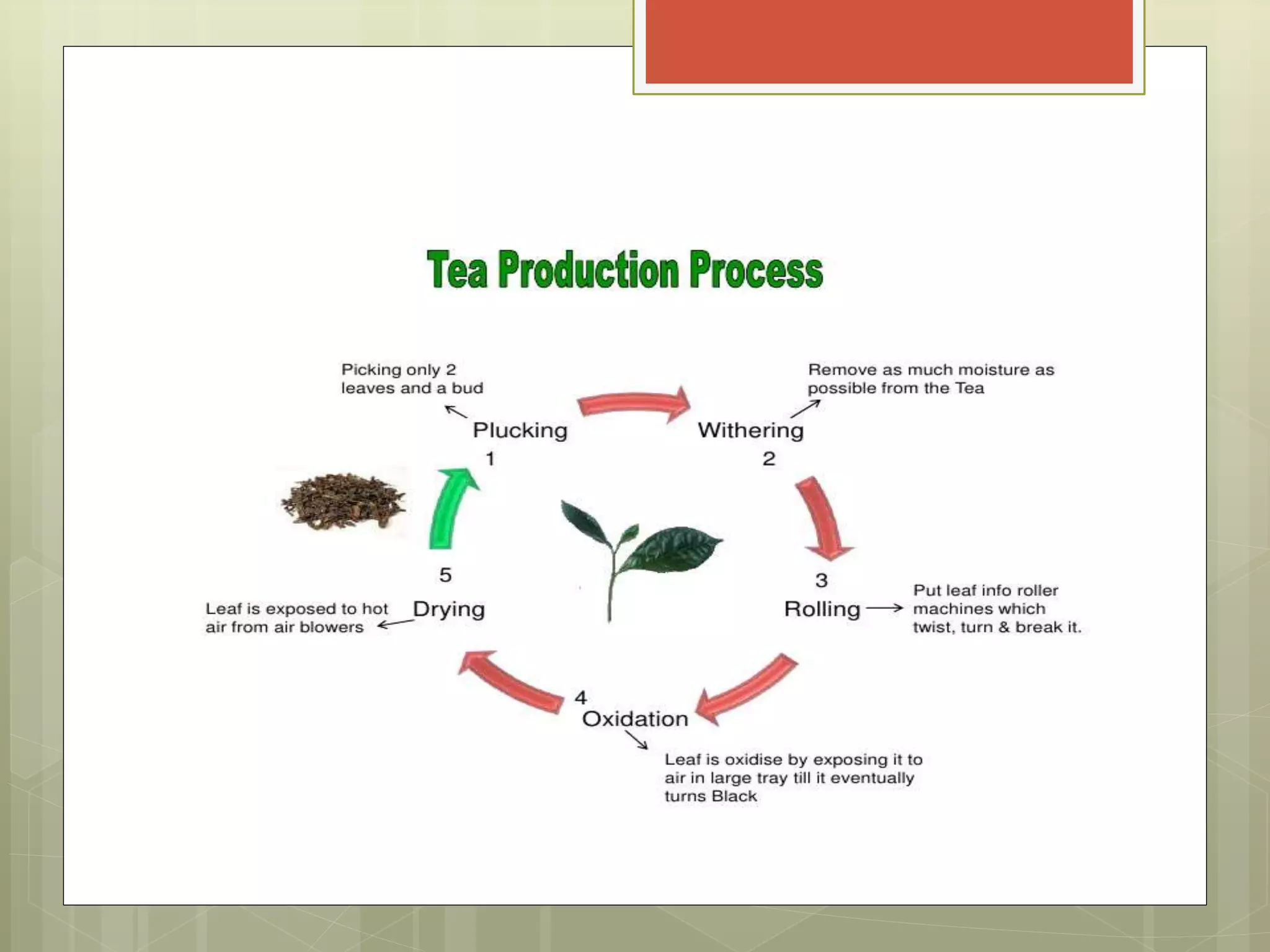
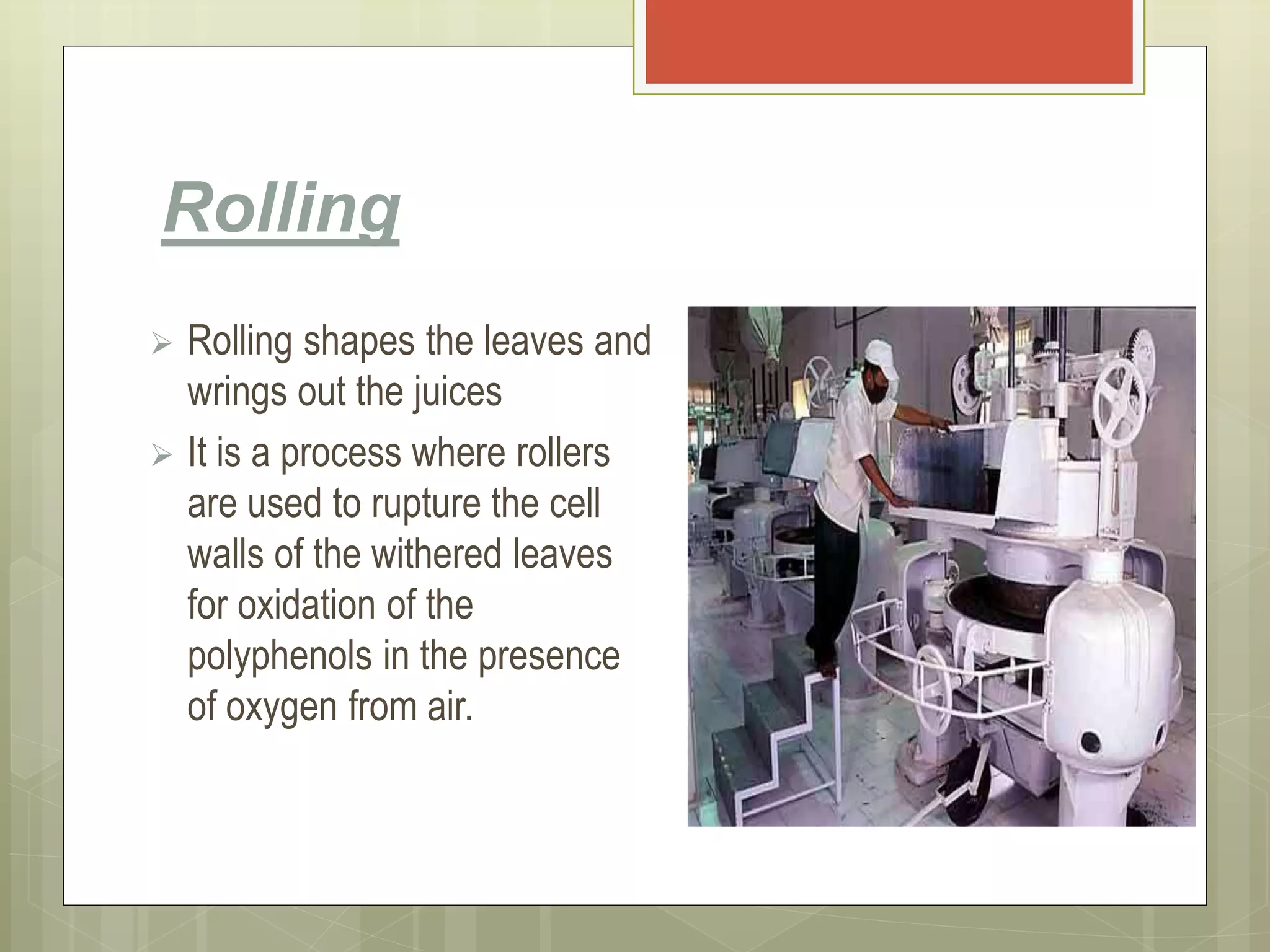
The document provides information about a group project including the group members' names and roll numbers. It then summarizes the process of manufacturing tea, including: the history of tea originating in 2737BC China; optimal growing conditions; health benefits; and the steps of plucking, withering, rolling, fermentation, drying, grading, cleaning, and packing. The key steps in the manufacturing process are plucking young tea leaves, withering them to reduce moisture, rolling to rupture cells, fermenting through oxidation, drying to stop oxidation, grading quality, cleaning, and final packing for sale.