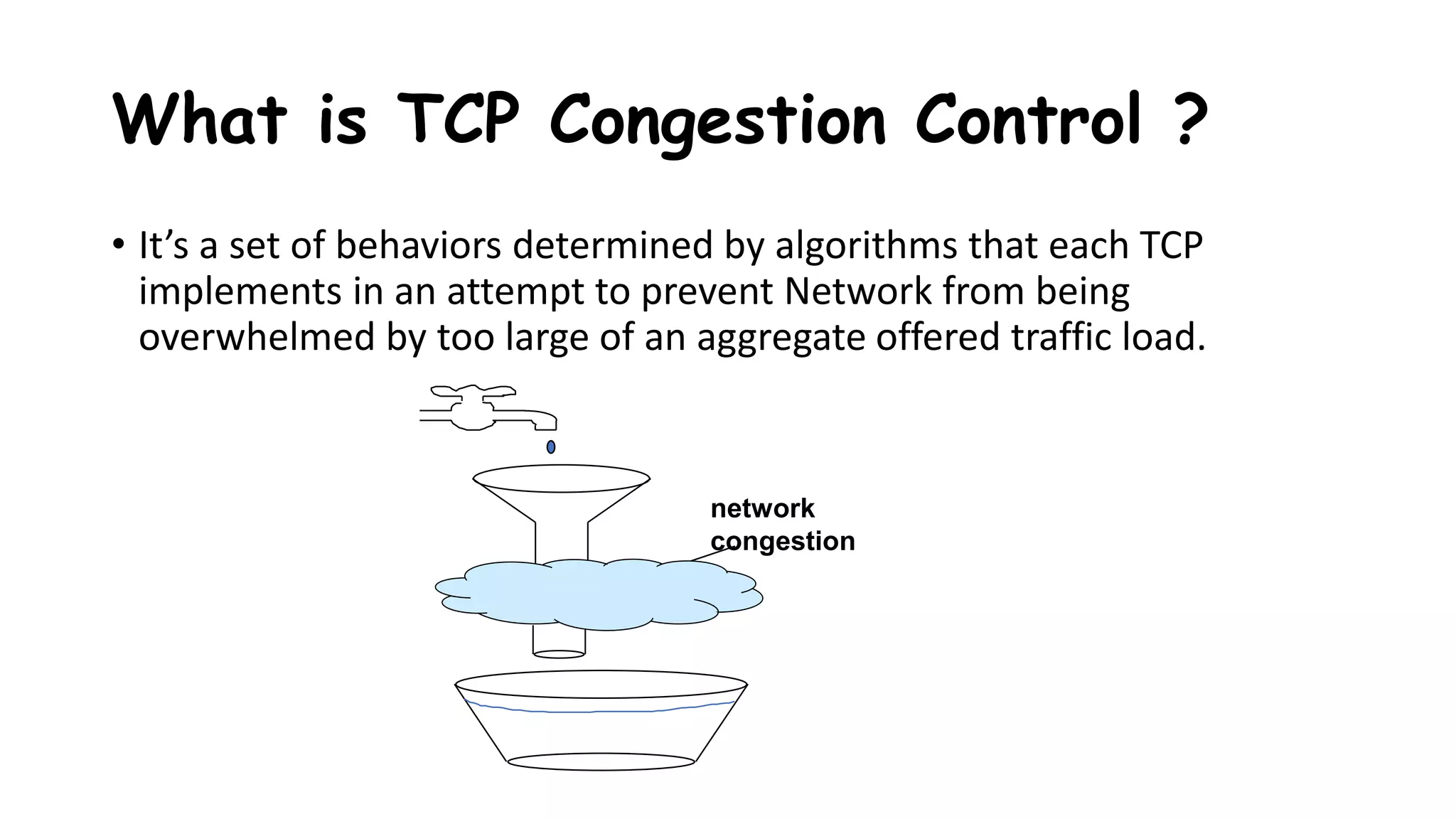
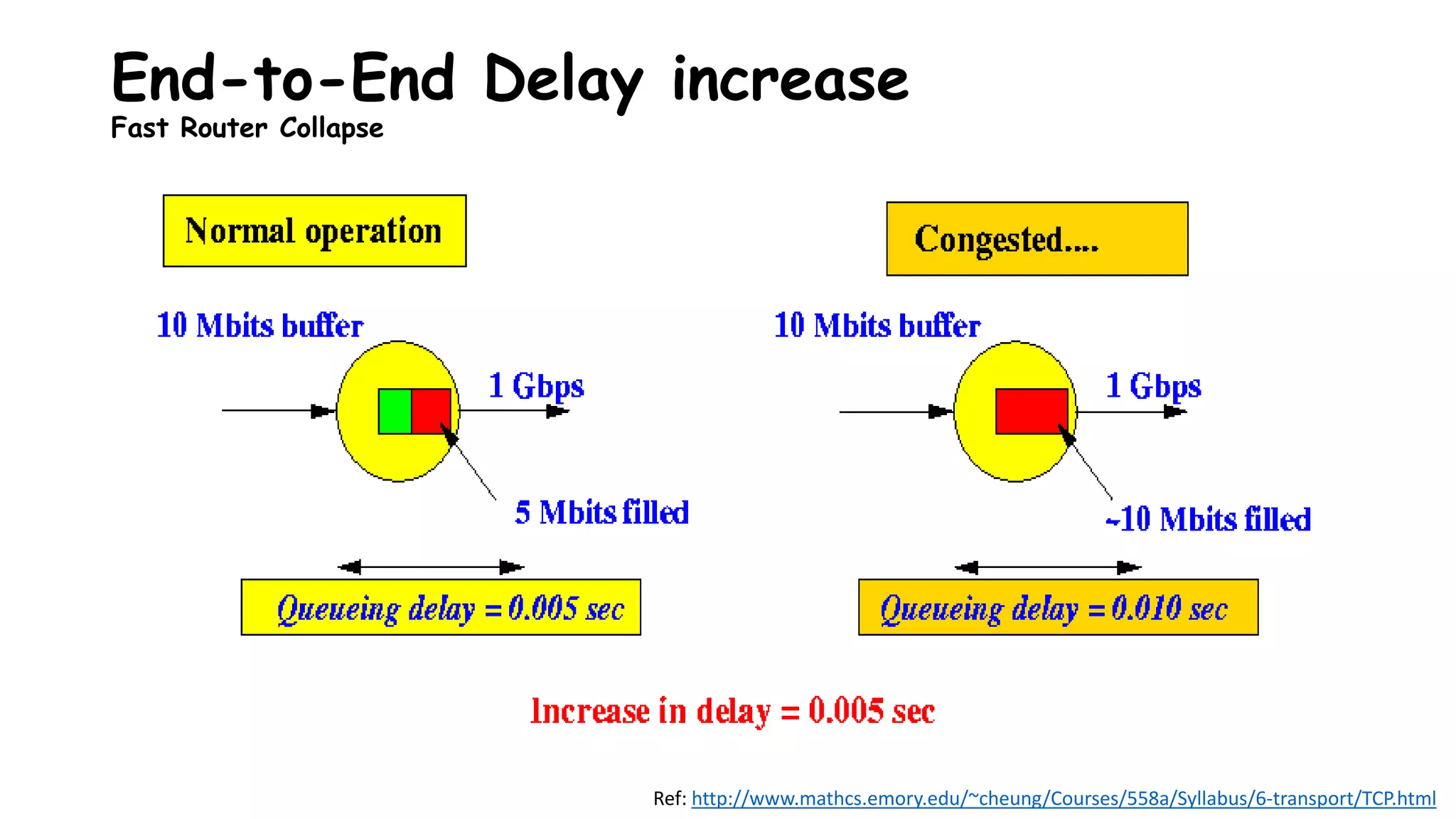
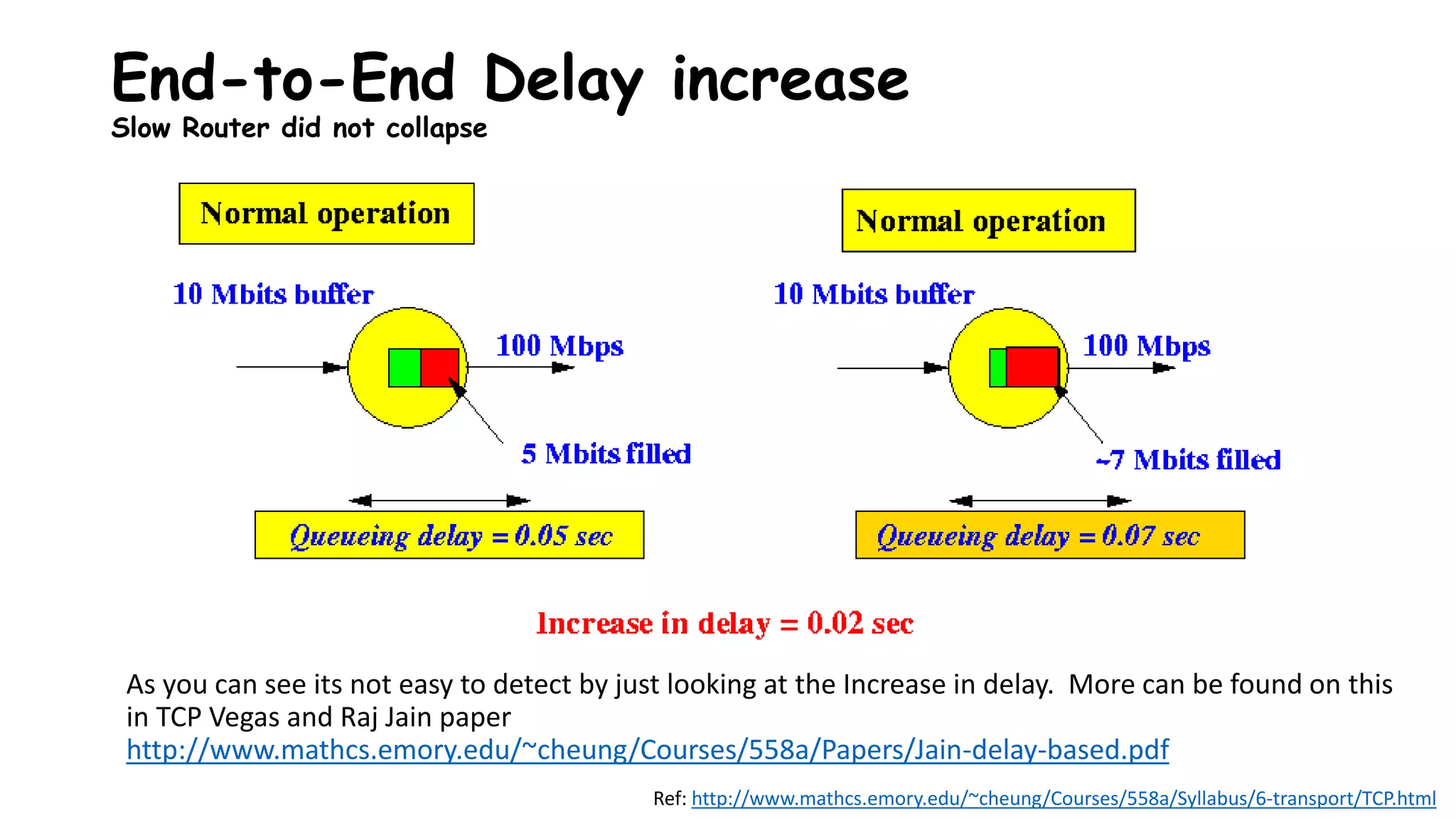
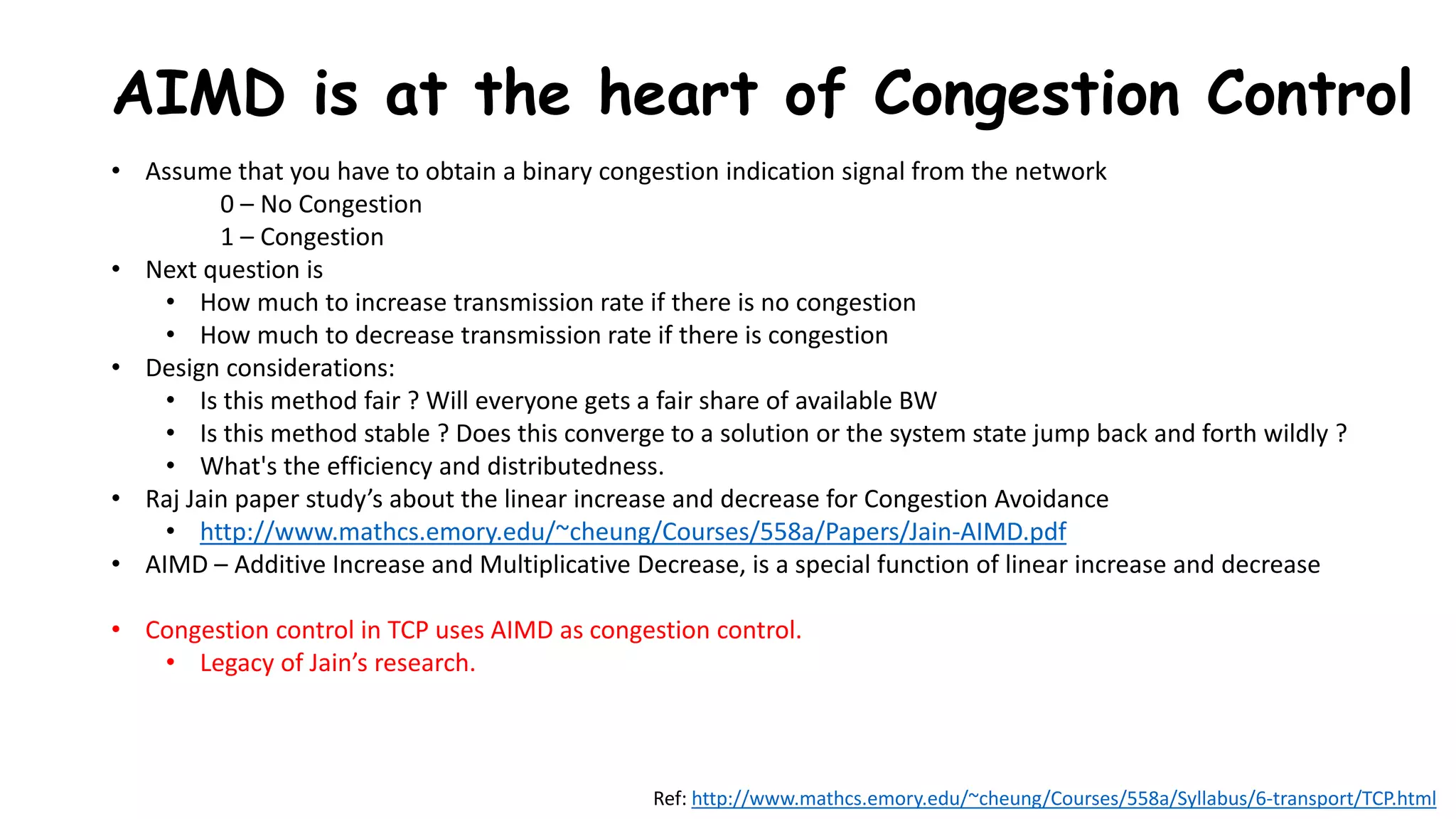
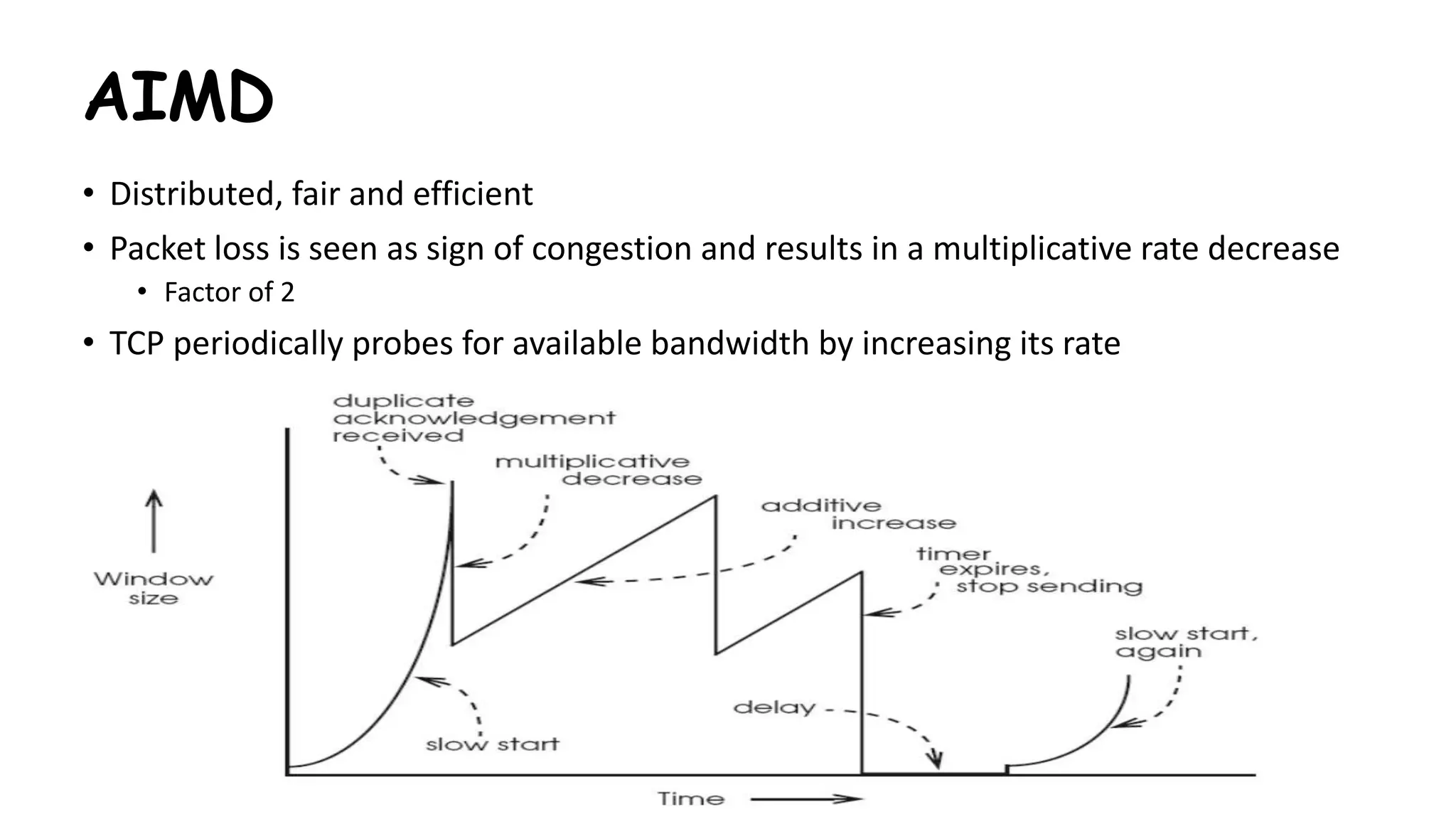
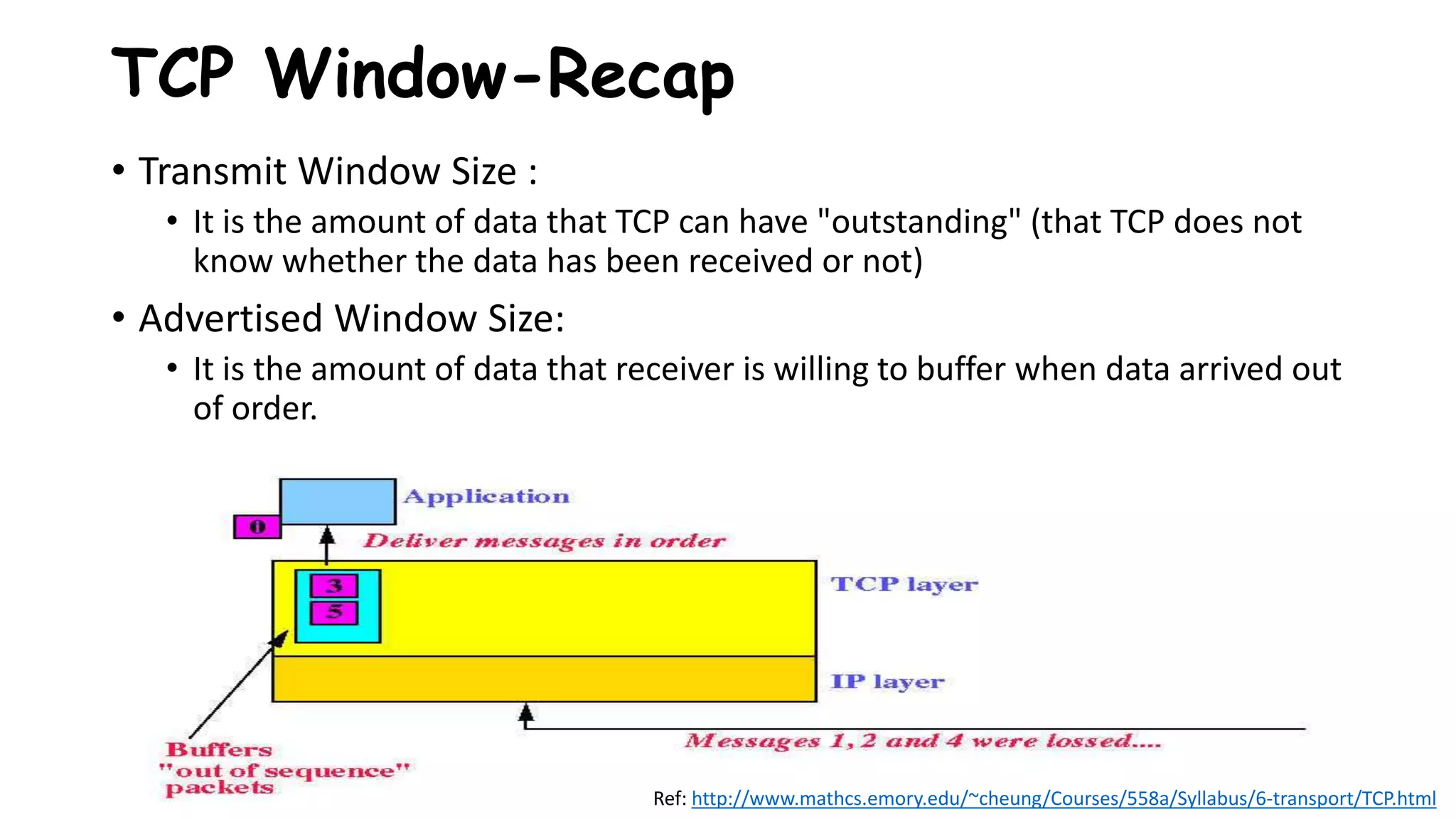
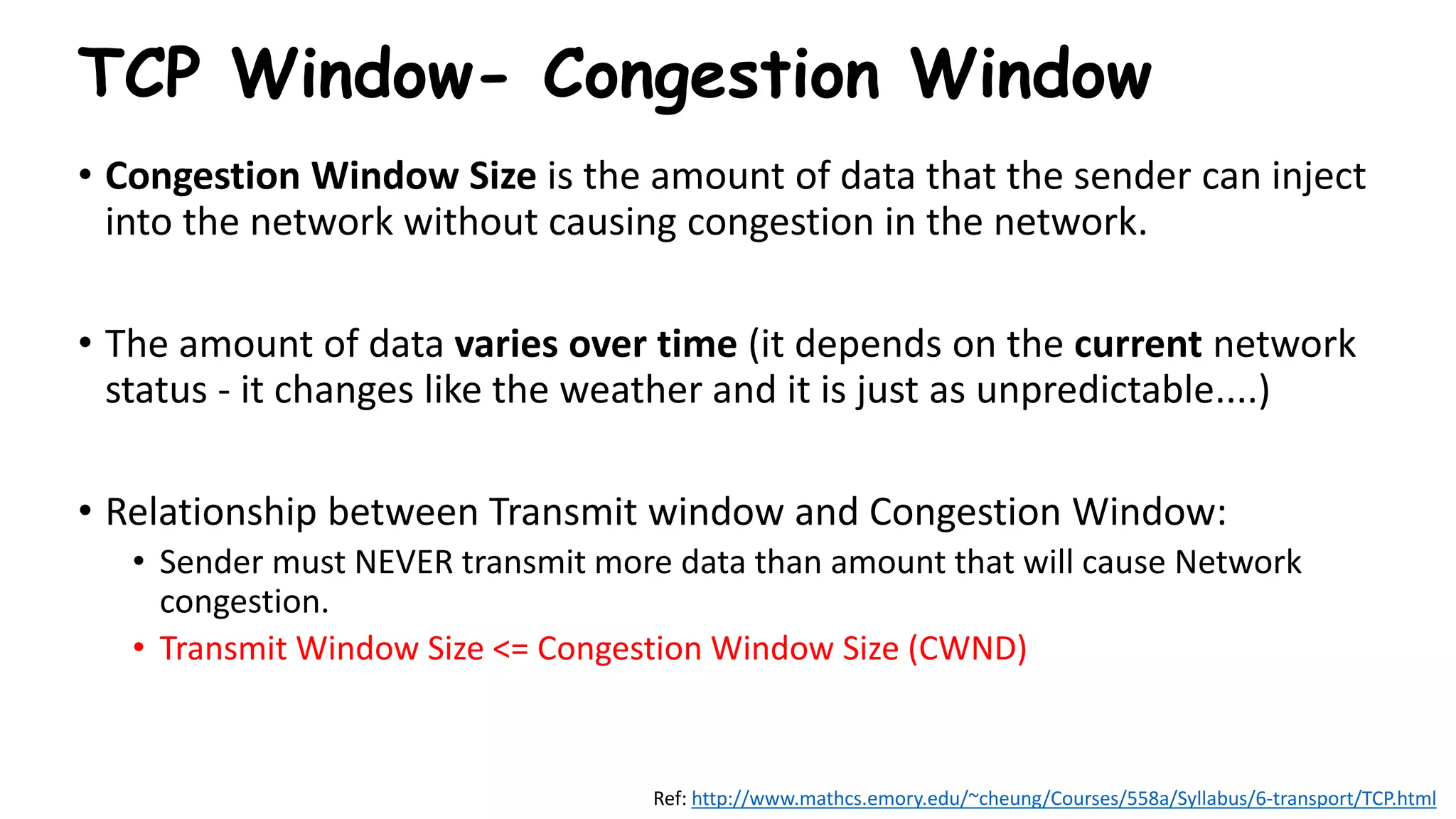
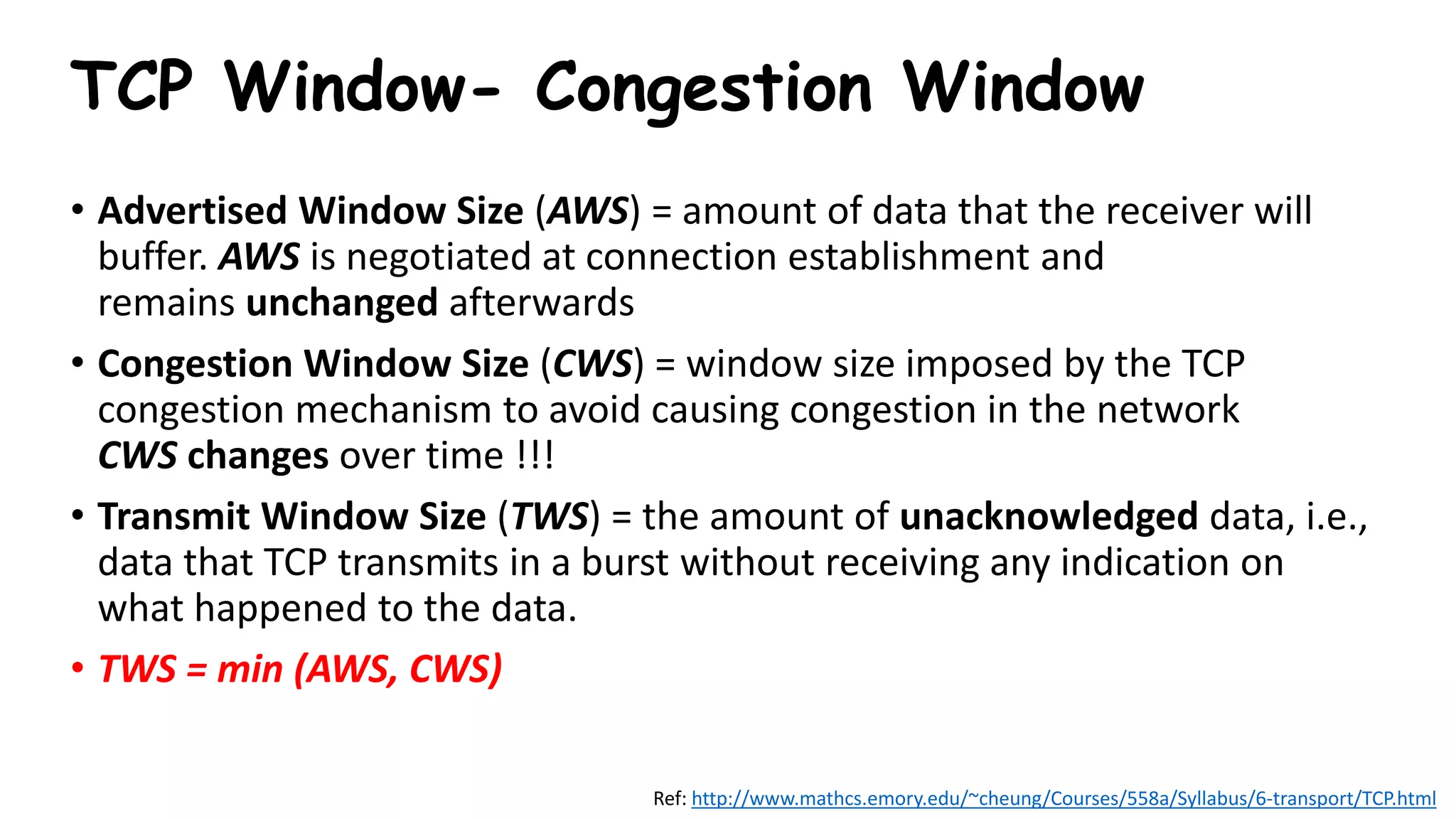
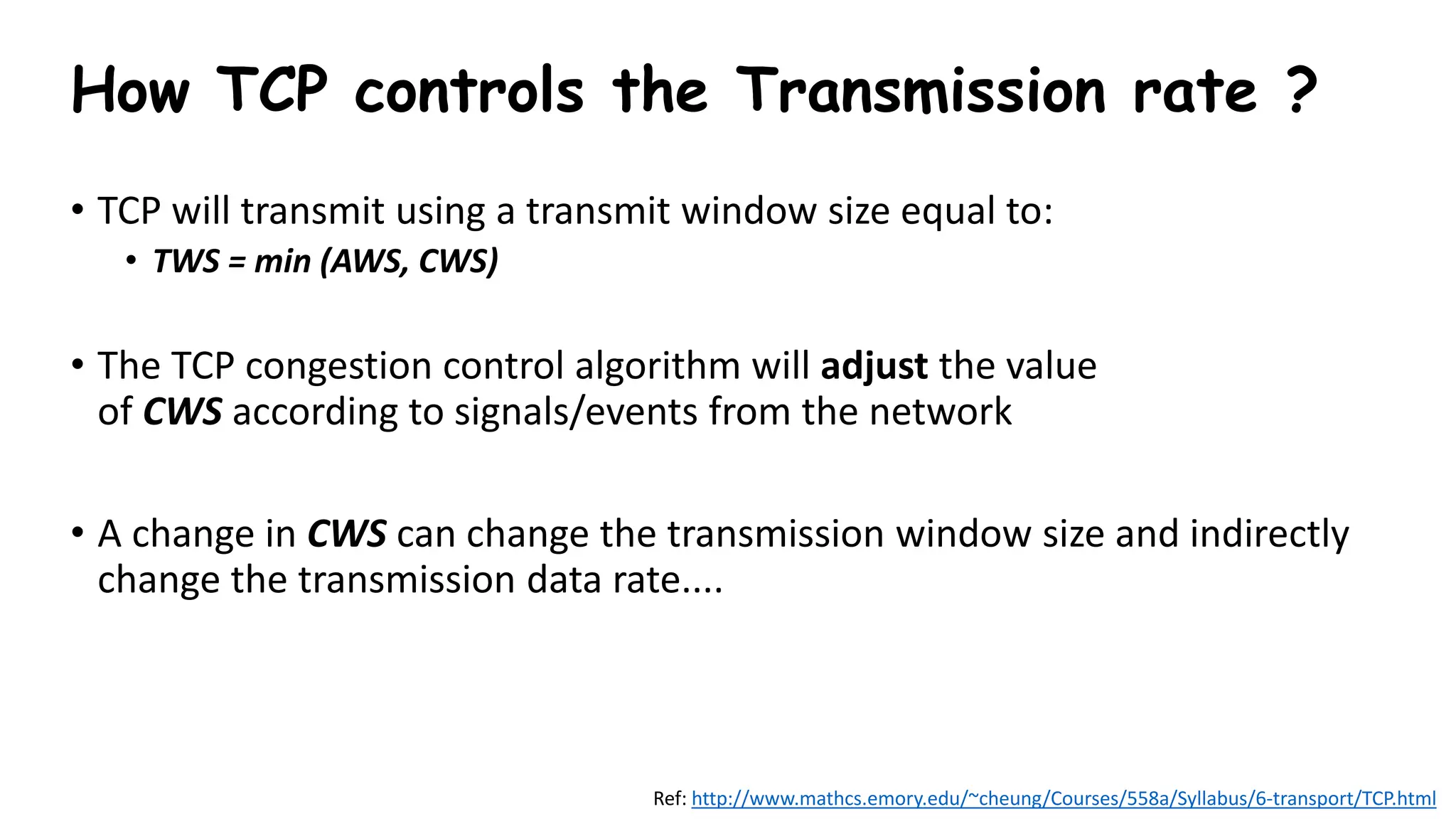
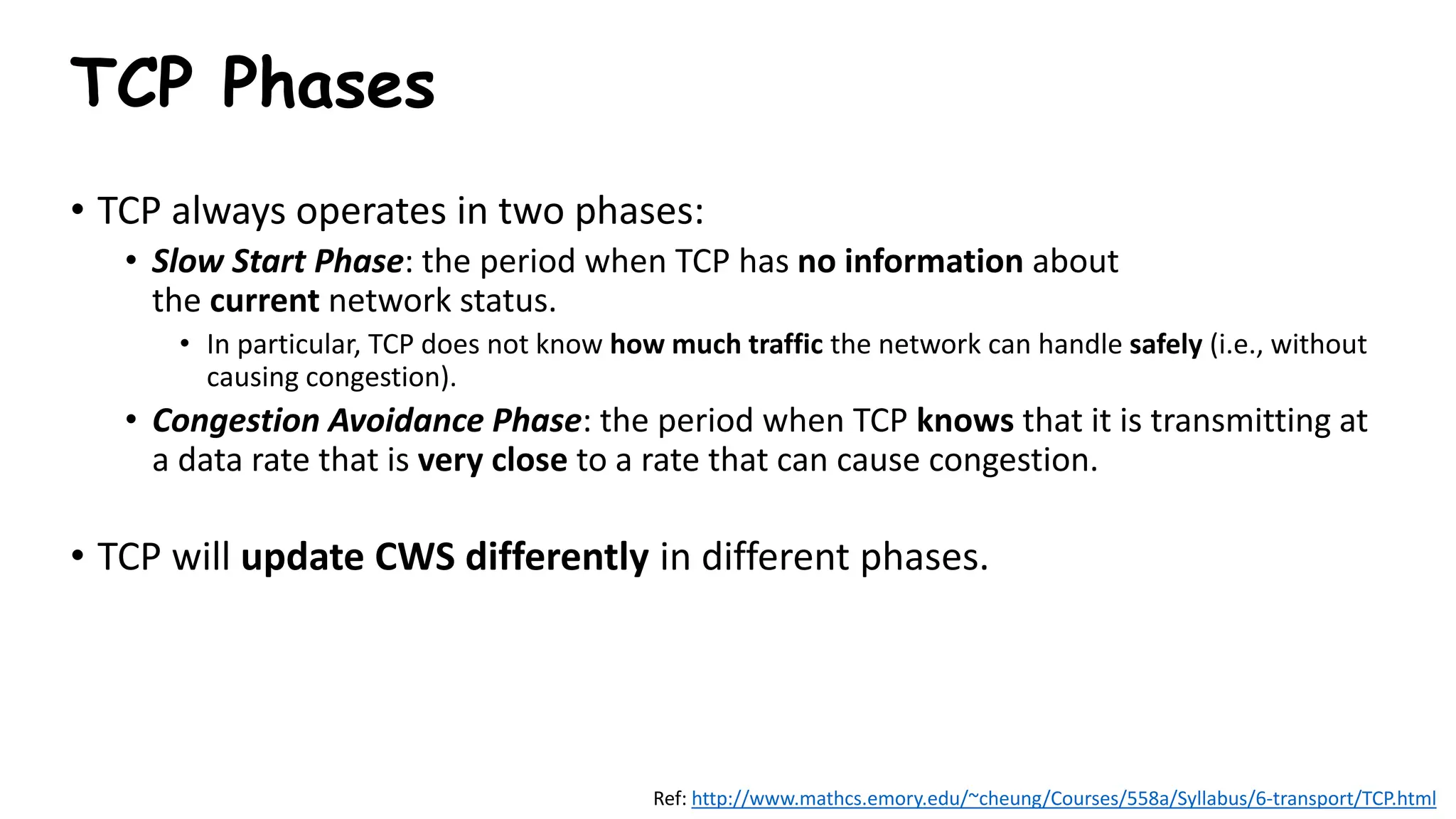
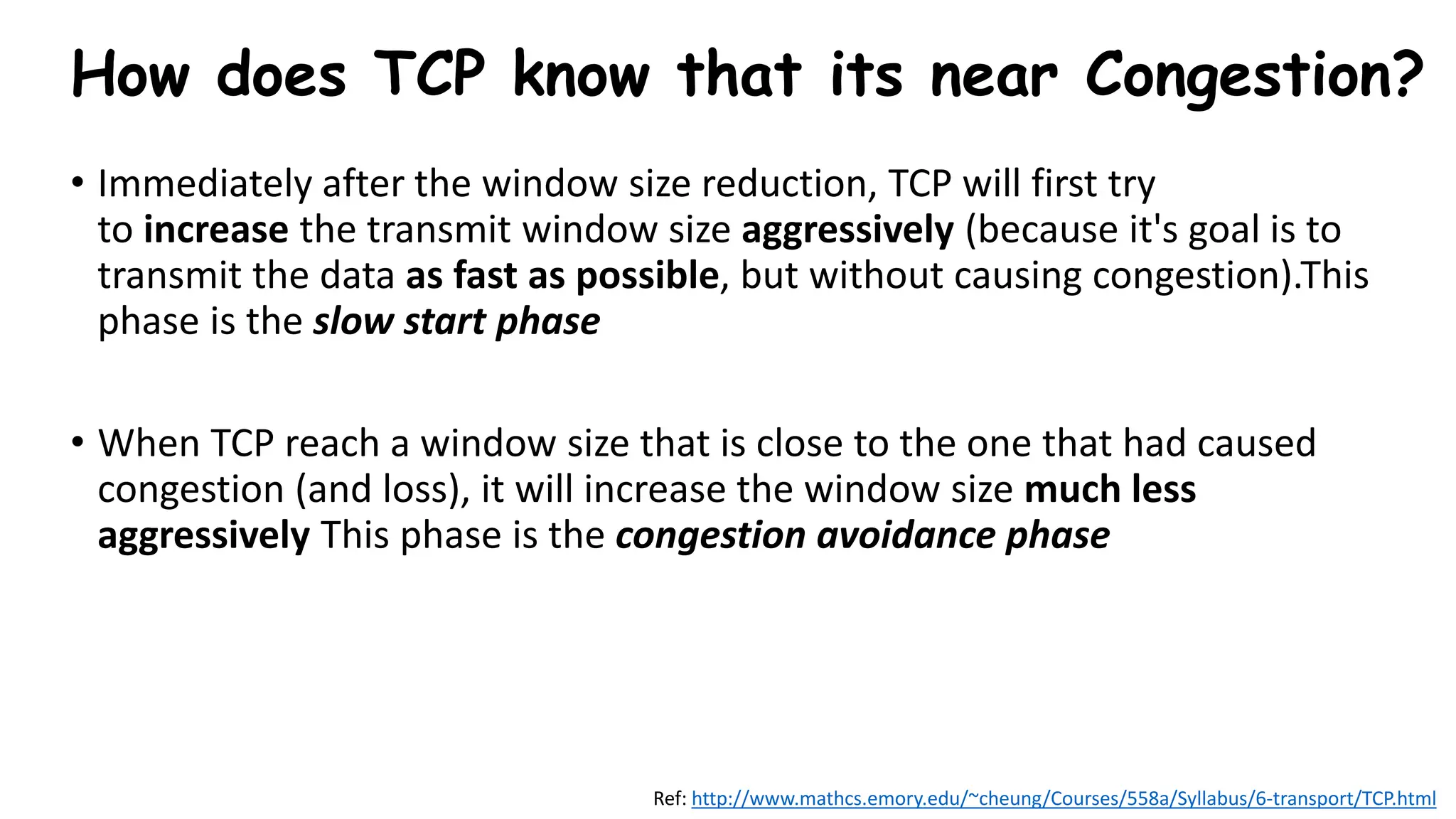
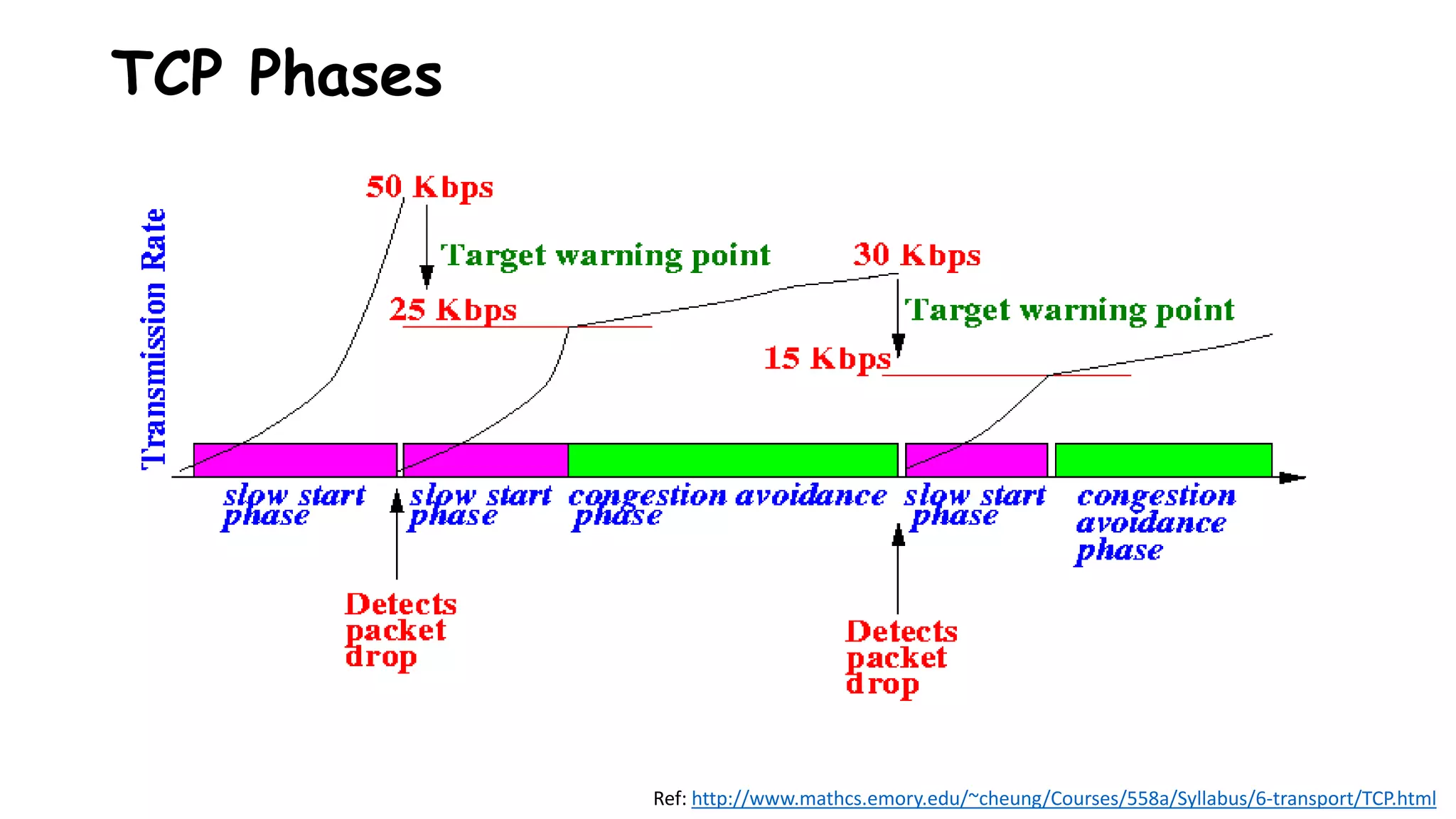
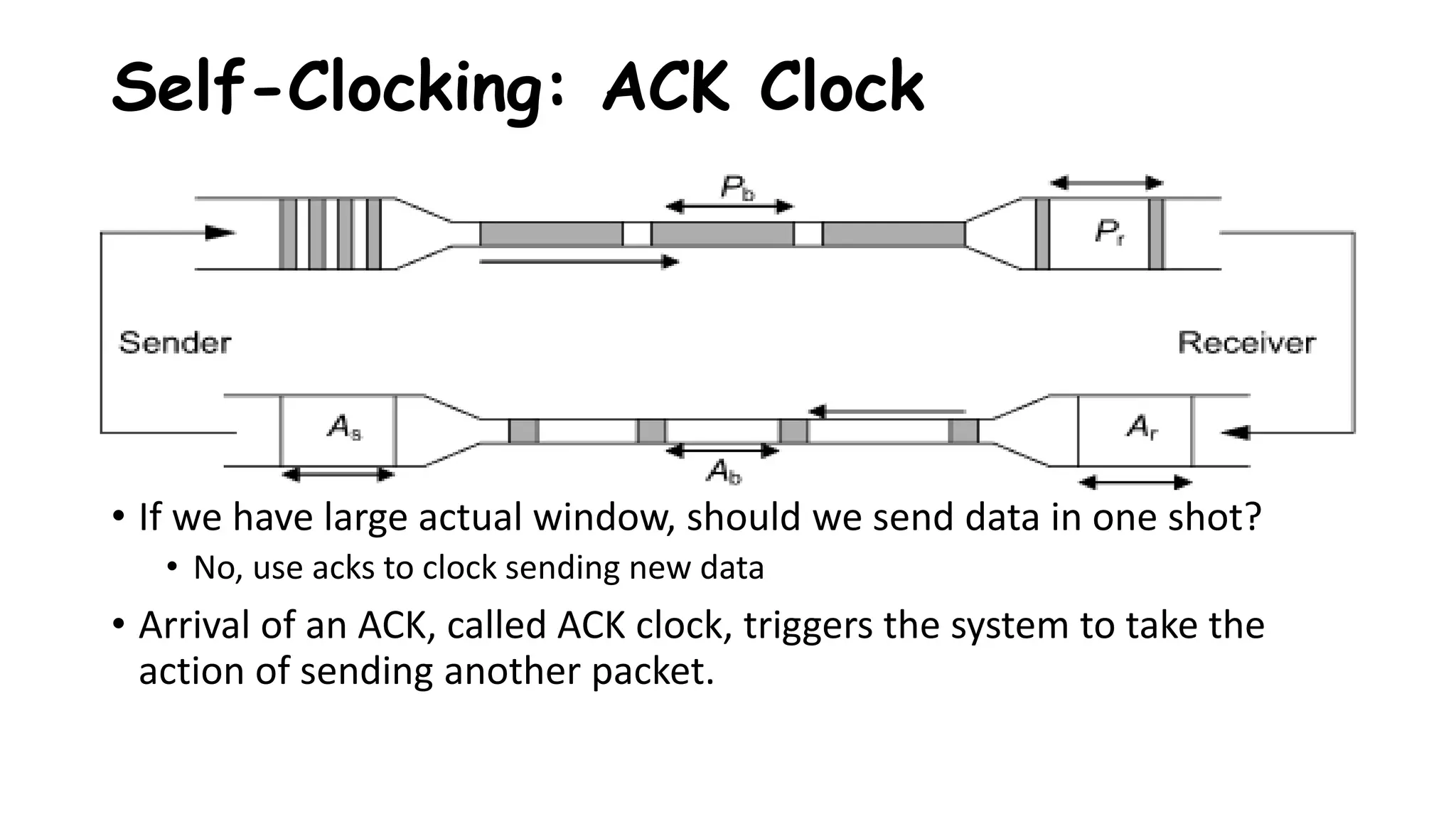
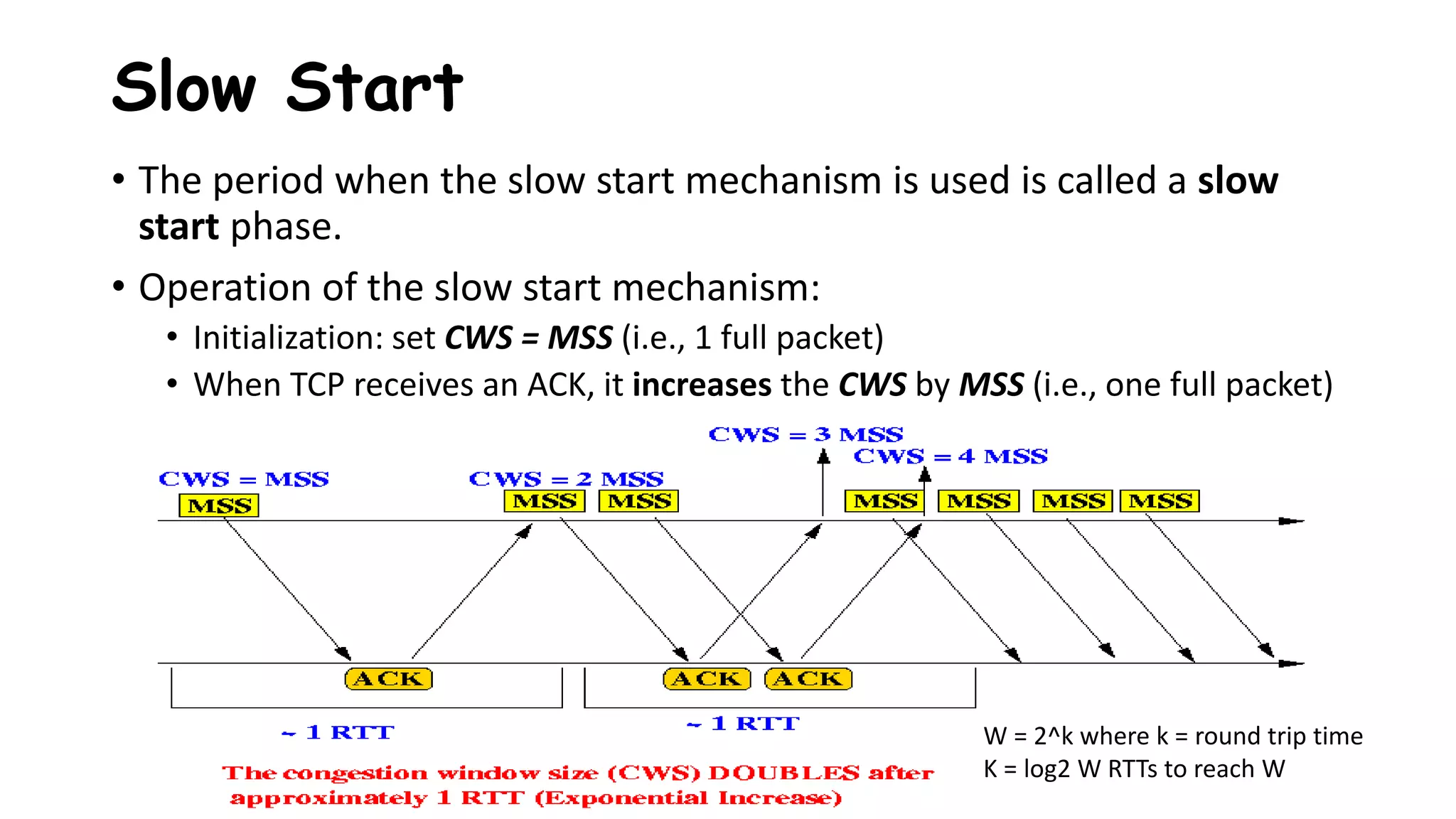
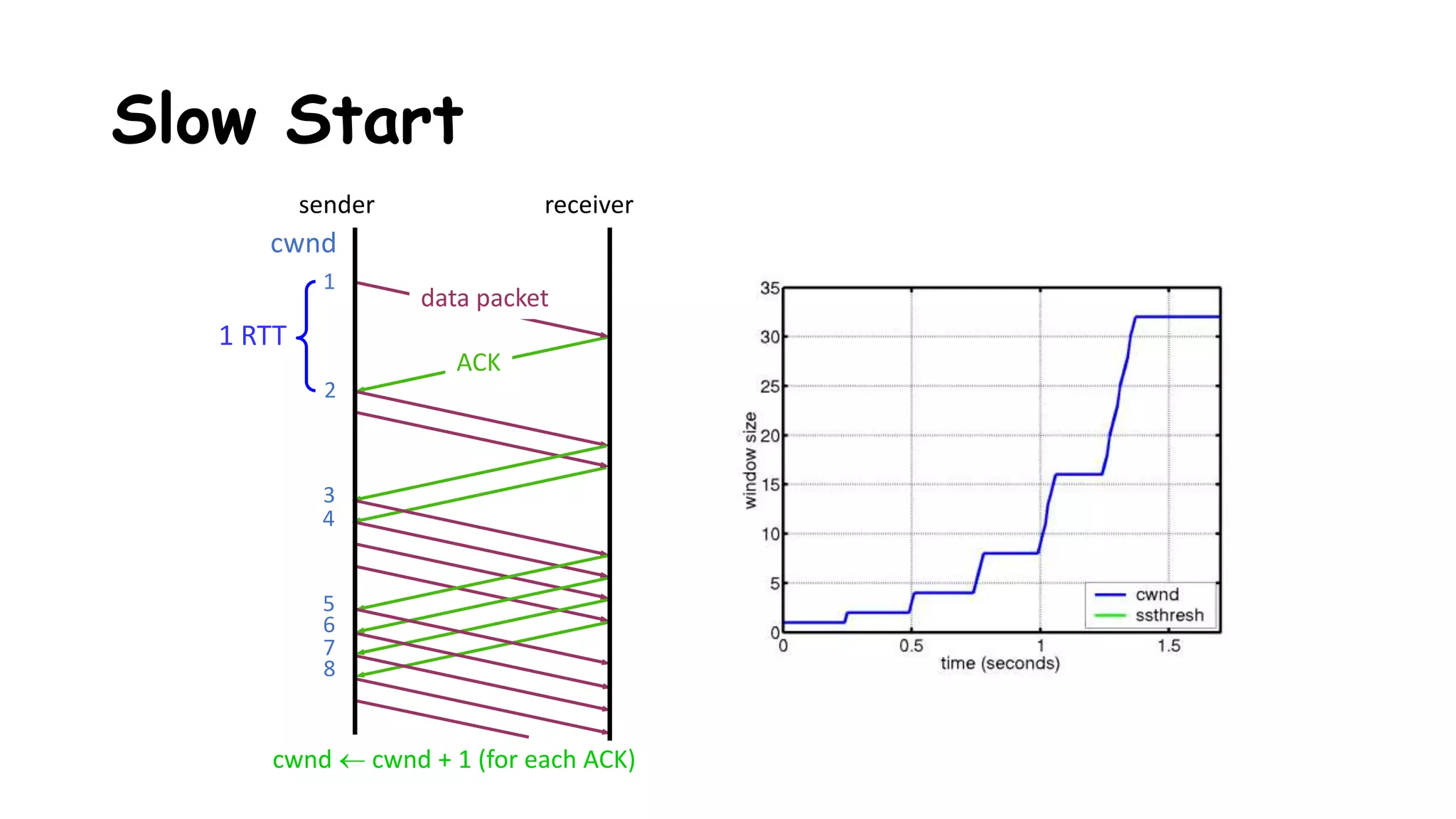
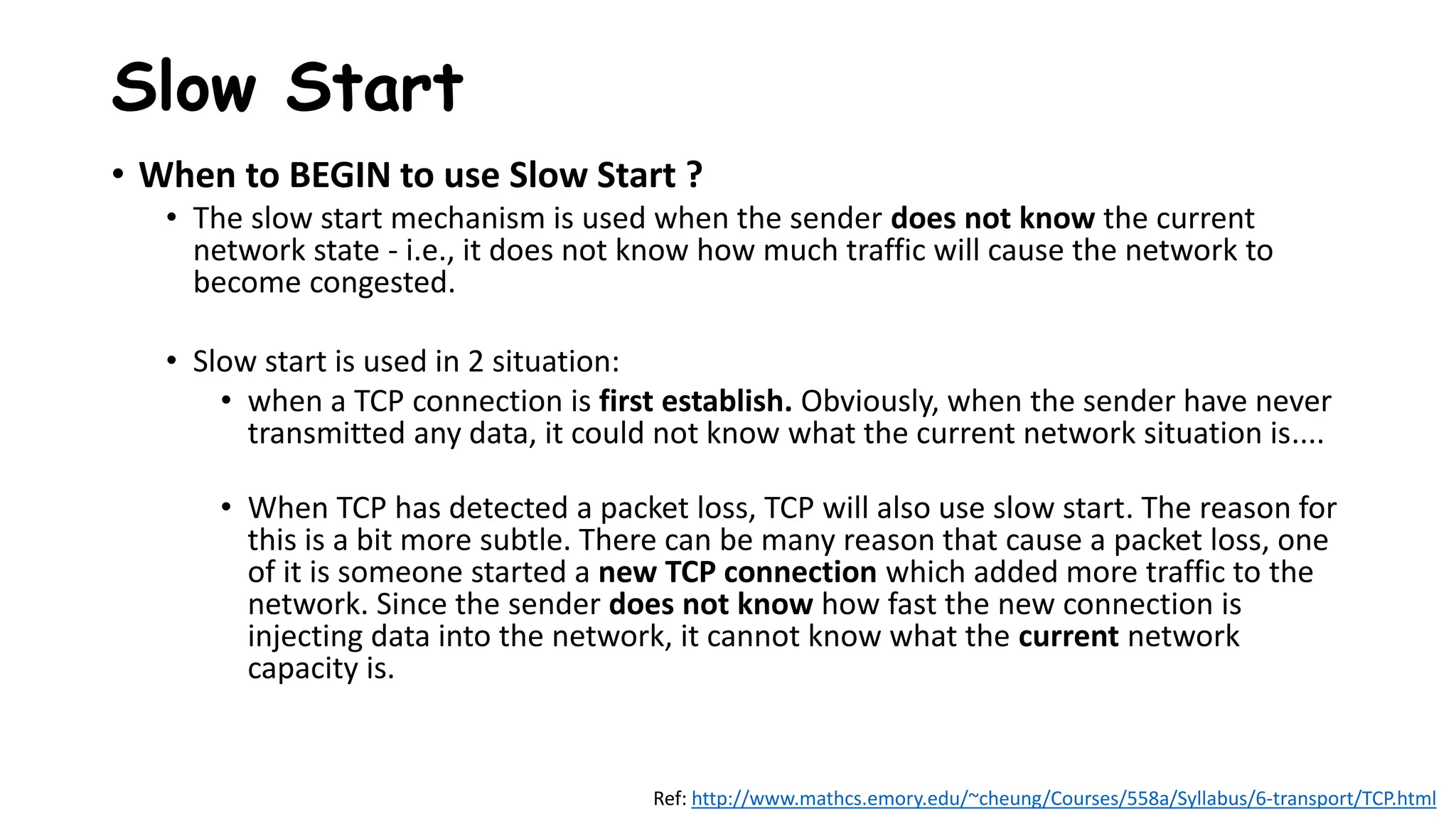
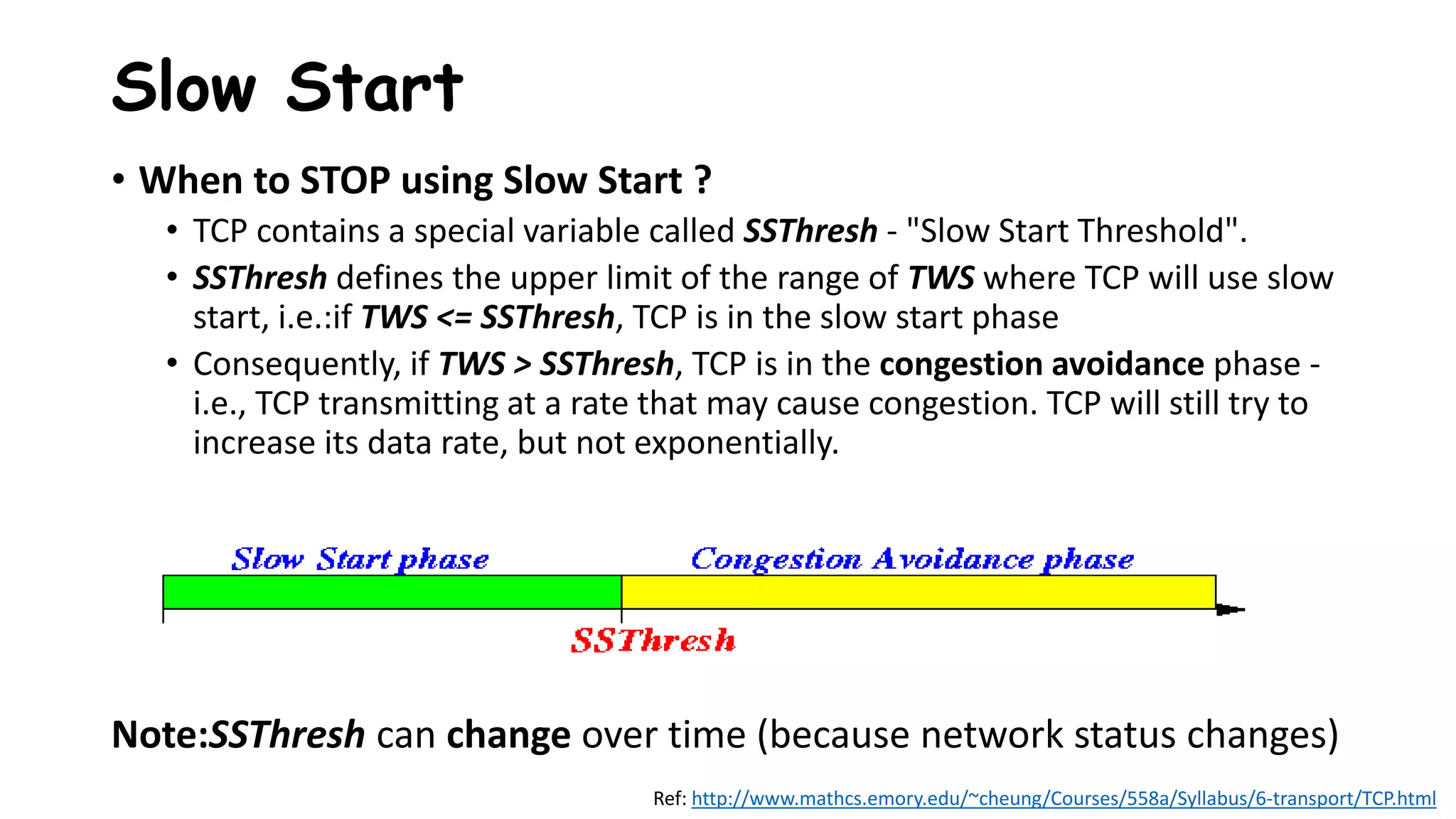
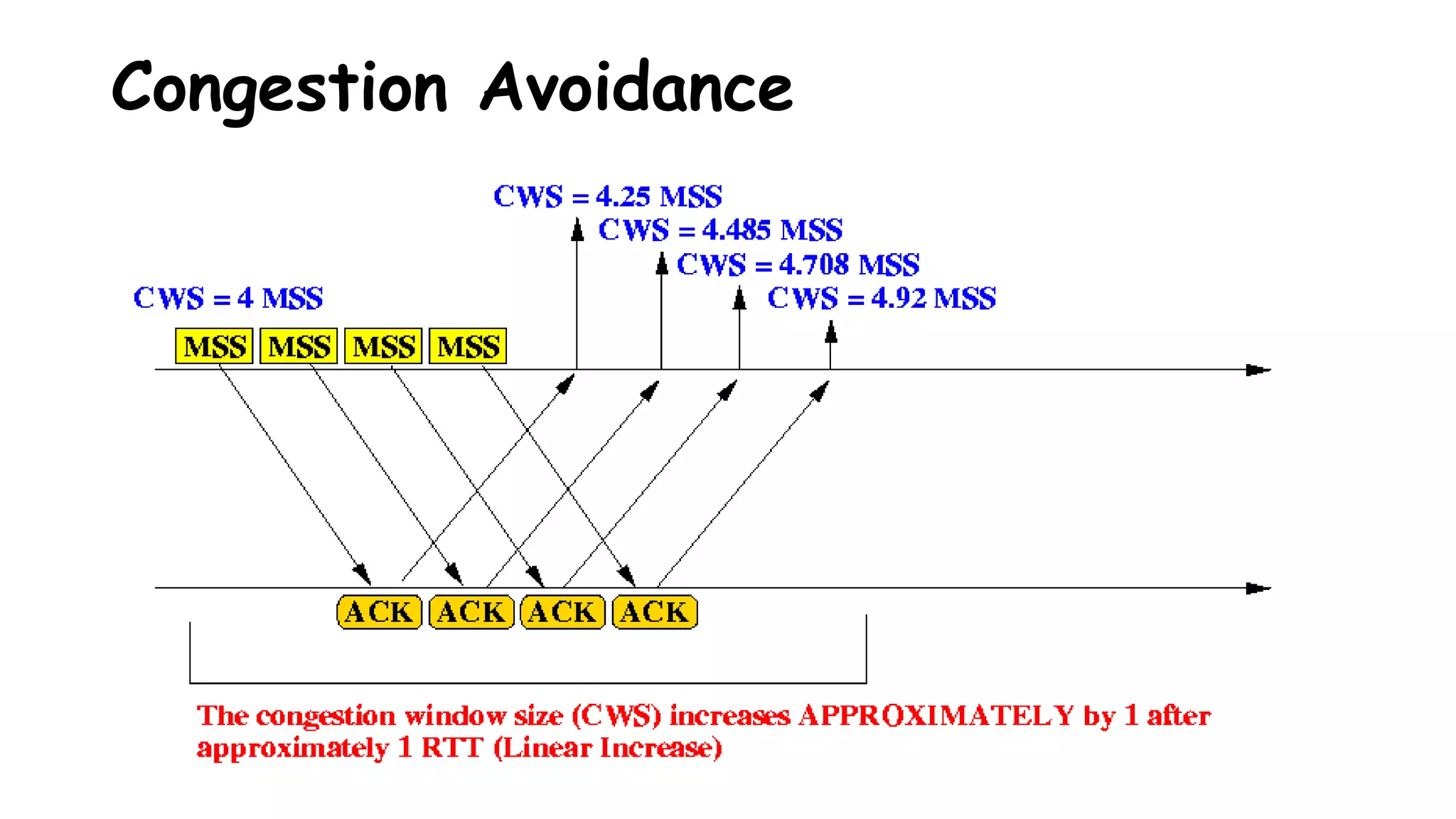
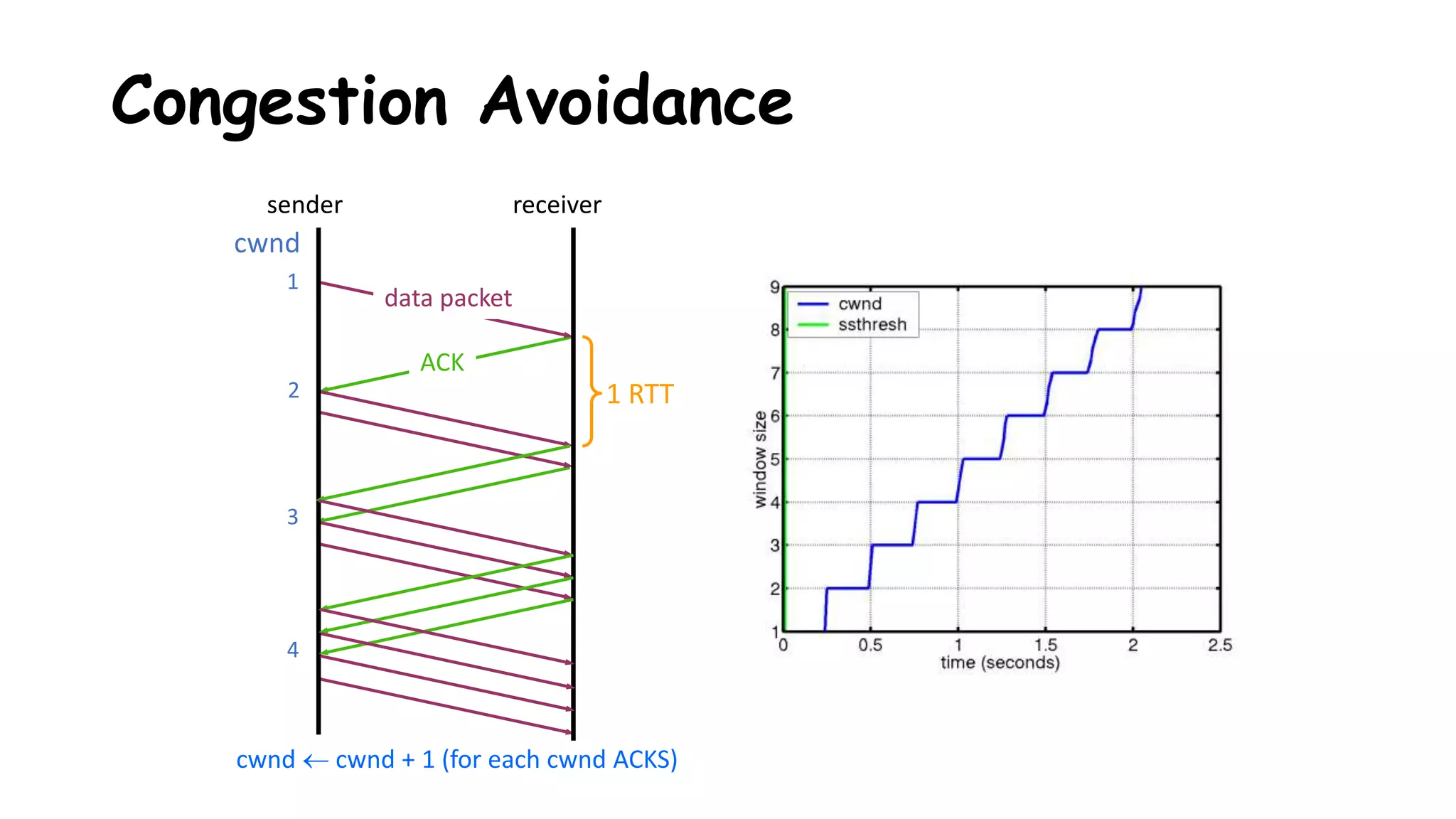
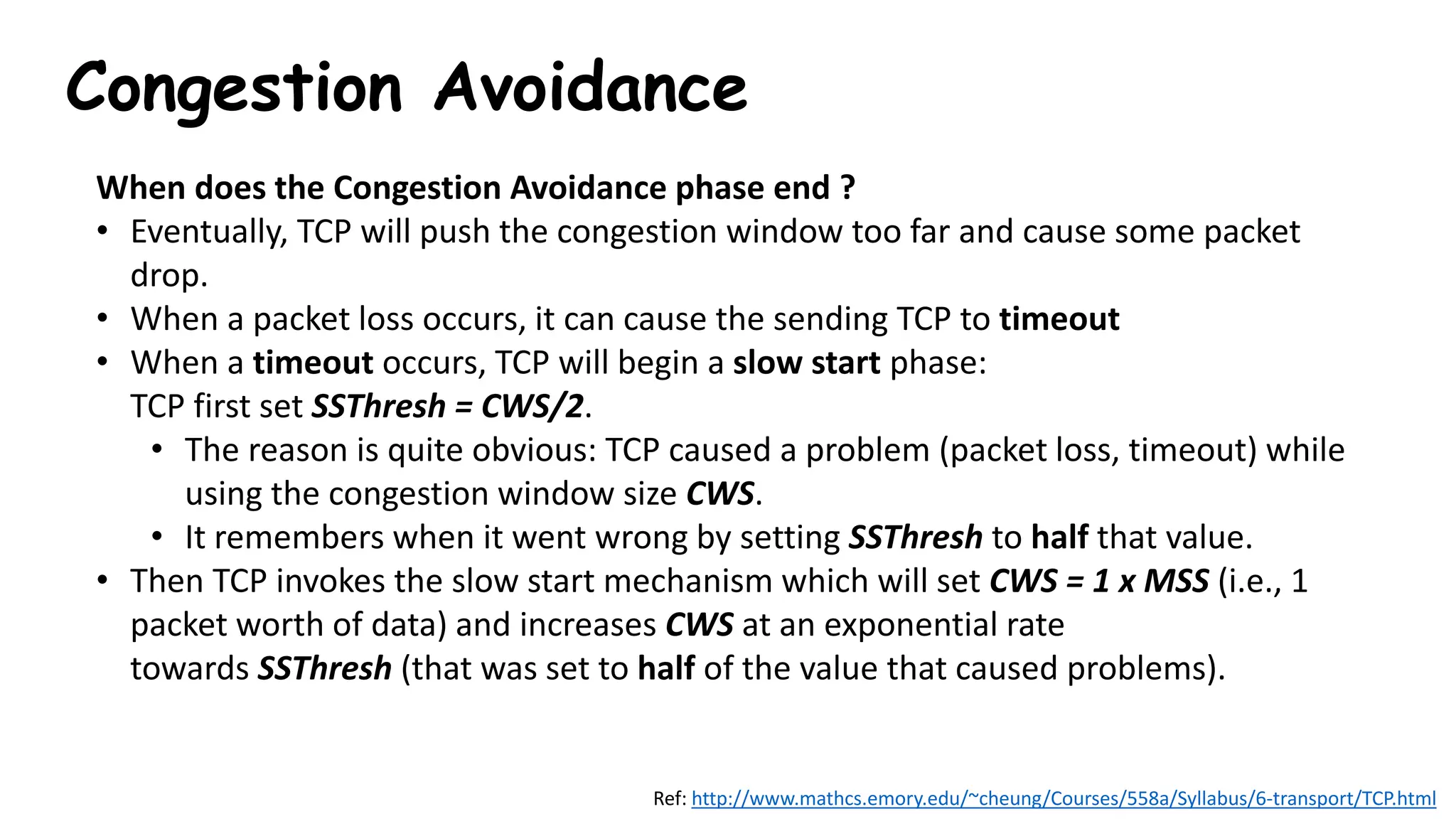
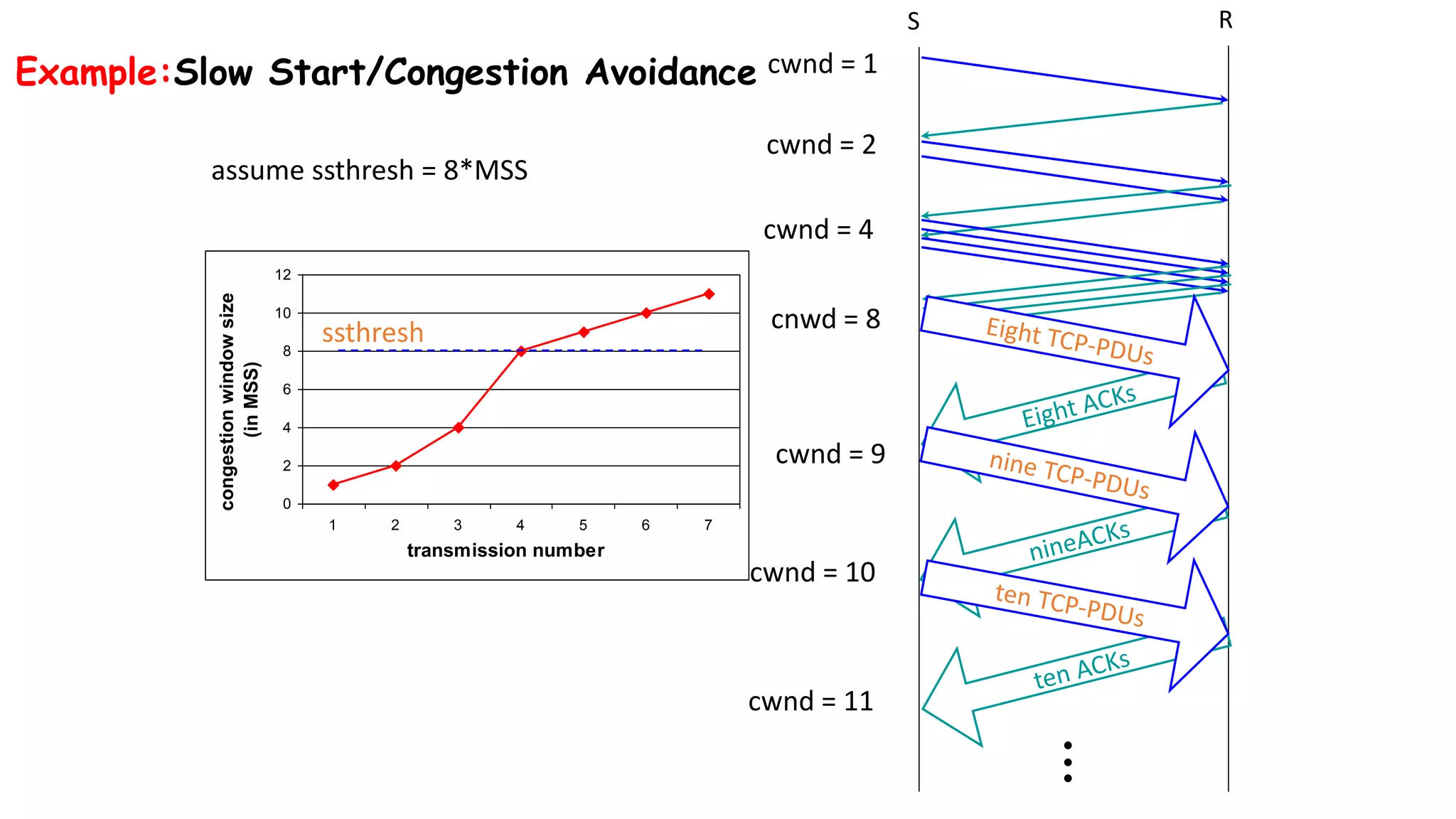
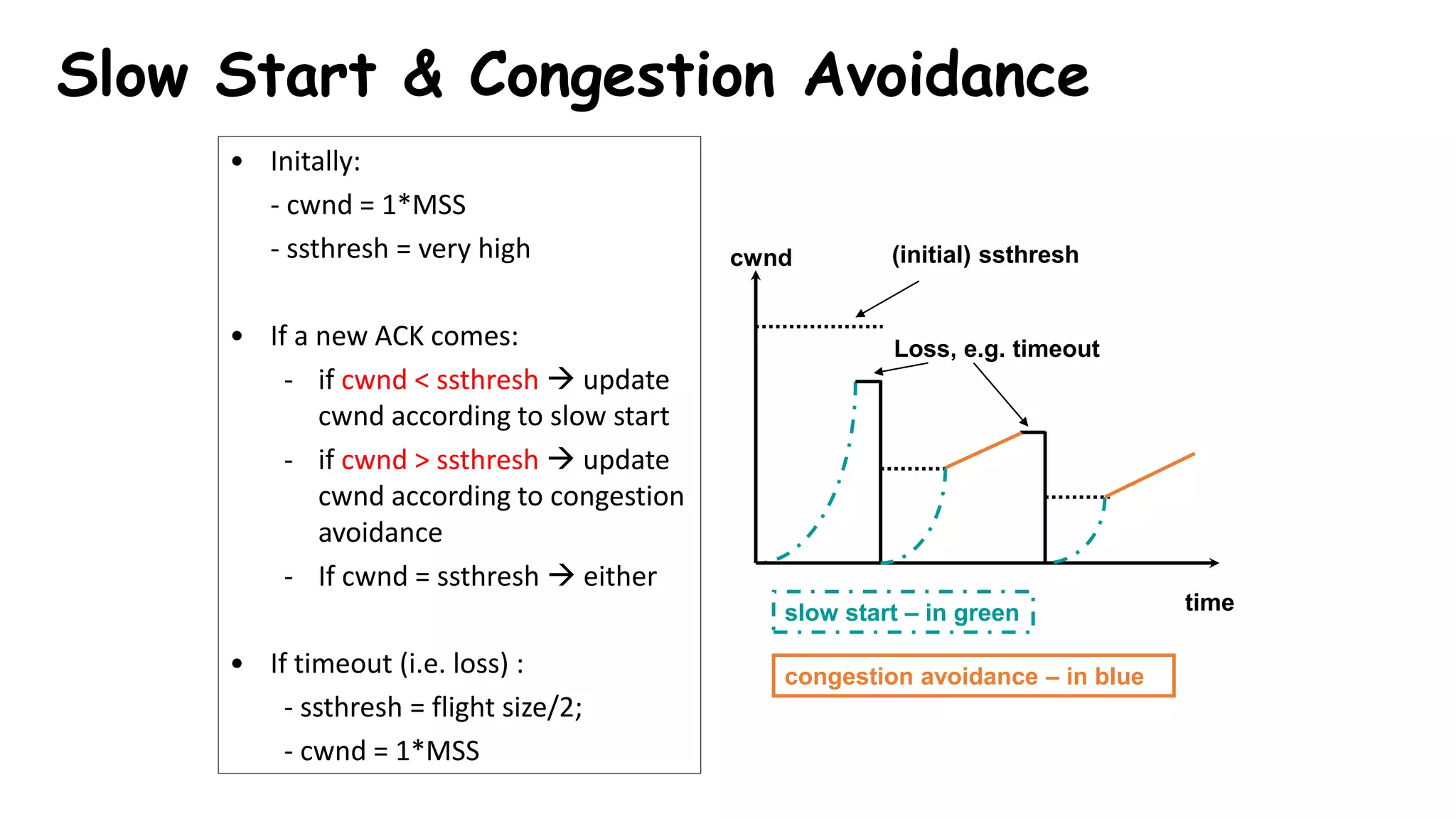
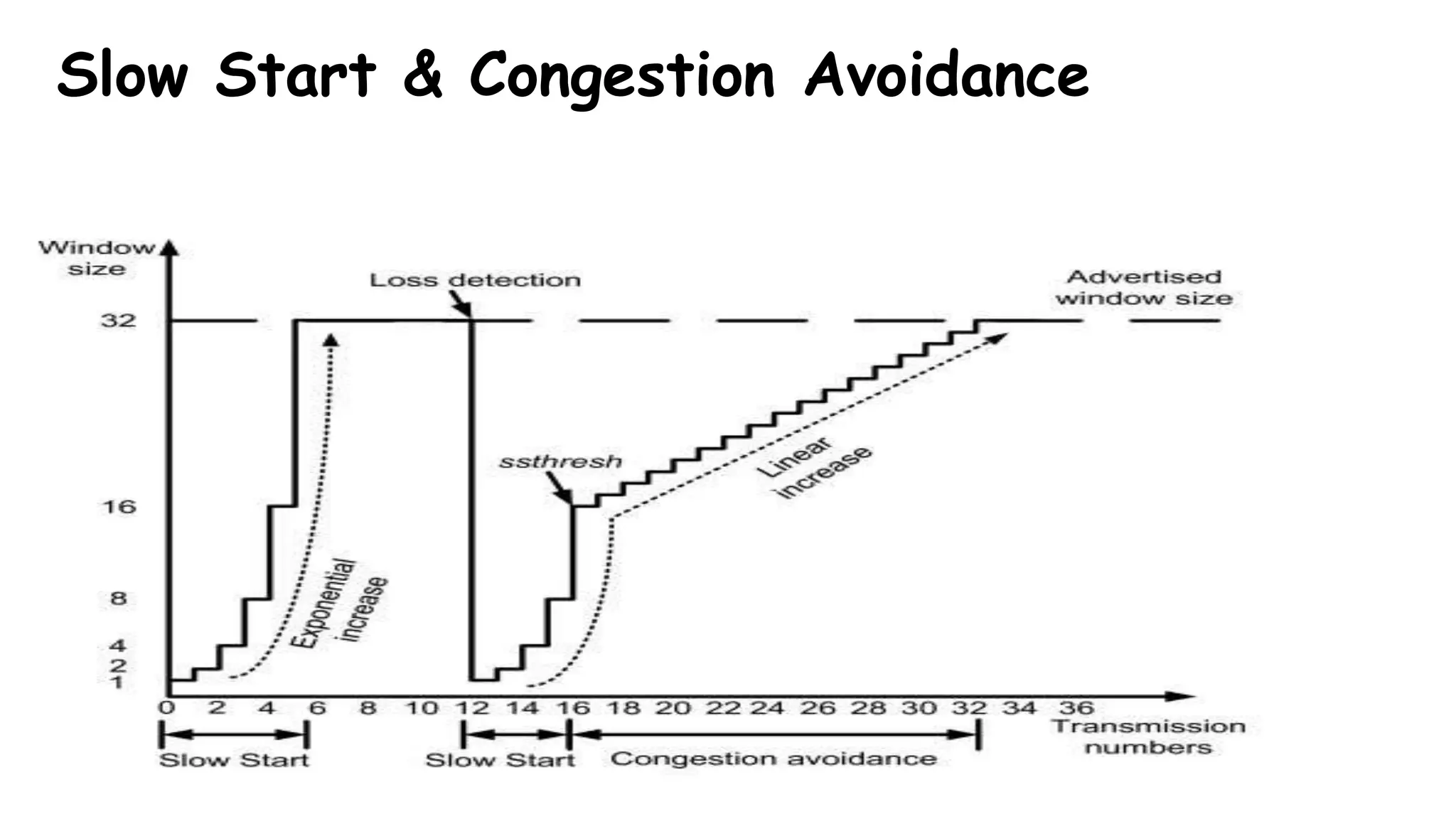
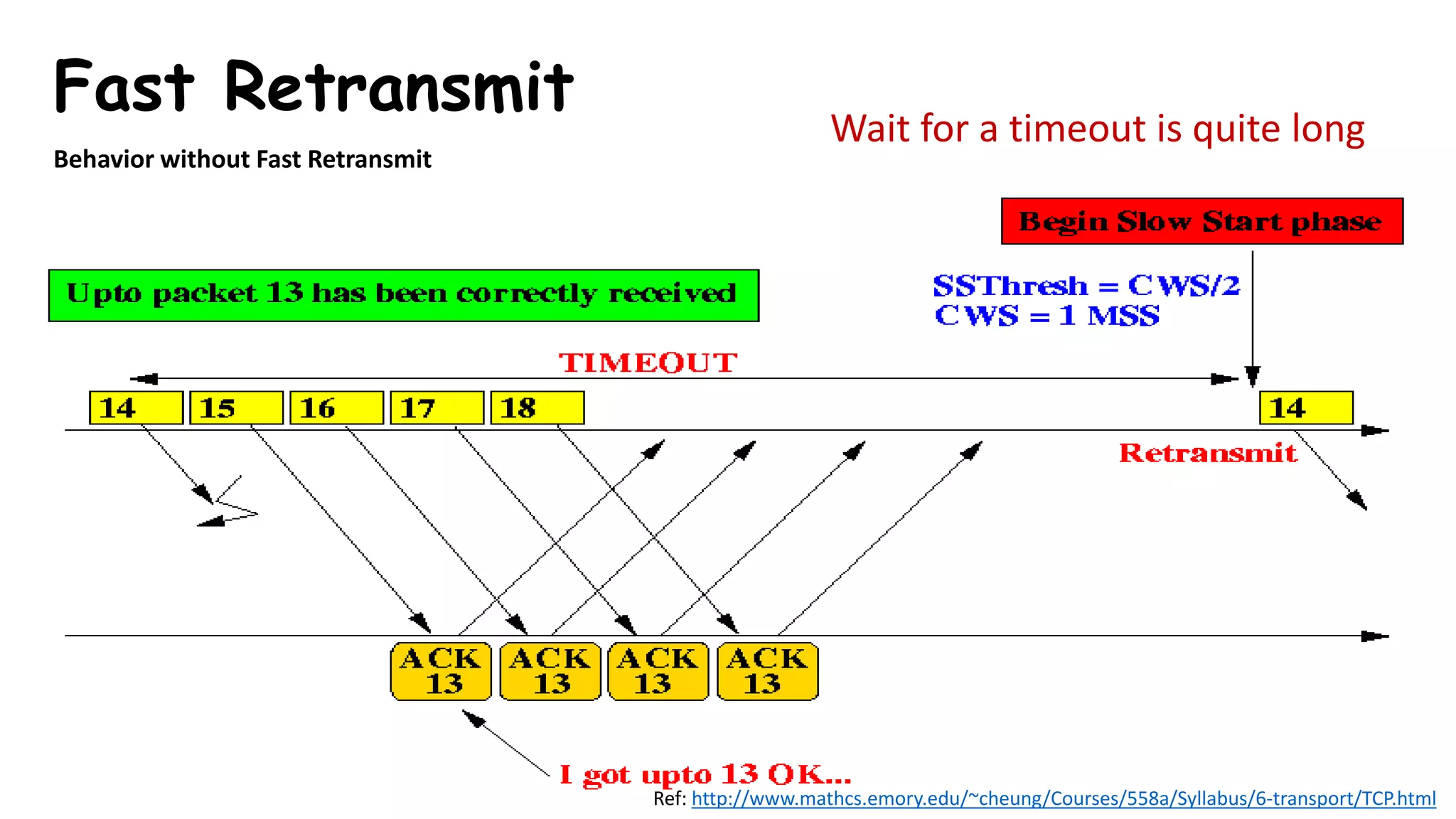
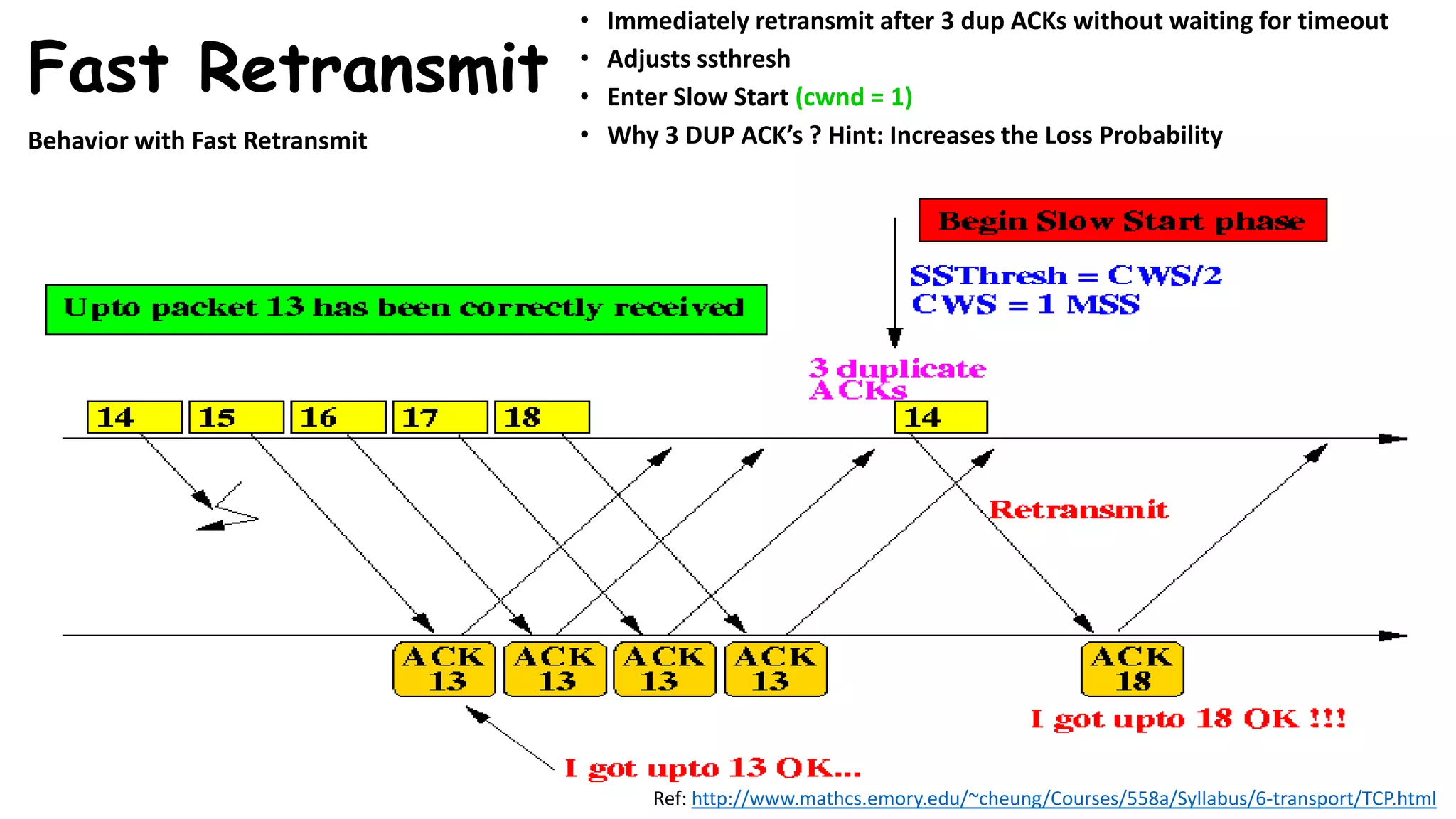
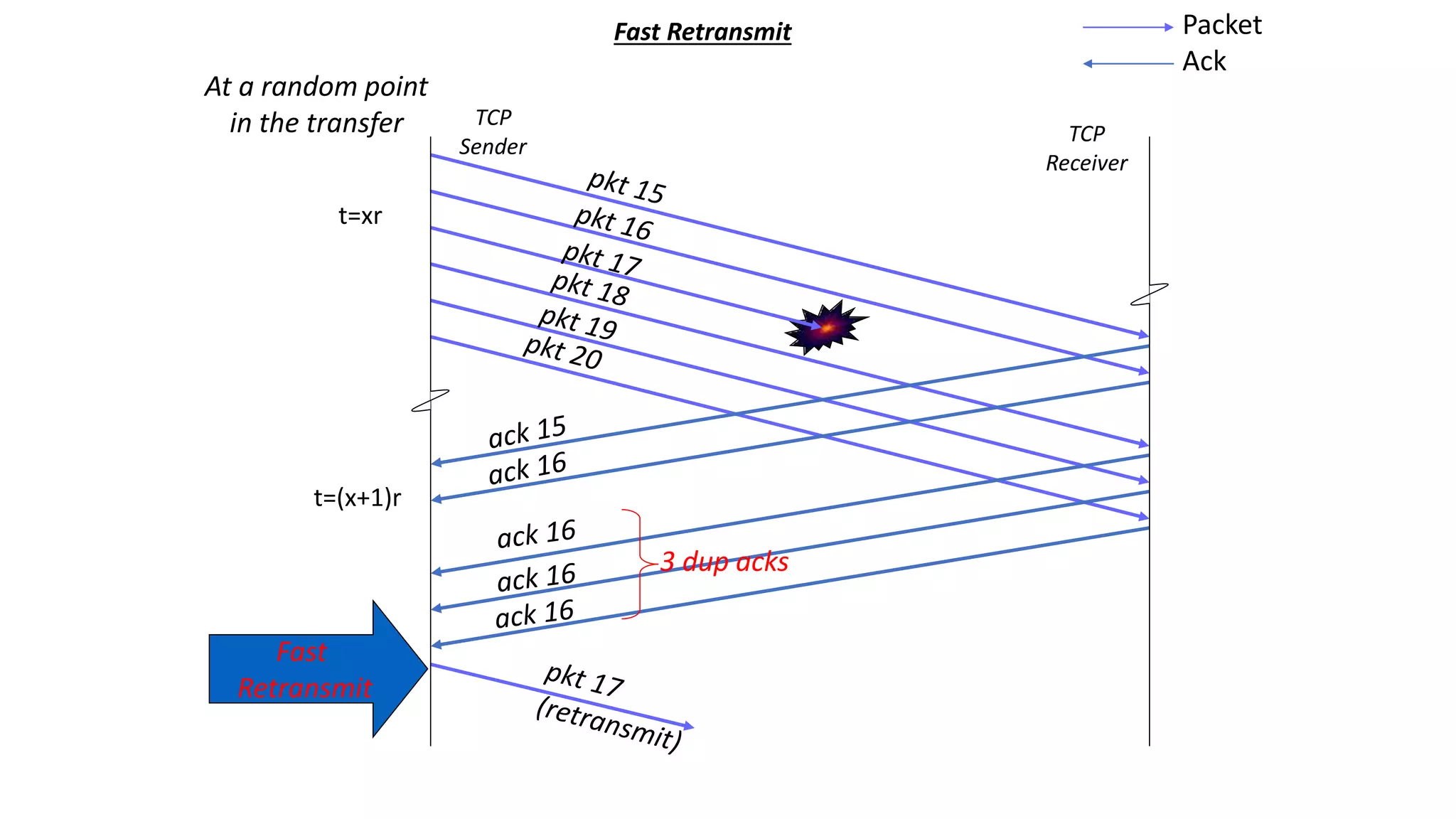
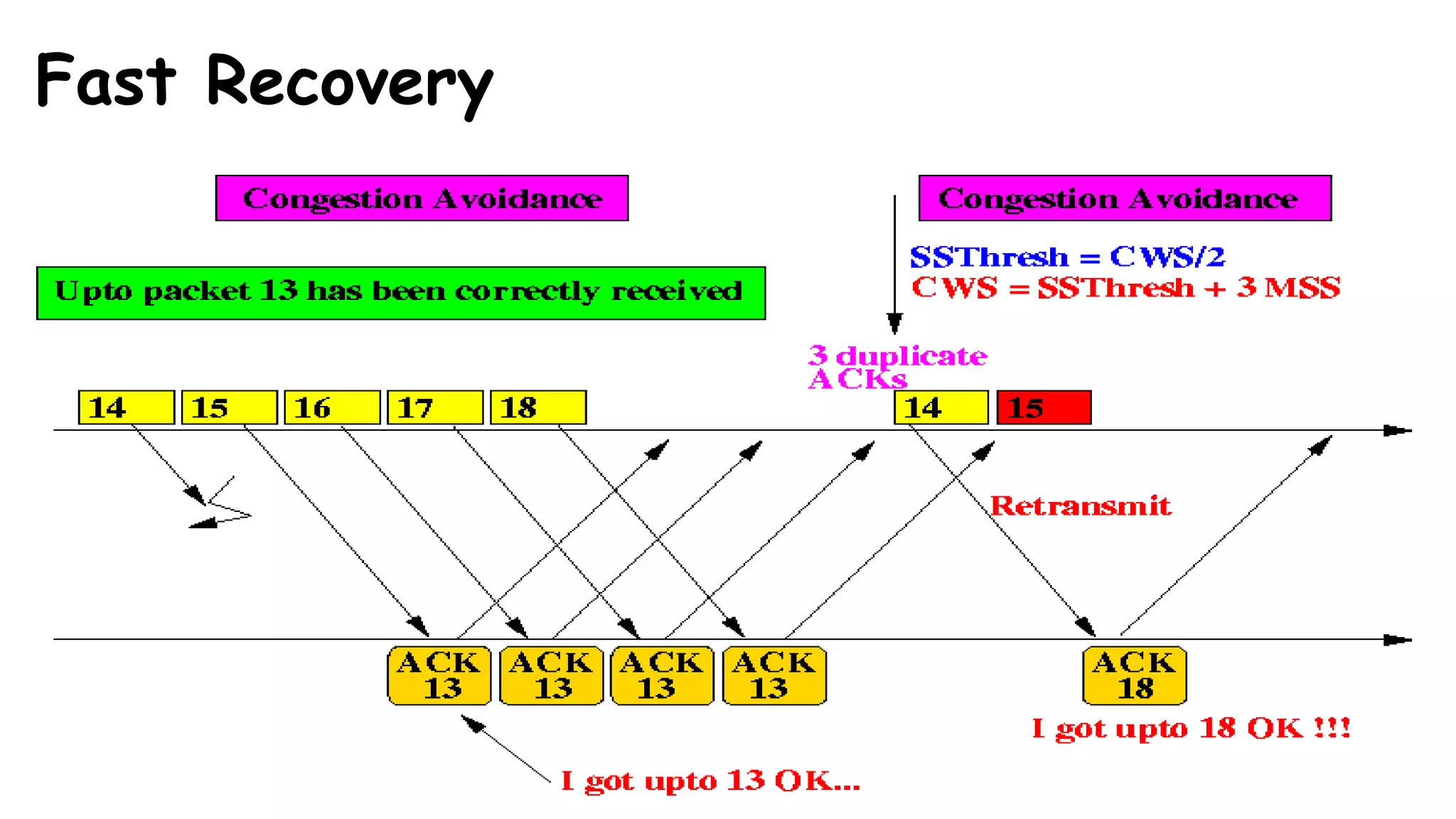
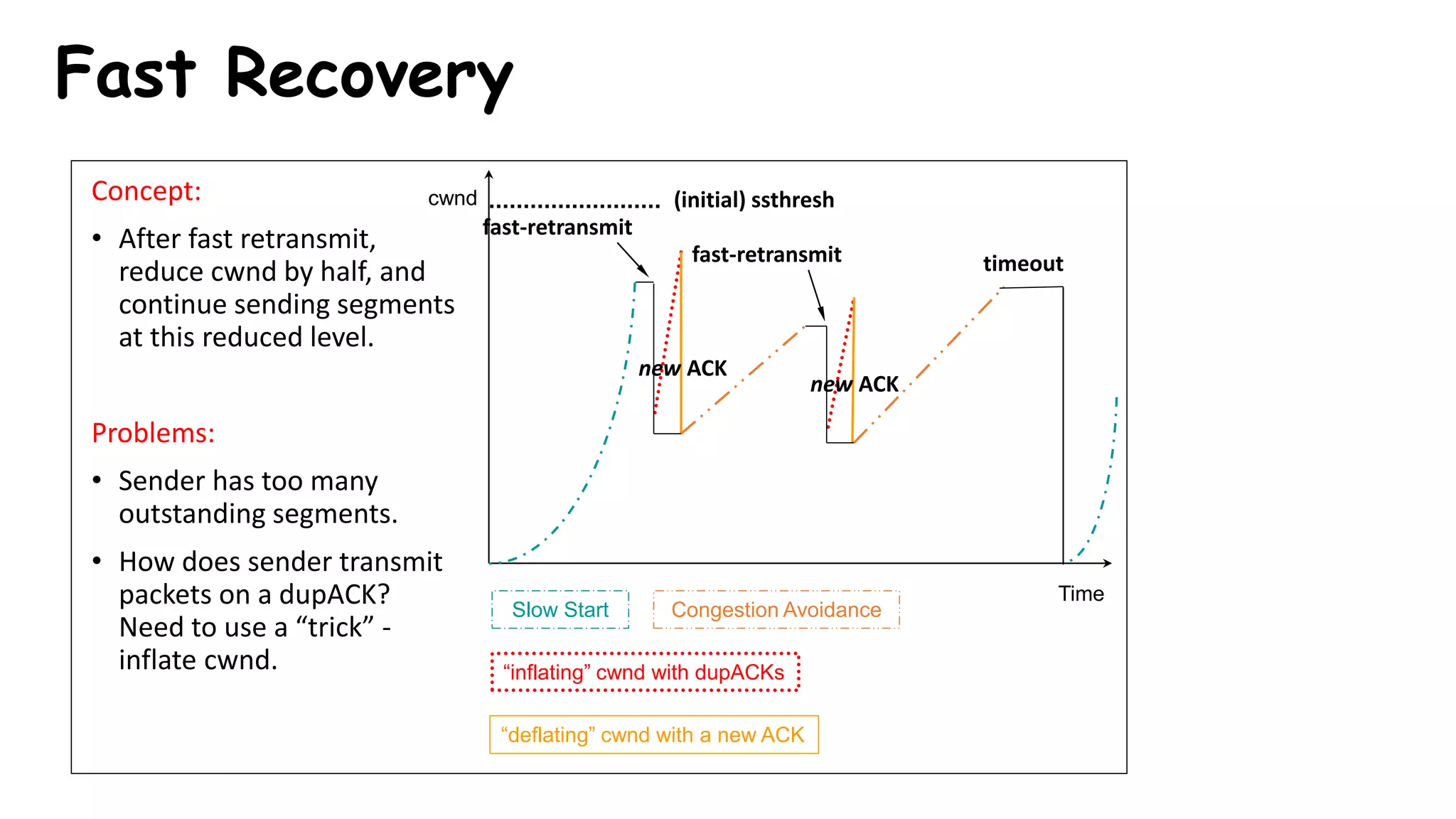
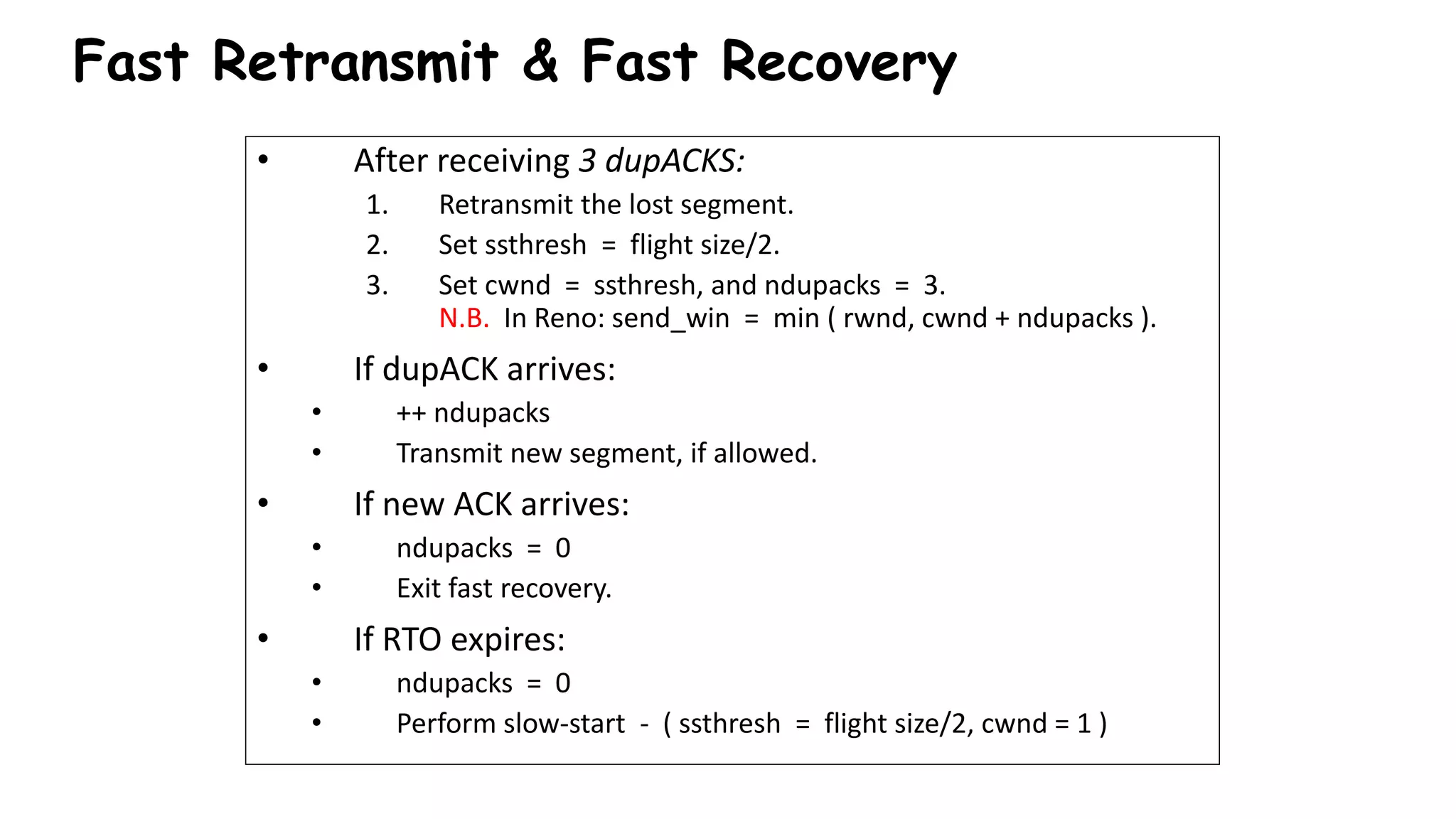
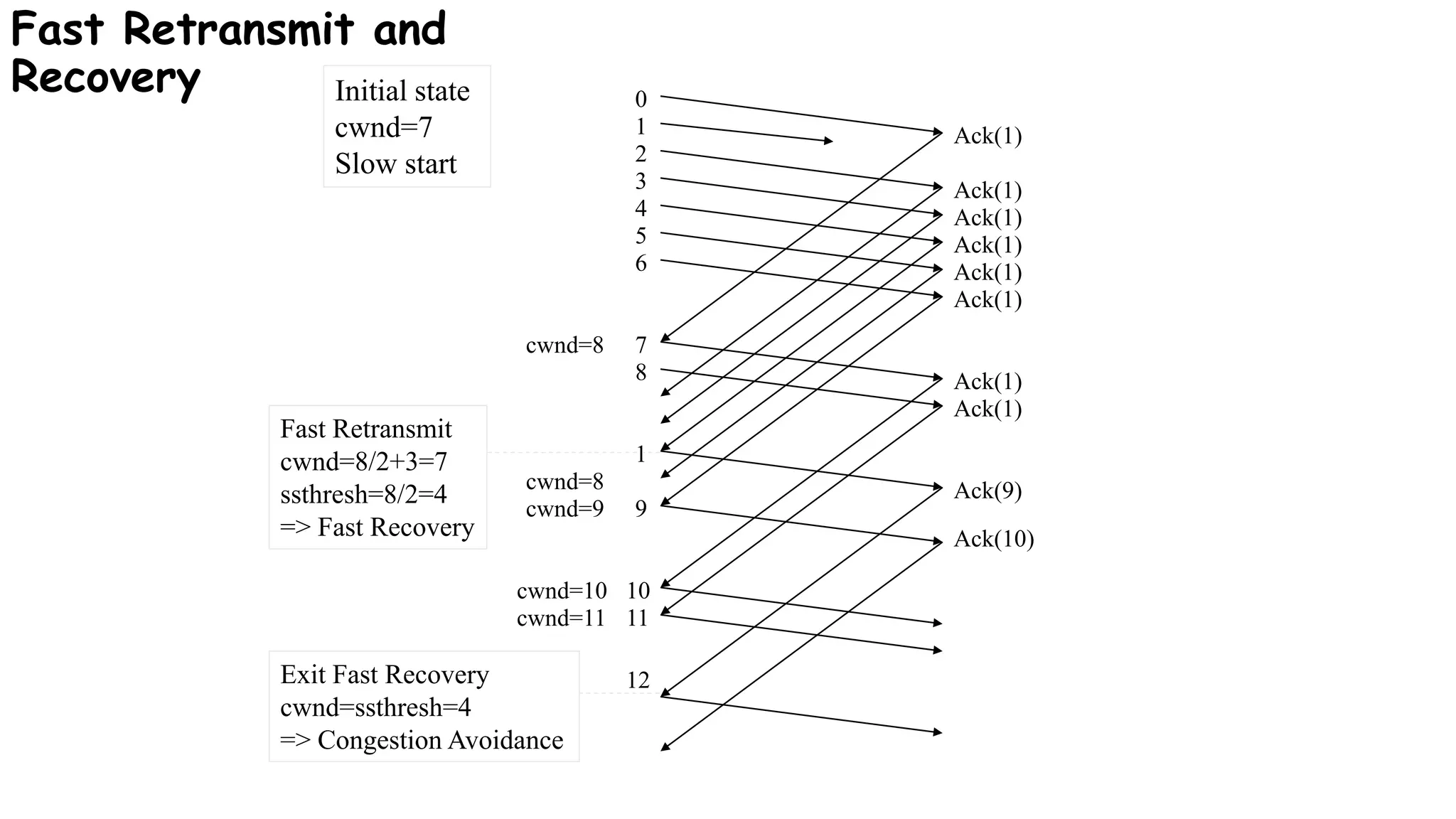
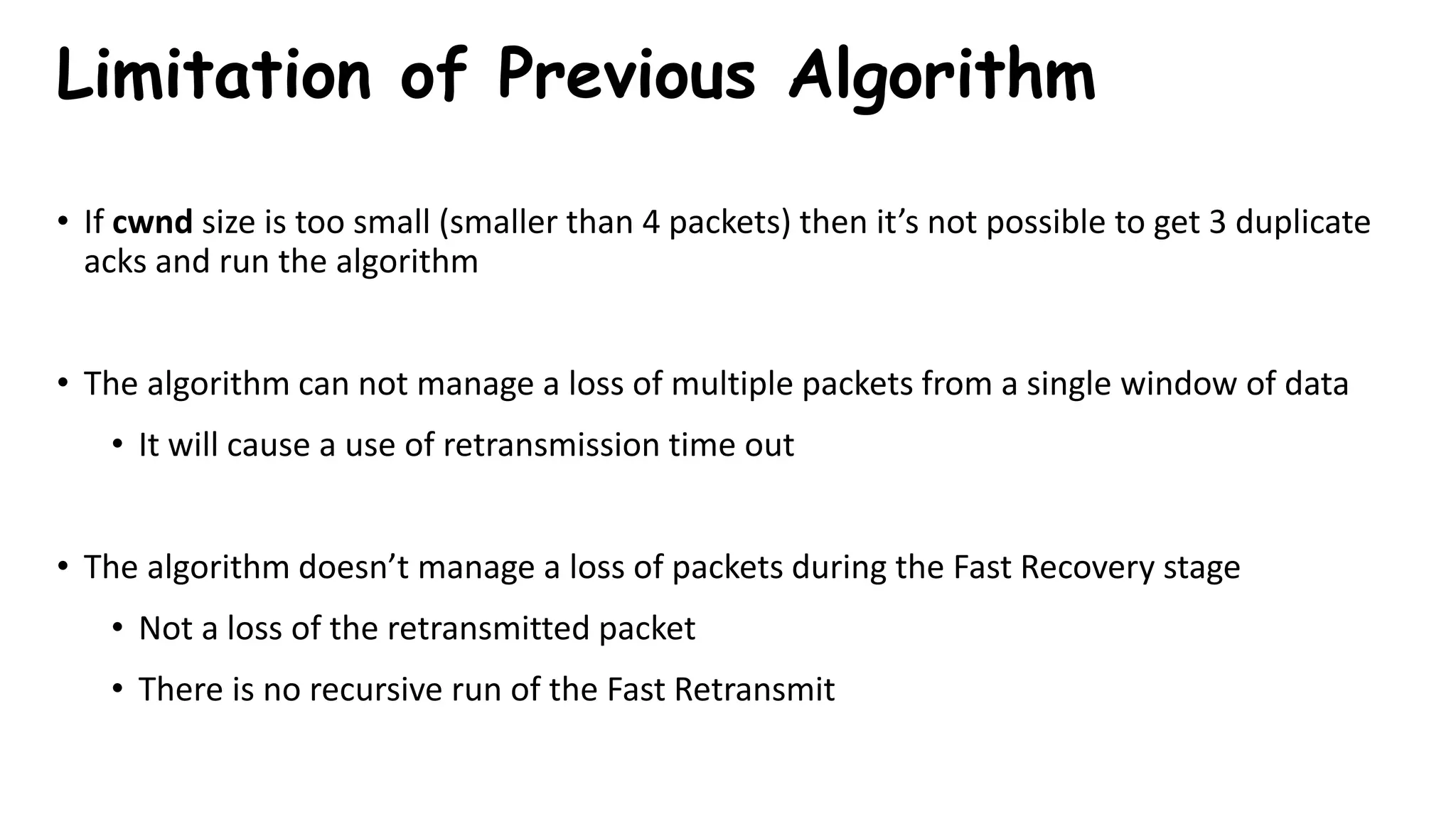
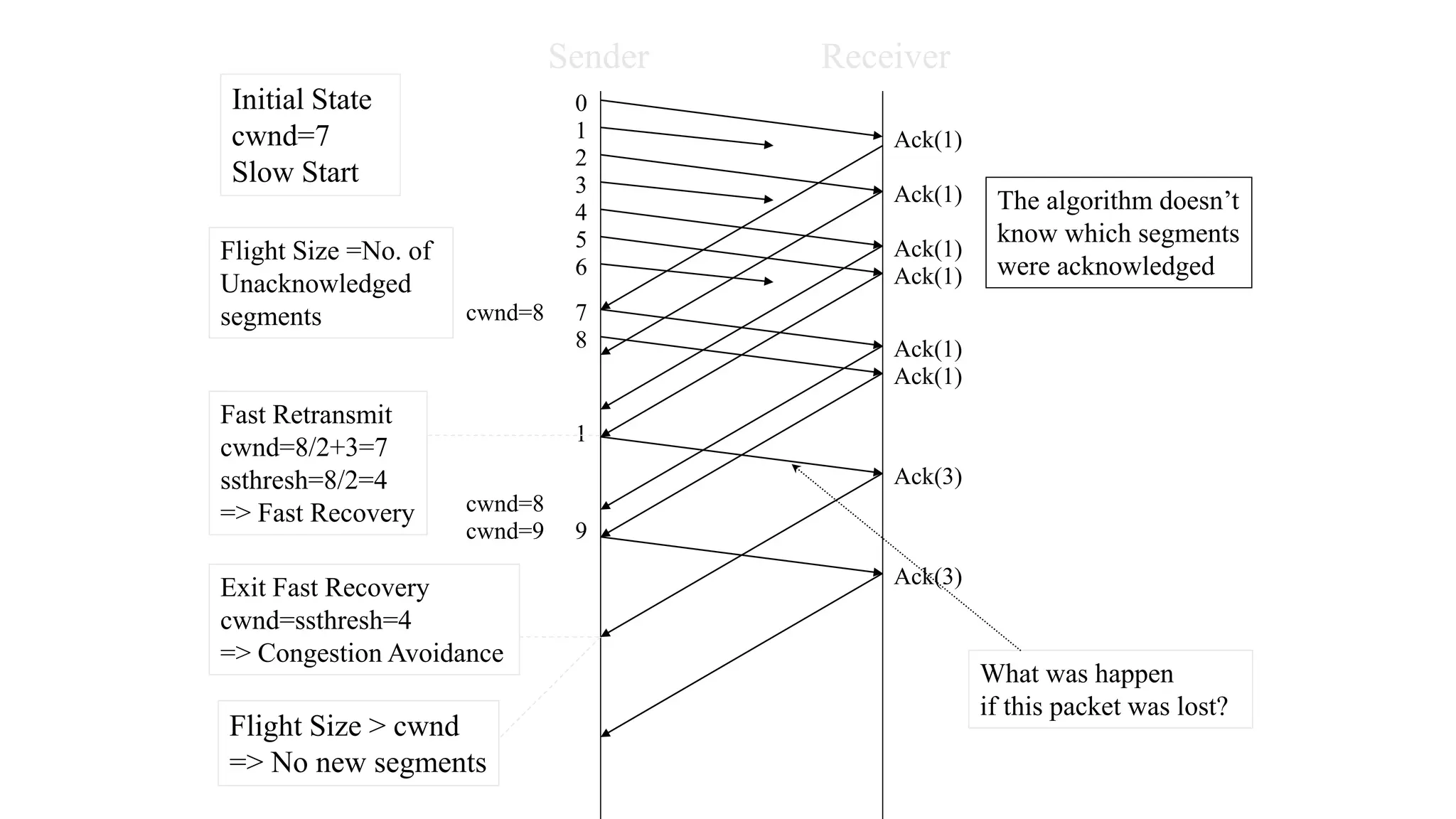
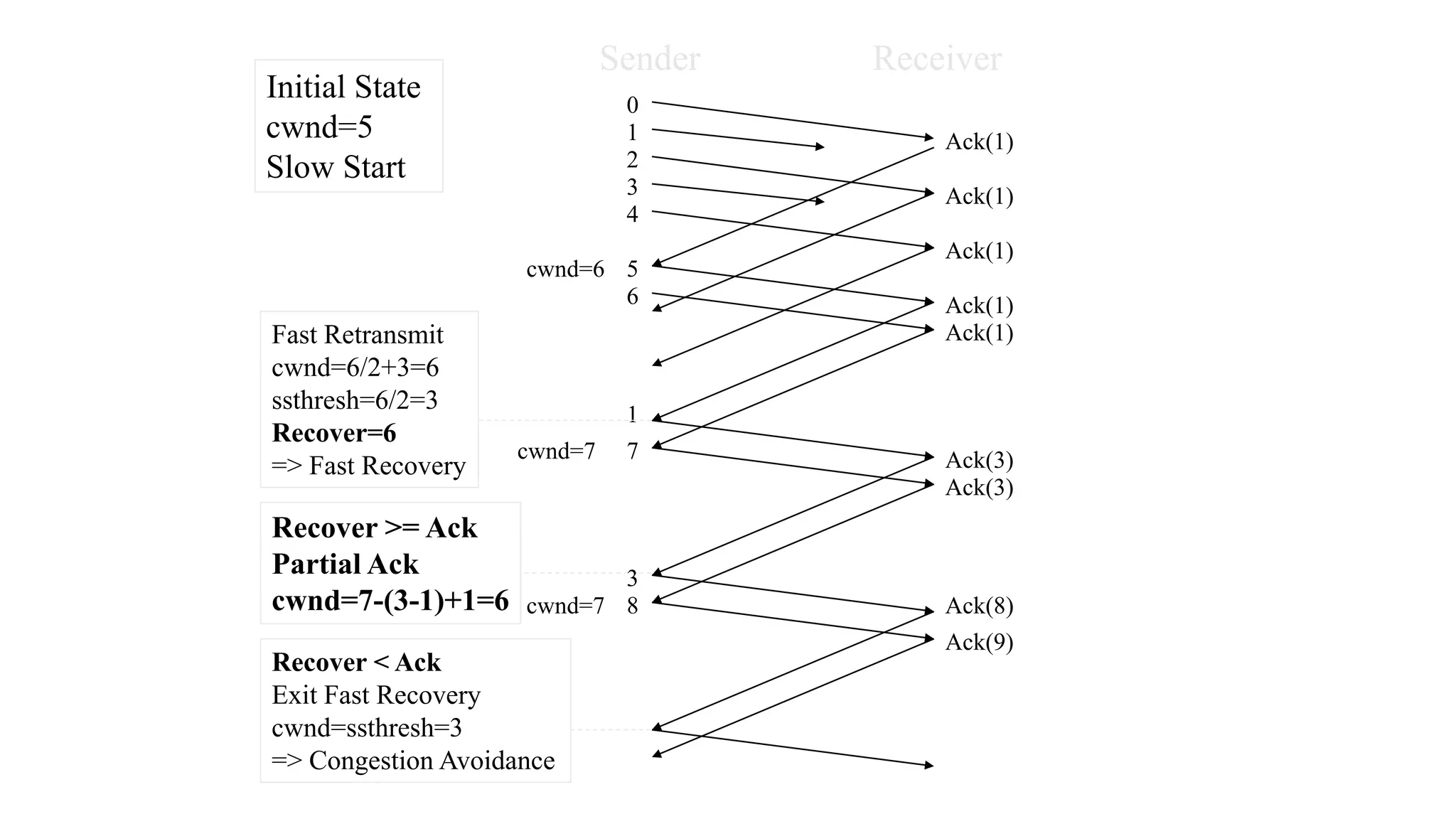
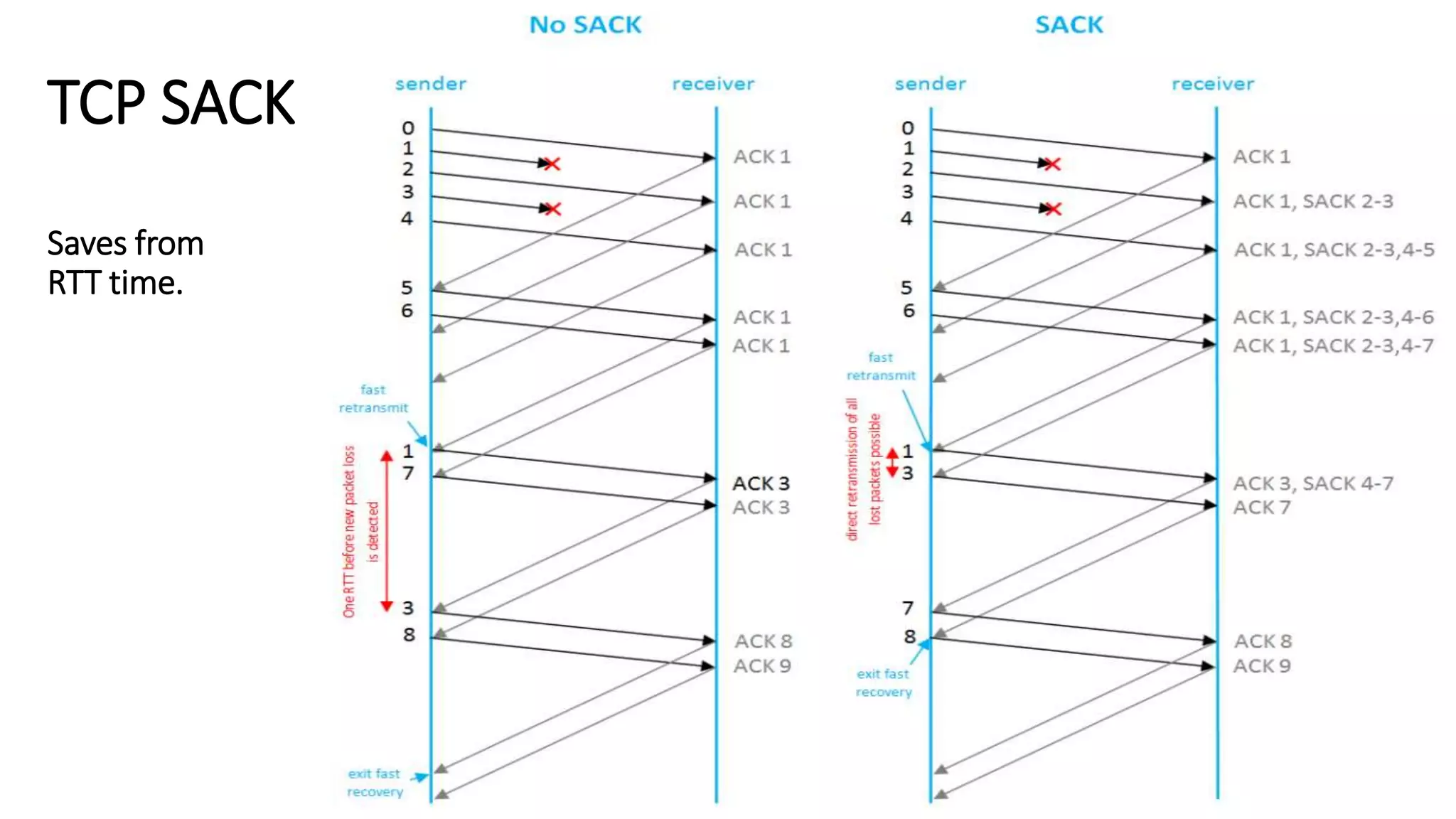
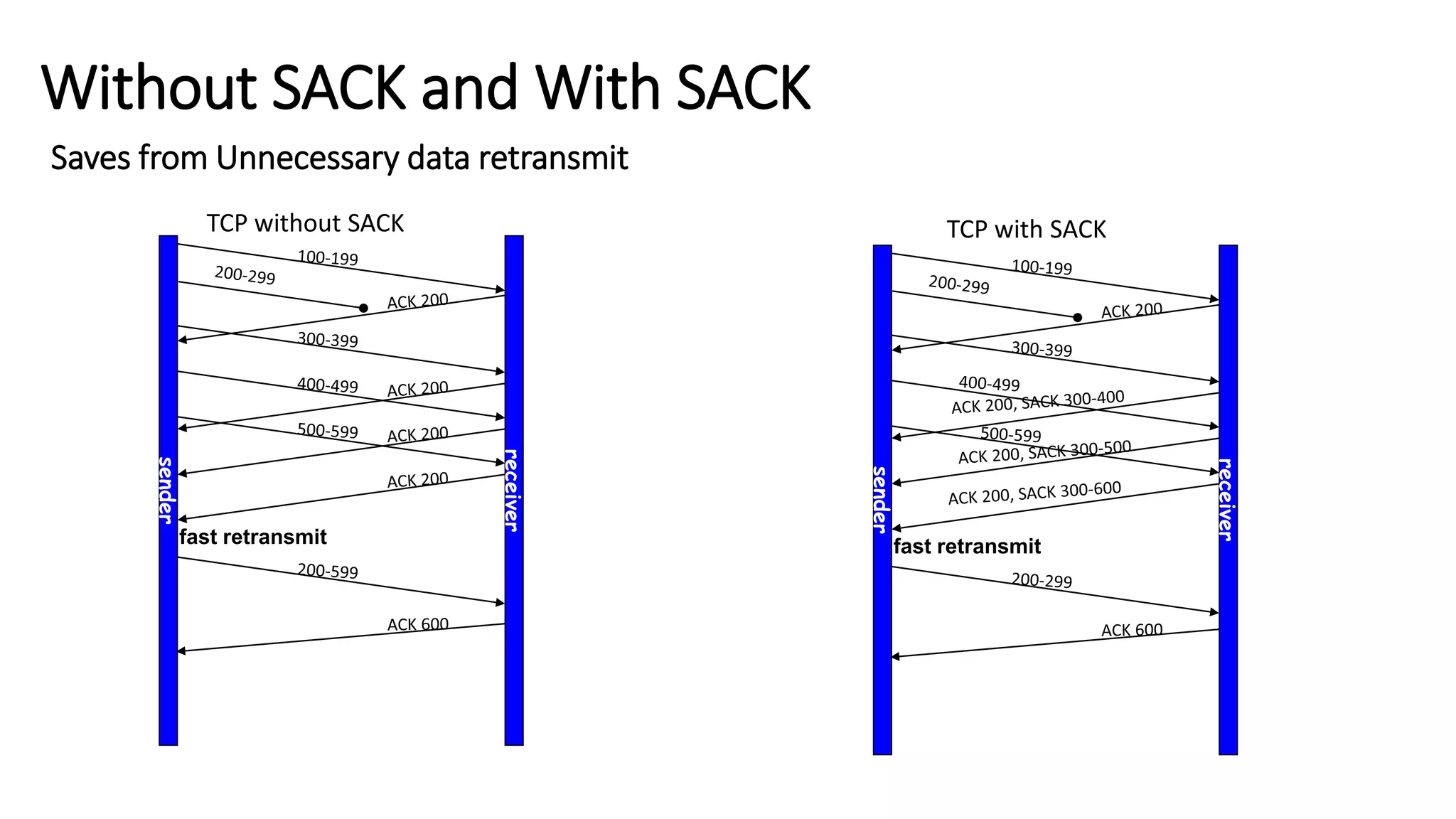
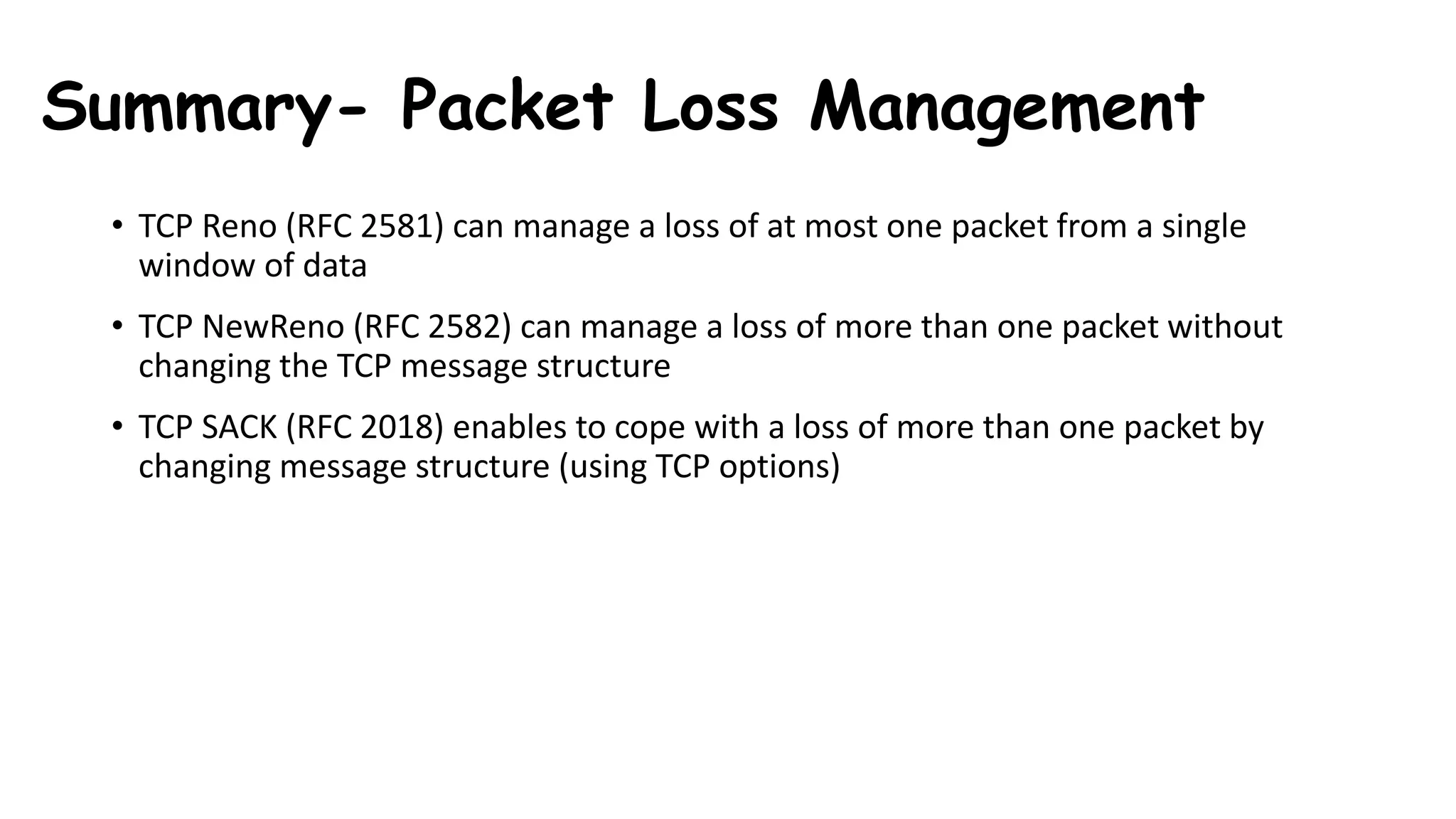
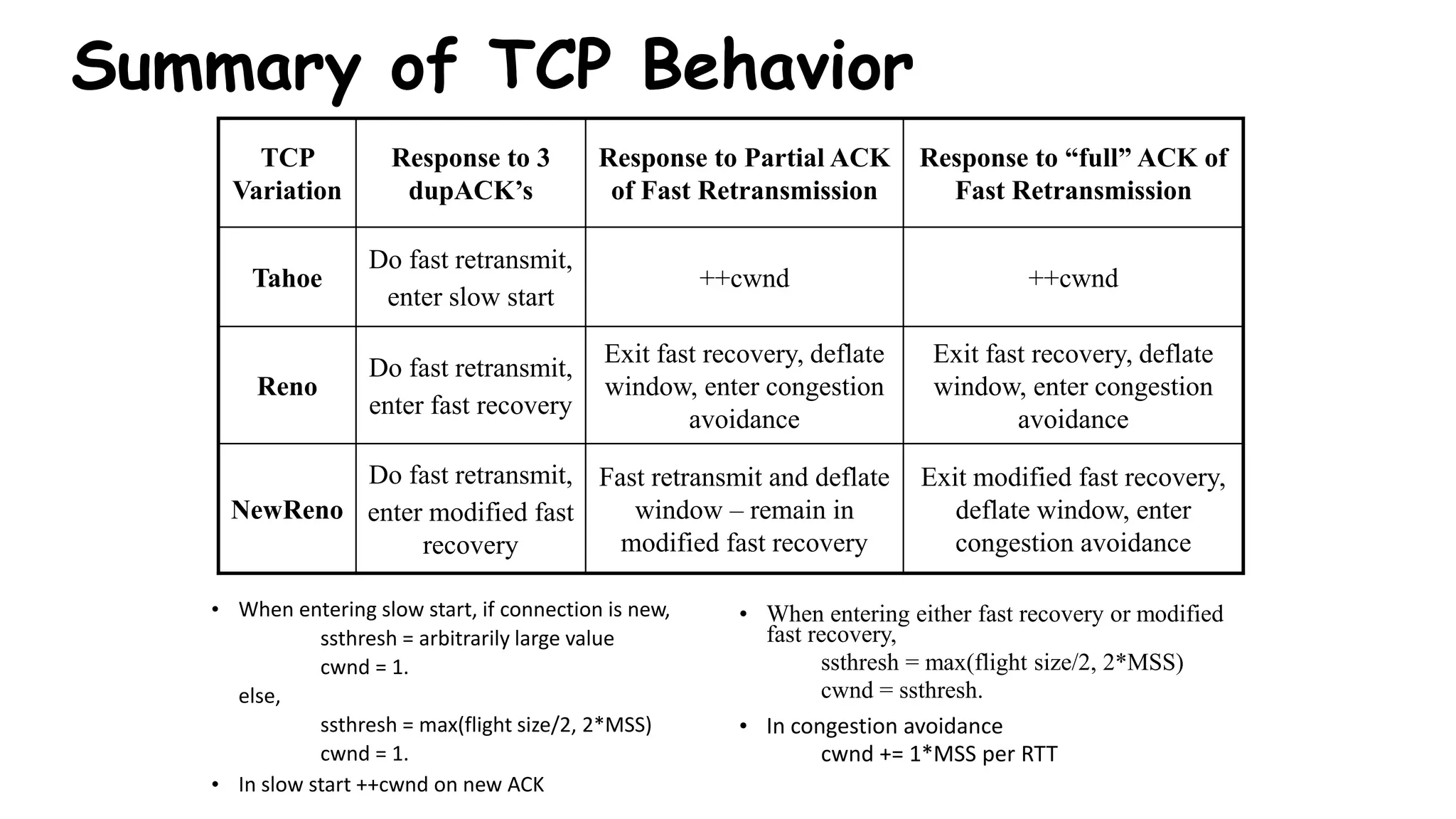
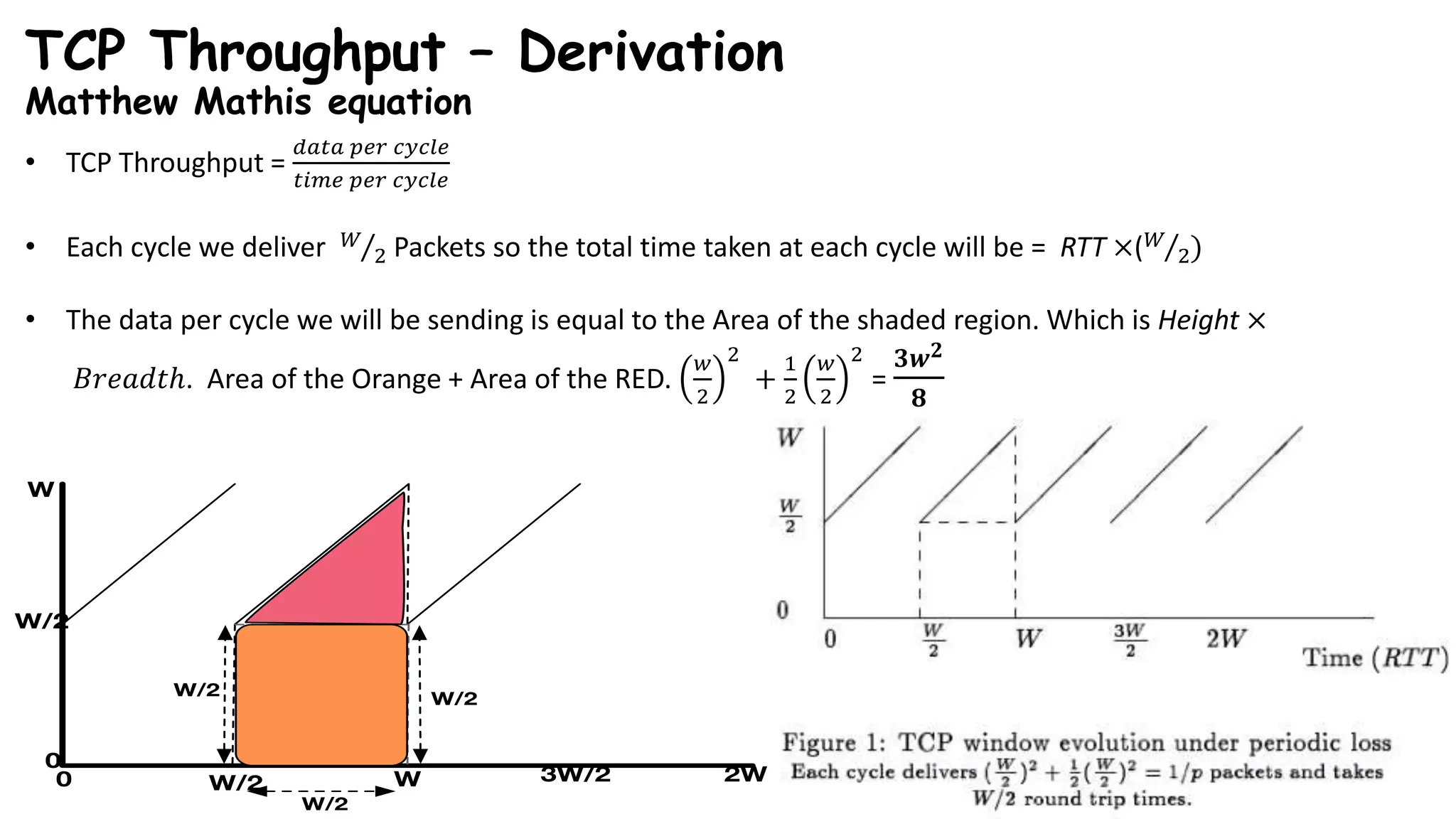
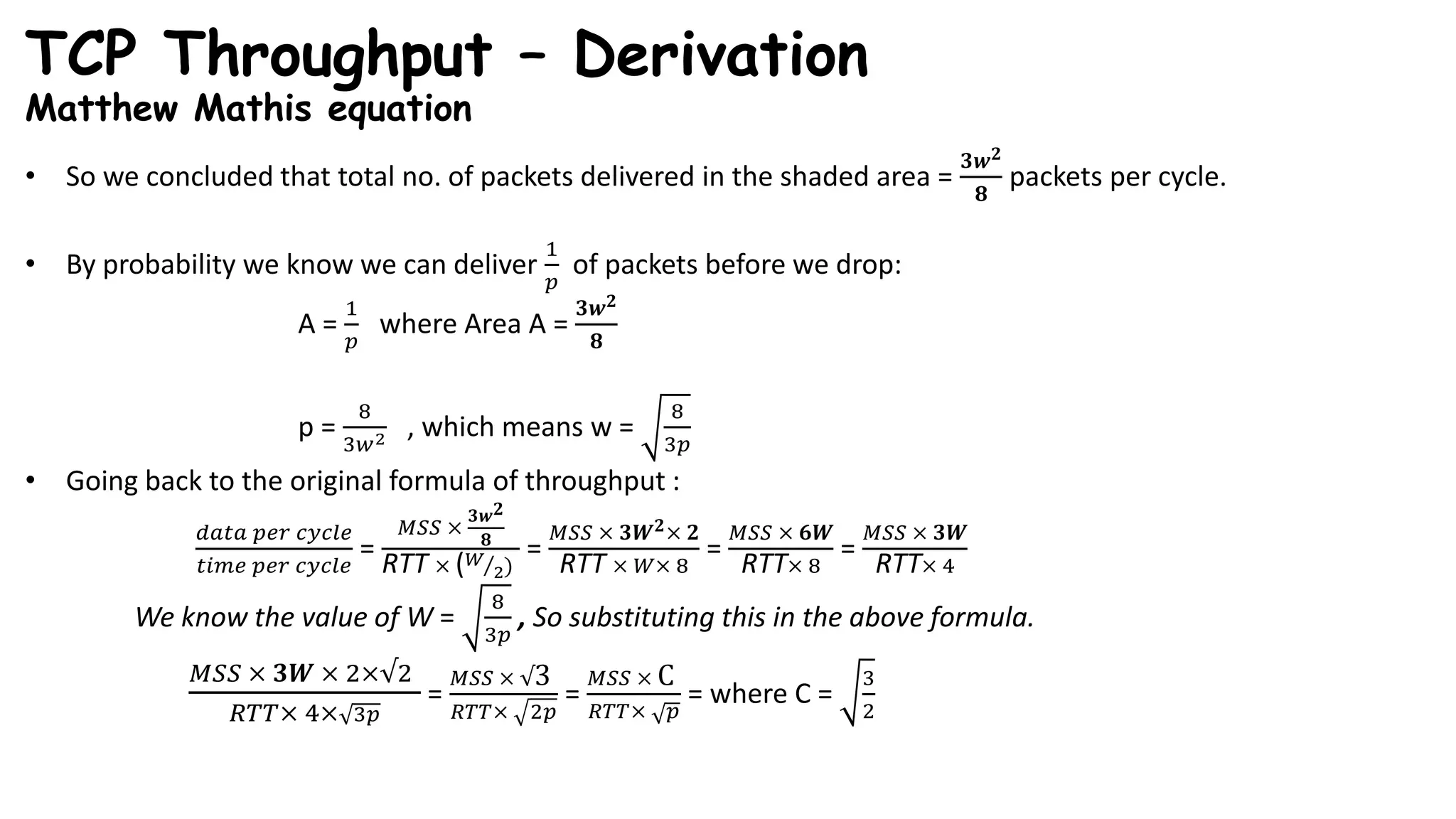
TCP uses congestion control algorithms to manage network congestion. These algorithms include slow start, which allows TCP to determine the network capacity by exponentially increasing the congestion window size each round trip time. This allows TCP to quickly find the maximum capacity without causing congestion. However, once the congestion window size reaches the slow start threshold, TCP enters congestion avoidance phase where it increases the window size more slowly to operate close to the maximum capacity without overshooting. The goal of congestion control is to maximize throughput while minimizing congestion through additive increase and multiplicative decrease of the transmission rate.



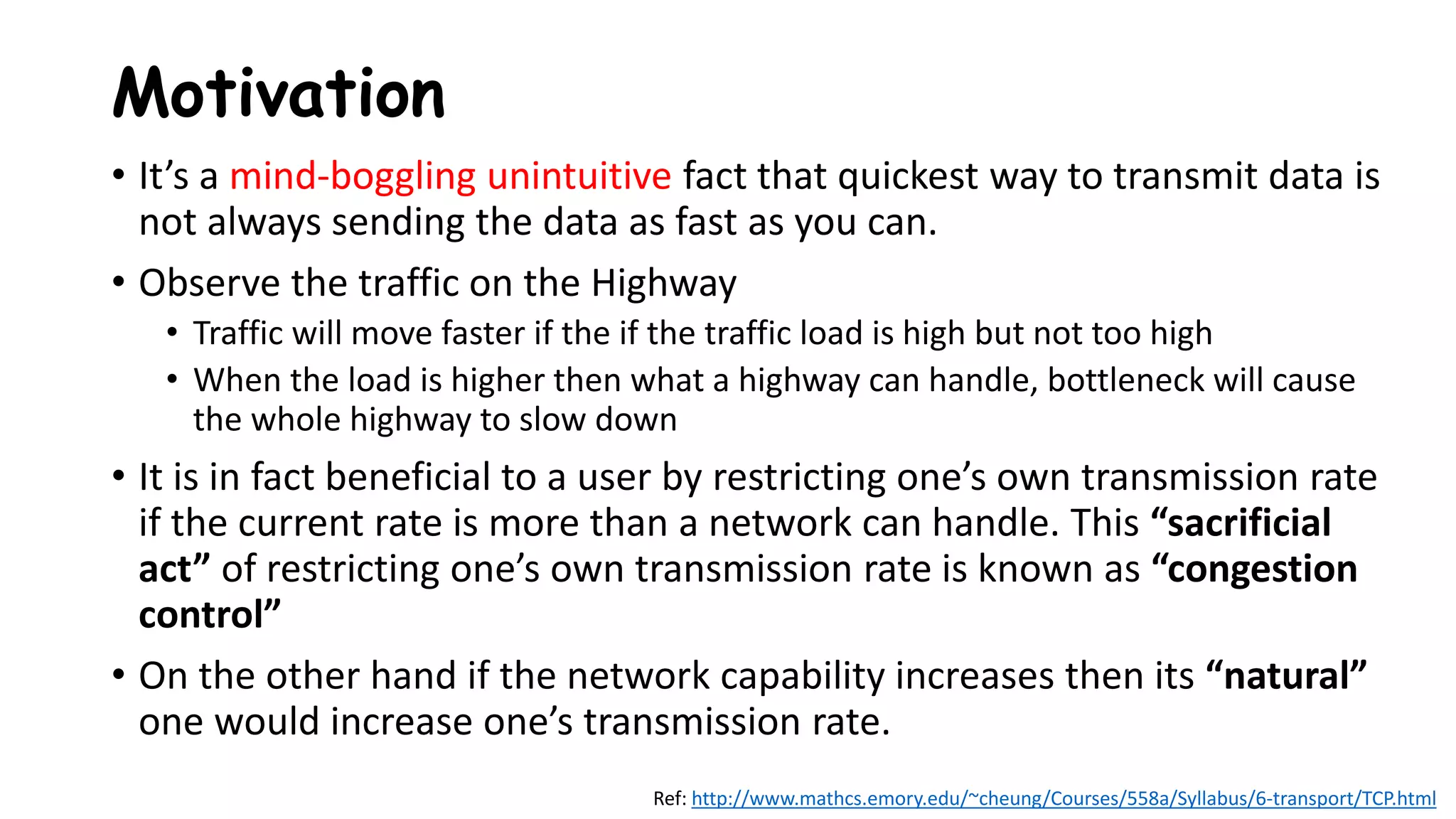
![Motivation
• Congestion Control is one of a few application of “Communism” that will actually work
because it benefit oneself if one will do it (as long as everyone else will do it also).
• Communist principle fails in general because it doesn't take into account the “self-
beneficial” motives of humanoids. Ordinary humans would only do something if it benefits
oneself. Marx had this crazy fantasy that everyone is a Saint (He must be smoking
something)
• Ref: http://www.philosophybasics.com/branch_communism.html
“Communism is a socio-economic structure that promotes the establishment of a classless, stateless society
based on common ownership of the means of production. It encourages the formation of a proletarian state in
order to overcome the class structures and alienation of labour that characterize capitalistic societies, and
their legacy of imperialism and nationalism. Communism holds that the only way to solve these problems is for
the working class (or proletariat) to replace the wealthy ruling class (or bourgeoisie), through revolutionary
action, in order to establish a peaceful, free society, without classes or government.
Communism, then,] is the idea of a free society with no division or alienation, where humanity is free
from oppression and scarcity, and where there is no need for governments or countries and no class divisions.
It envisages a world in which each person gives according to their abilities, and receives according to
their needs. Its proponents claim it to be the only means to the full realization of human freedom.”
Ref: http://www.mathcs.emory.edu/~cheung/Courses/558a/Syllabus/6-transport/TCP.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcpnoipreview-part2-161216205130/75/Tcp-no-ip-review-part2-5-2048.jpg)