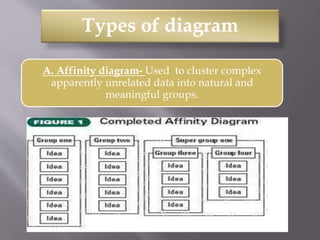
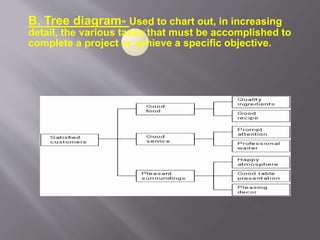
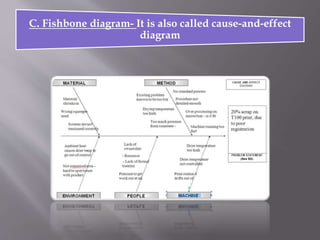
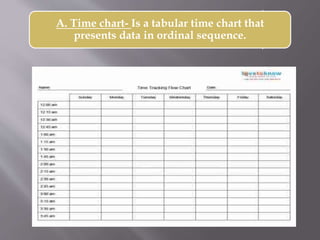
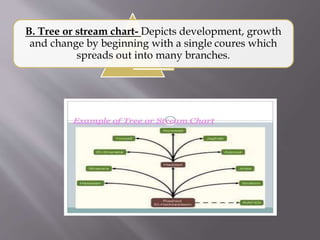
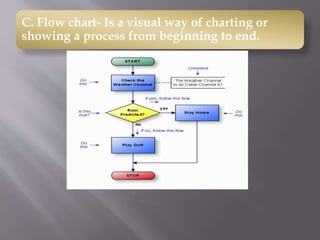
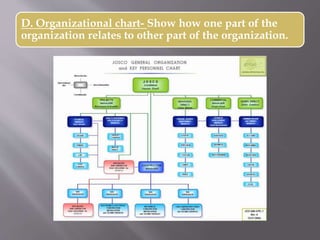
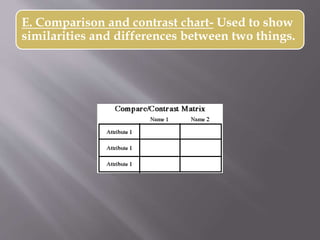
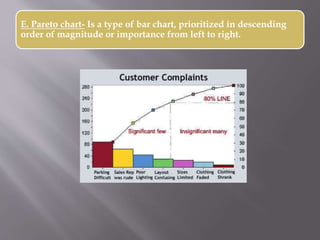
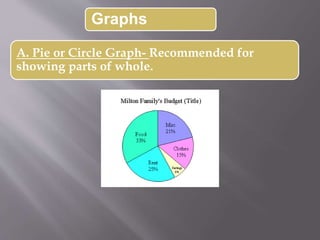
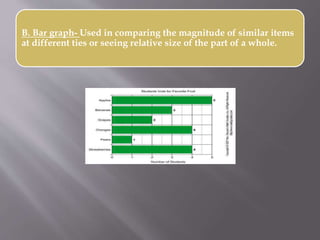
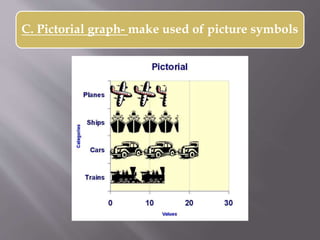
This document discusses different types of visual symbols that can be used in teaching, including drawings, cartoons, strip drawings, diagrams, charts, graphs, and maps. It provides examples of each type such as affinity diagrams, tree diagrams, fishbone diagrams, time charts, flow charts, organizational charts, bar graphs, pie graphs, and physical, relief, political, and economic maps. These visual symbols are useful aids that can bring novelty to teaching by representing concepts in a concrete way without needing extensive captions or text. Guidelines for correctly interpreting charts, graphs, and maps include understanding scales, symbols, colors, and geographic grids.