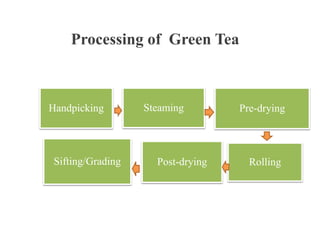
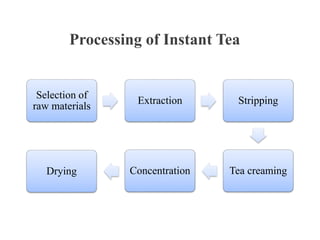
The presentation covers the manufacturing and packaging process for tea, including types of green tea like sencha and gunpowder, how they are processed, and quality control measures. It discusses tasting tea properly by smelling, slurping, and spitting, and the production of instant tea which involves extraction, stripping, creaming, concentration and drying. The presentation also covers organic tea production, semi-fermented teas that are 20-70% fermented, and ensuring quality through cleaning, hygiene, drying, waste management and certification.