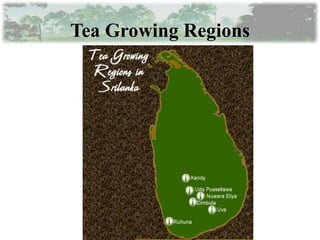
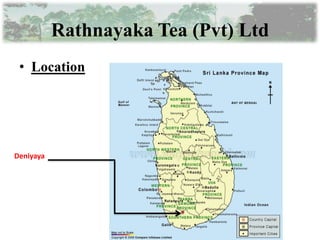
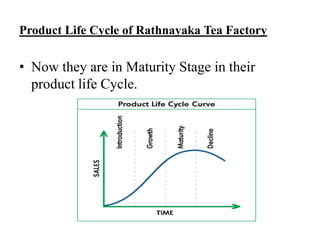
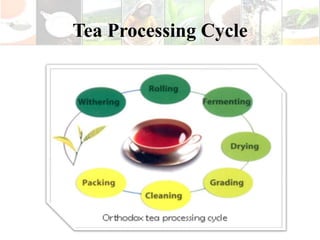
The document provides information about tea processing at Rathnayaka Tea (Pvt) Ltd in Sri Lanka. It discusses the history of the company and details each step of tea processing, including plucking, withering, rolling, and fermentation. The summary concludes with key facts about the company's current operations and export of black tea to Russia.