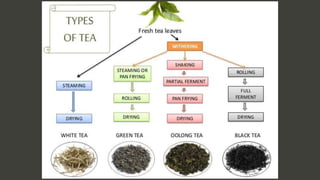
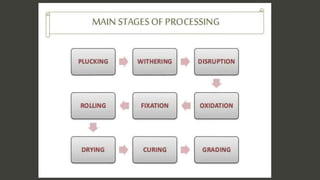
Tea processing transforms leaves from the Camellia sinensis plant into dried leaves for brewing, involving various methods of oxidation and other treatments. The process includes stages like plucking, withering, oxidation, drying, and curing, which influence the distinct types of tea, such as green, yellow, white, oolong, and black. The history of tea processing is closely linked to its cultural significance in Chinese society and has evolved with different techniques over time.










![Rolling / shaping
● The damp tea leaves are
then rolled to be formed
into wrinkled strips, by
hand[9] or using a rolling
machine which causes the
tea to wrap around itself.
● The strips of tea can then
be formed into other
shapes, such as being rolled
into spirals, kneaded and
rolled into pellets, or tied
into balls, cones and other
elaborate shapes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/processingofteabytanyathakuea43126180241-220922100710-5b73f90b/85/Processing-Of-Tea-12-320.jpg)