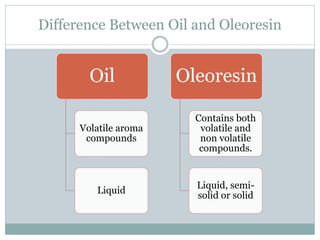
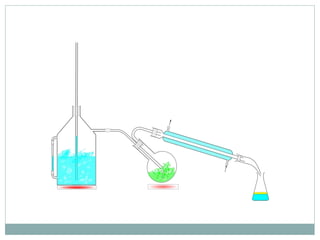
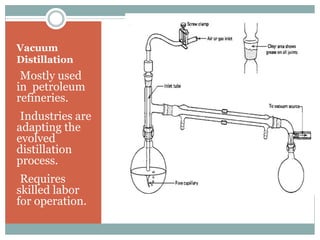
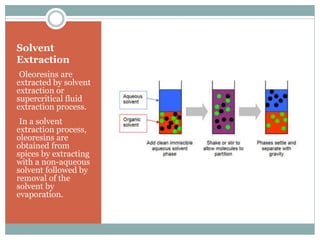
This document discusses different methods for extracting essential oils from spices, focusing on steam distillation. It begins by introducing spices and their uses in food, then describes three types of spice extracts - essential oils, oleoresins, and oil/oleoresin derivatives. It explains that steam distillation is commonly used to extract temperature-sensitive essential oils without decomposition. The document outlines the steam distillation process, applications, and limitations. It also discusses evolved extraction methods like vacuum distillation and solvent extraction that are now more commonly used industrially.