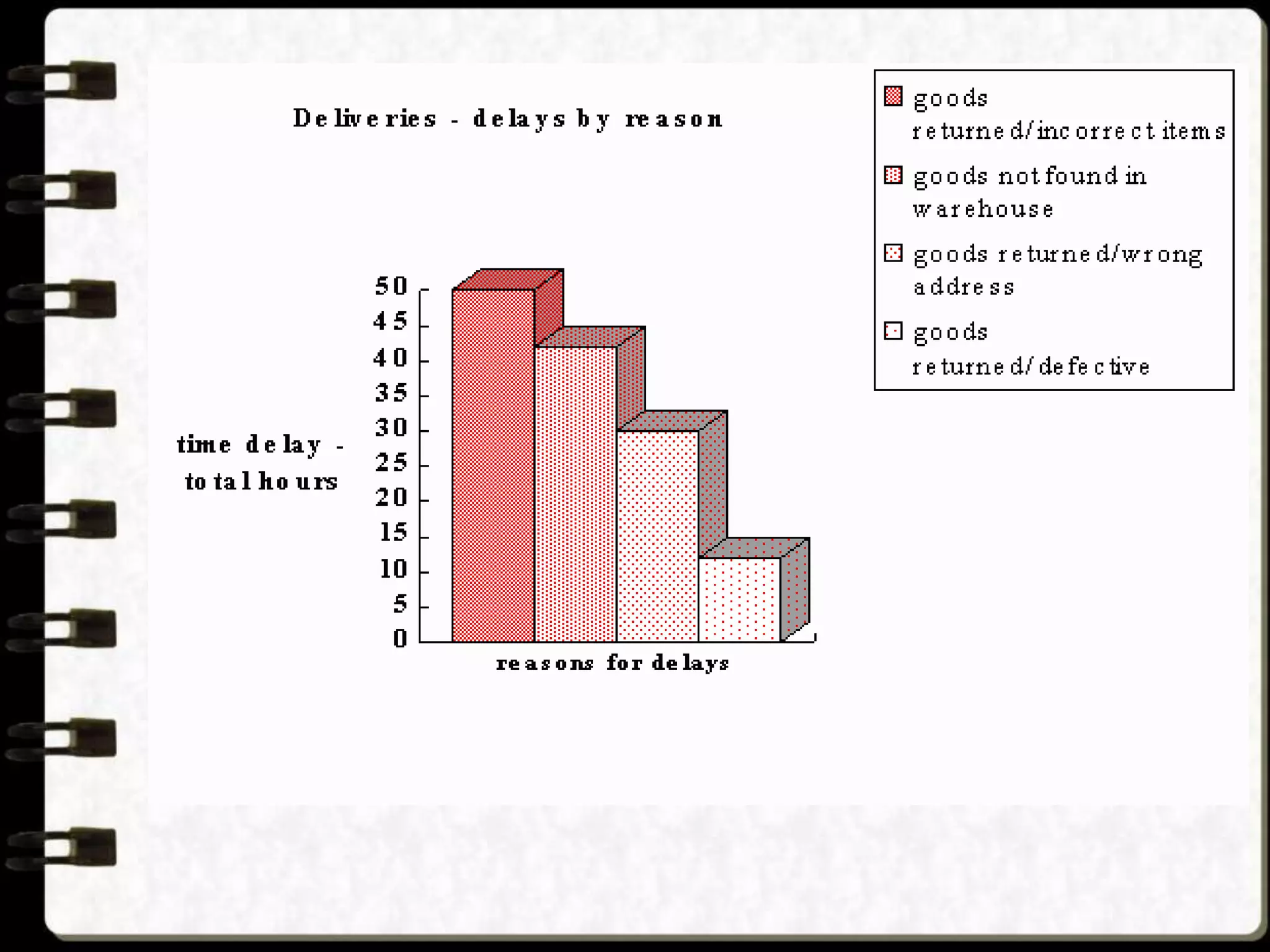
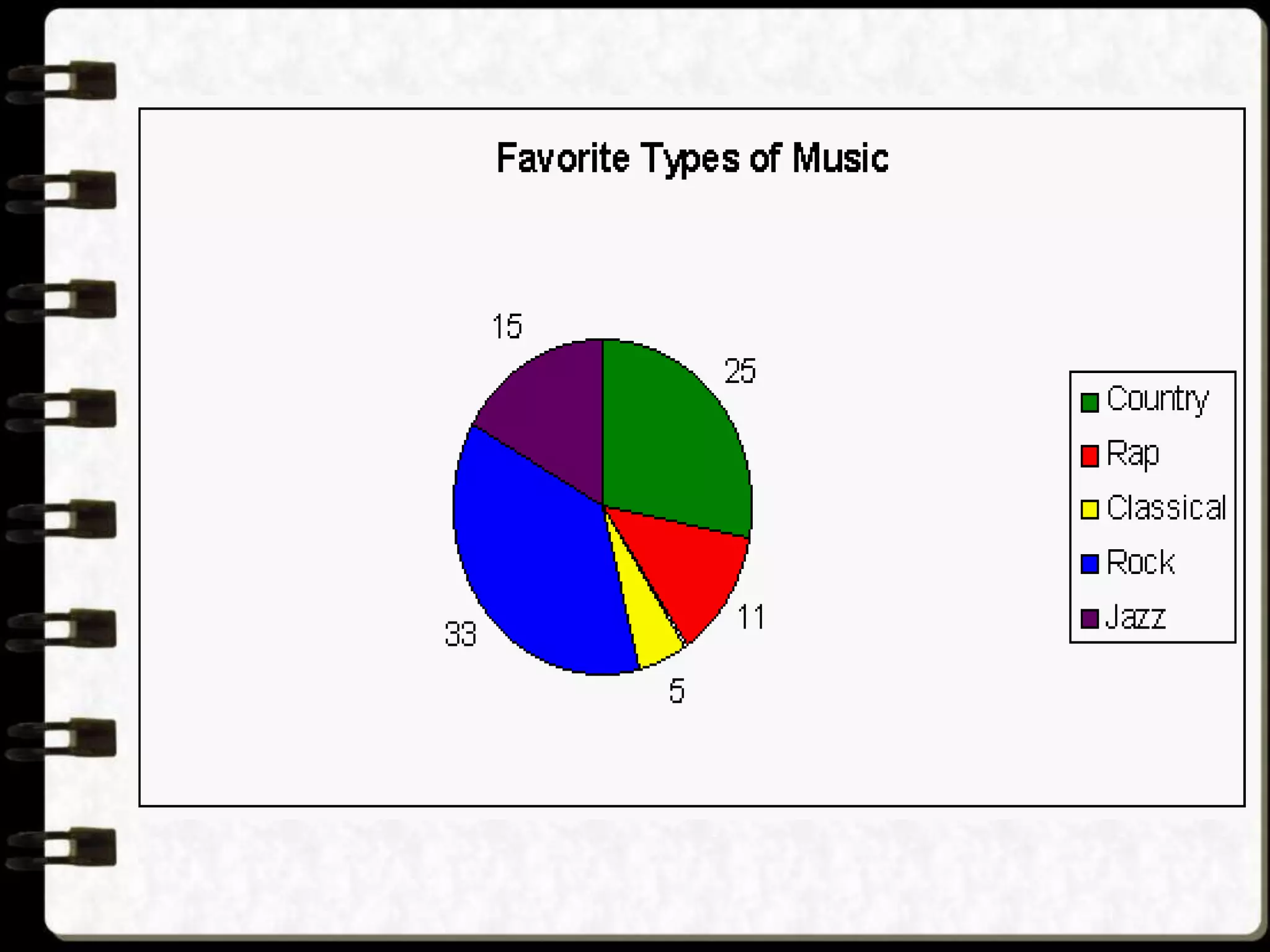
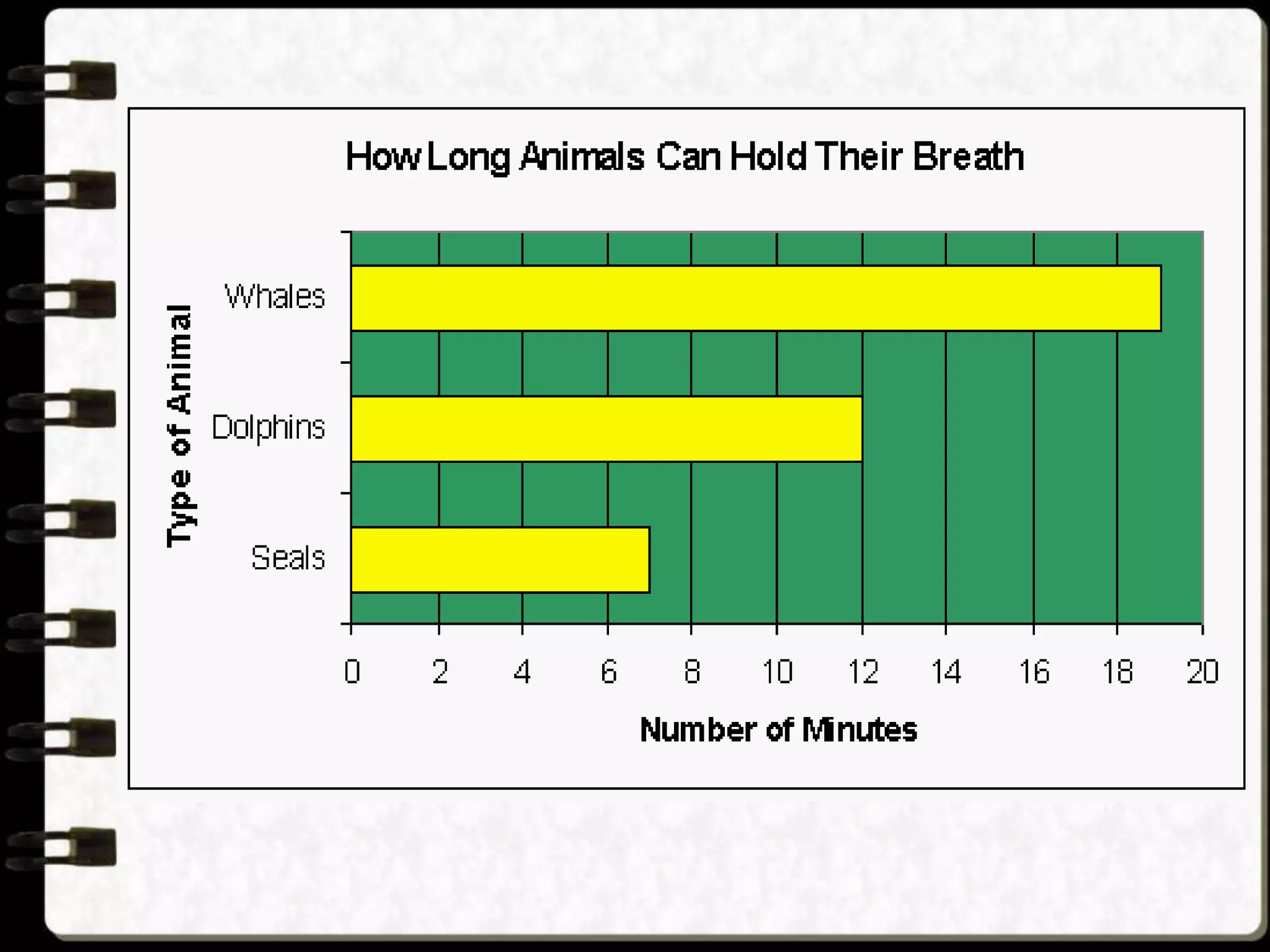
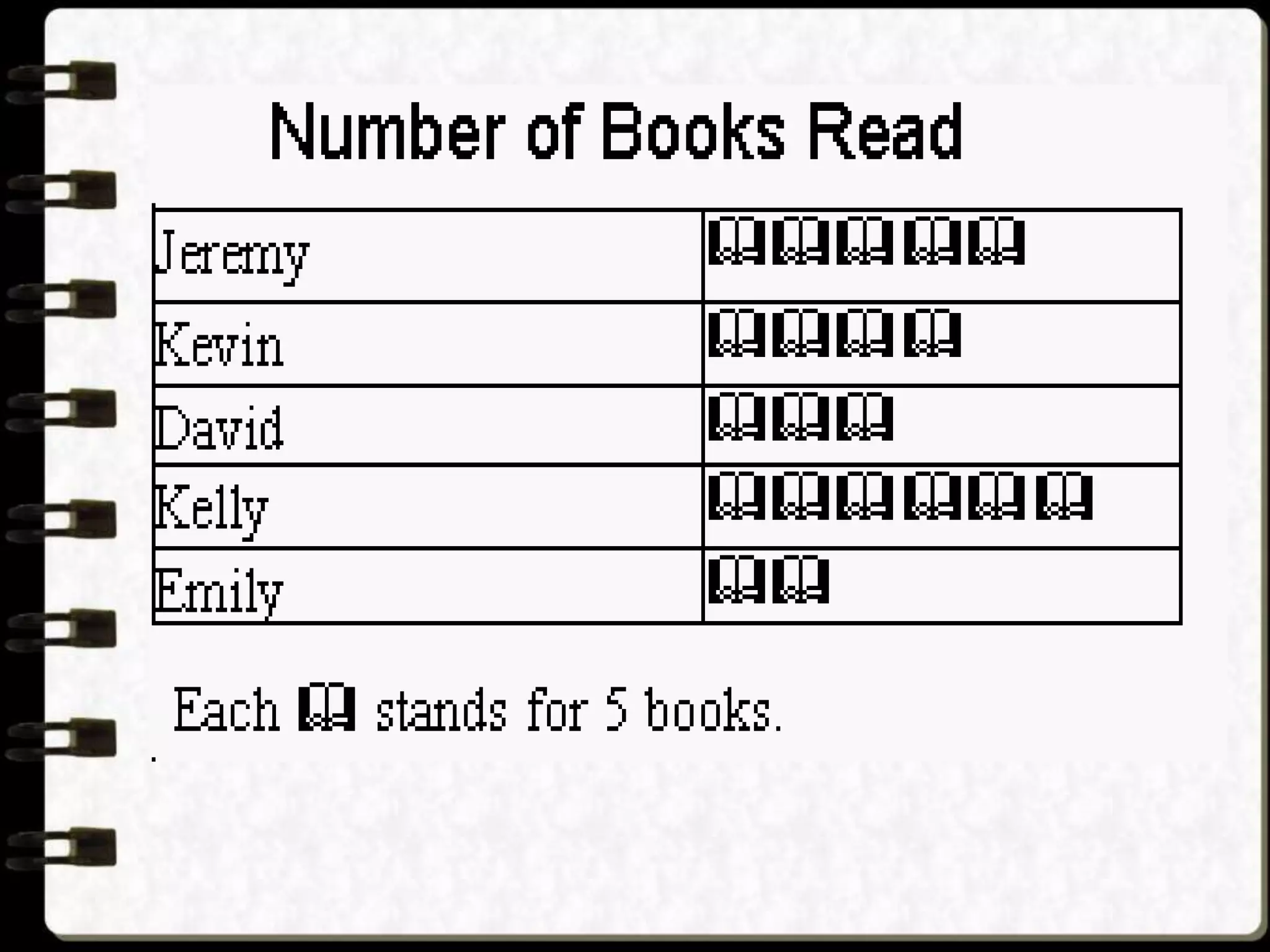
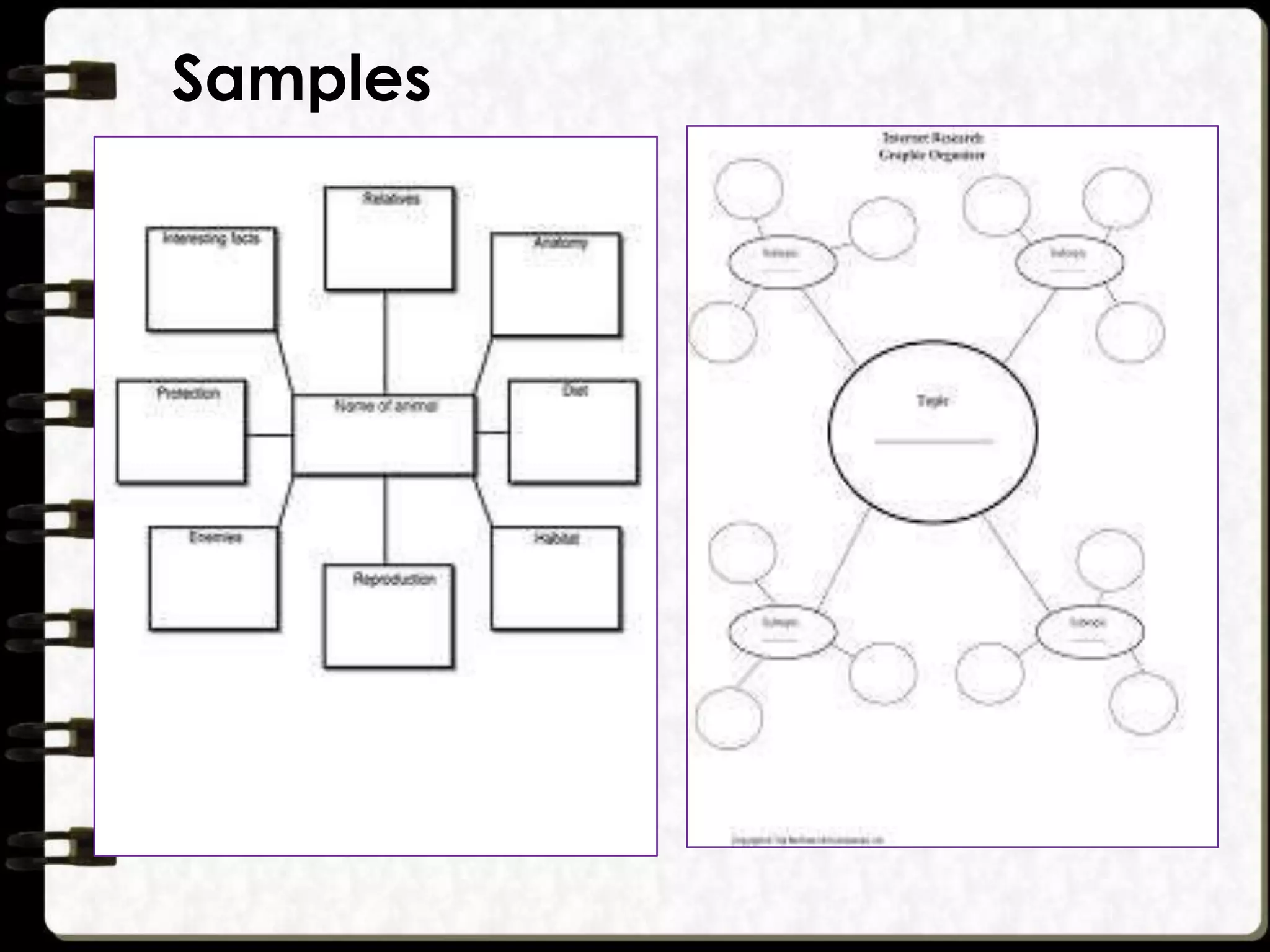
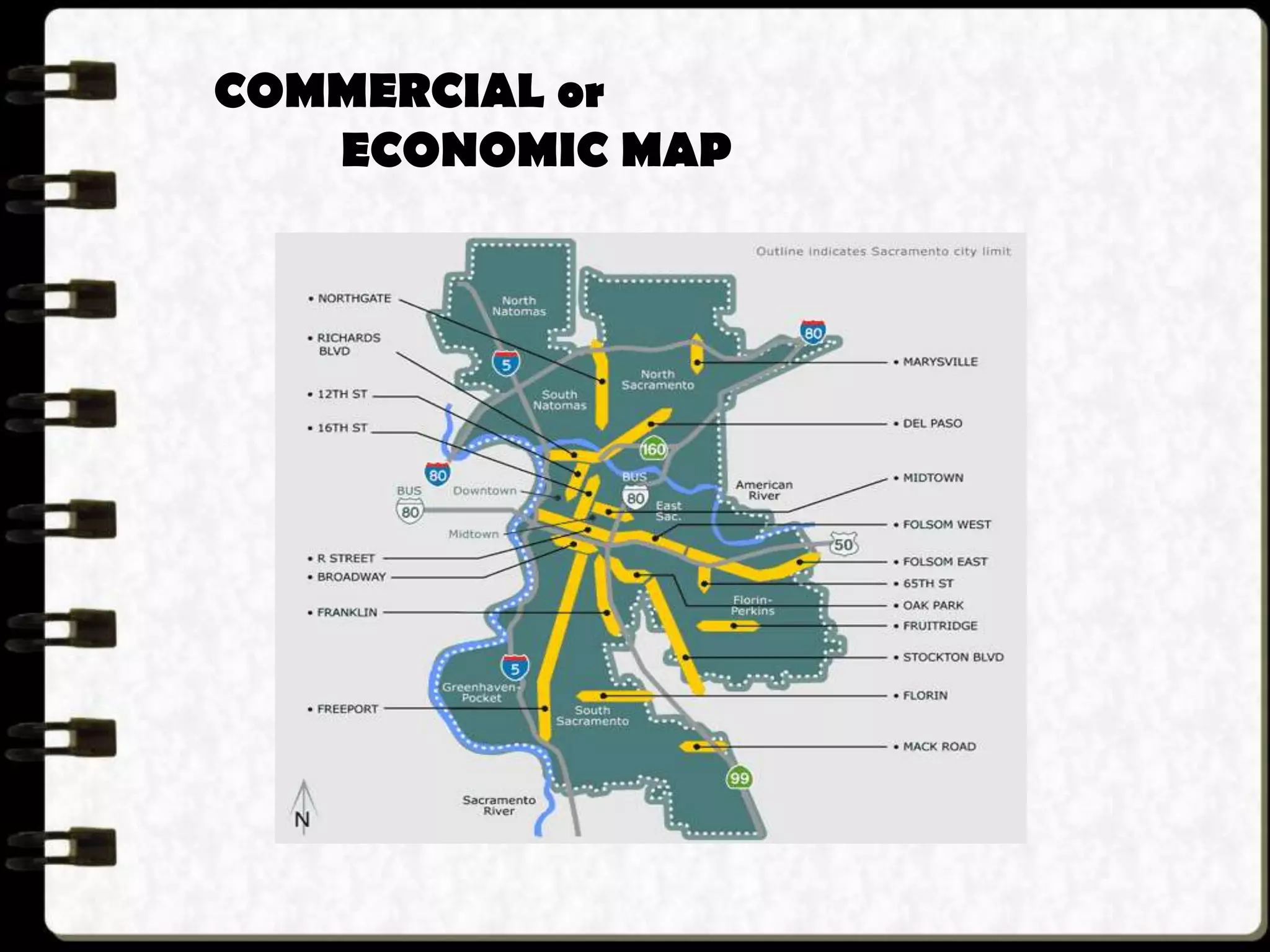
Visual symbols like drawings, cartoons, diagrams and charts can help teach complex concepts. Drawings directly represent real things, while cartoons use metaphor. Diagrams show relationships and organization through lines and positioning. Common diagrams include tree, fishbone, affinity and flow charts. Charts organize data through tables, timelines, flow processes and comparisons. Graphs visualize numerical data through bars, circles, pictures and maps show real world locations and features through symbols, scales, colors and geographic grids. Together, visual symbols make abstract ideas more concrete and aid student understanding of lessons.