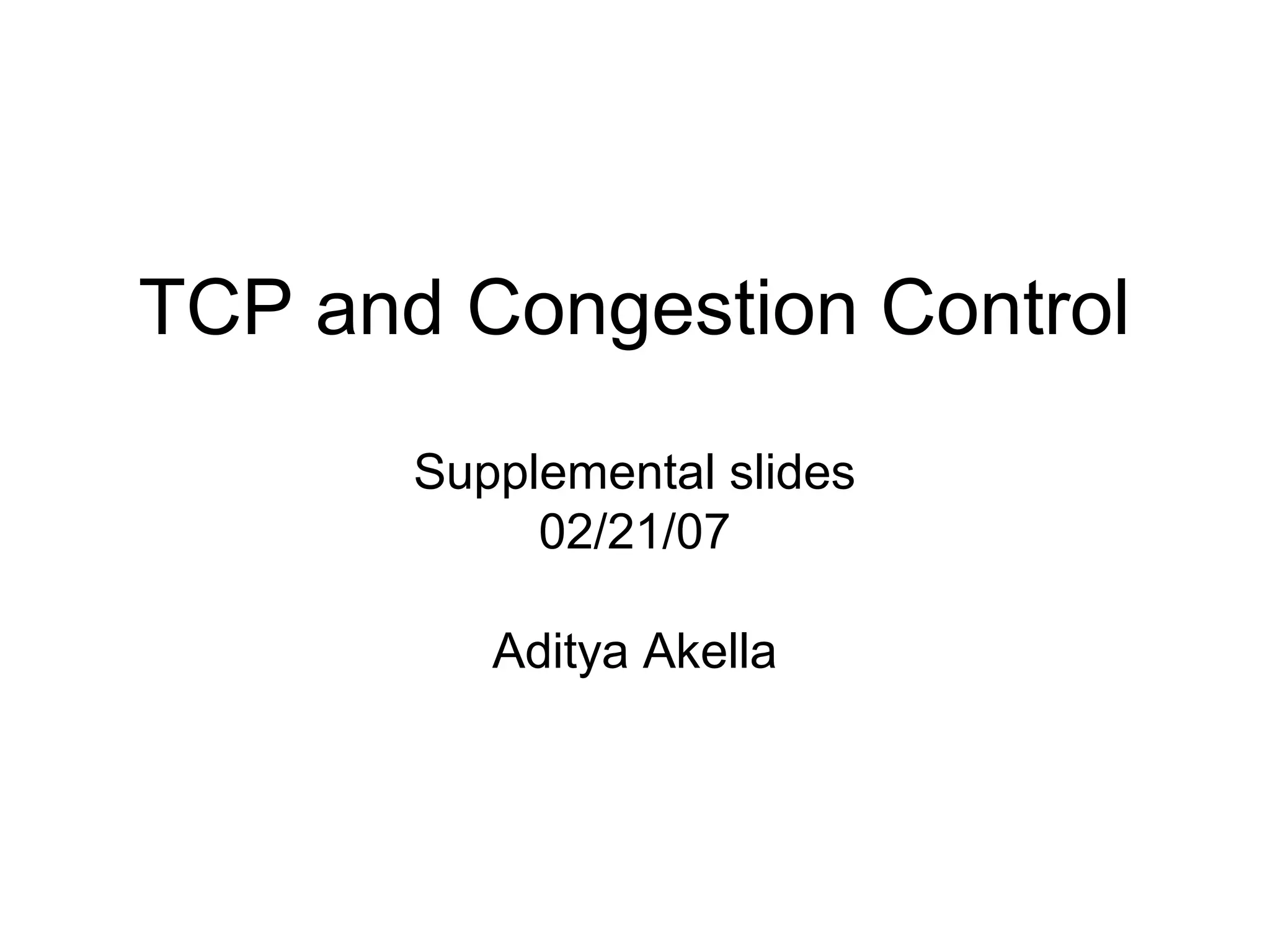
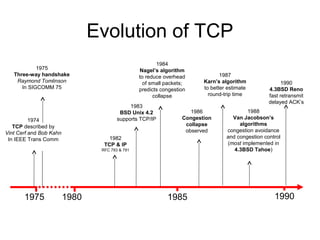
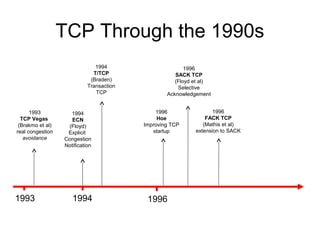
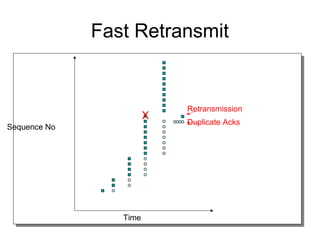
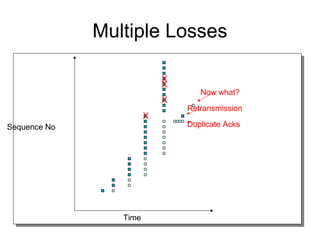
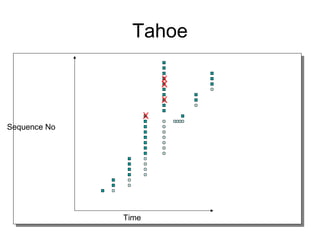
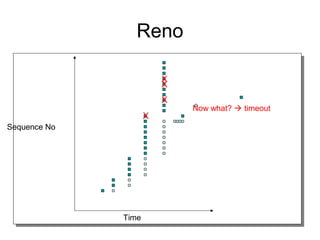
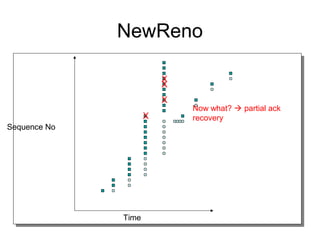
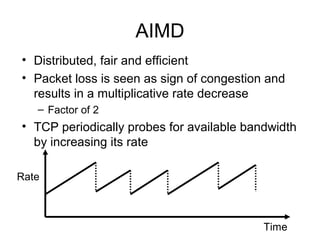
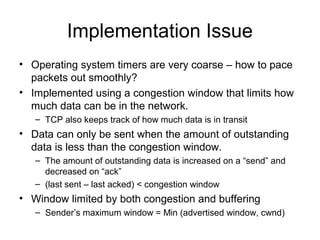
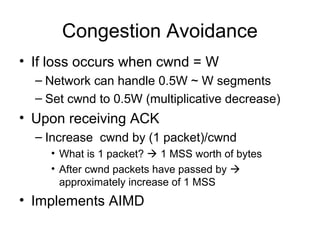
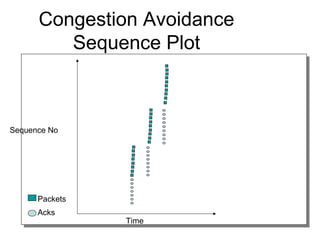
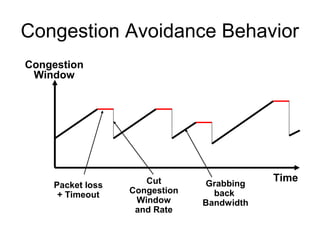
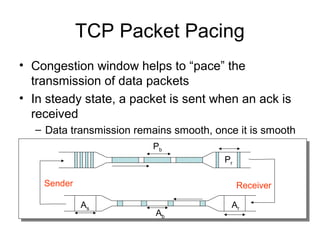
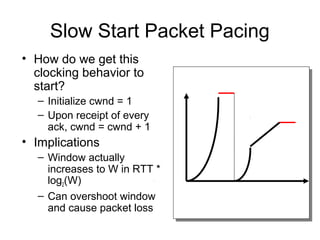
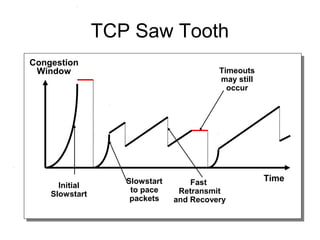
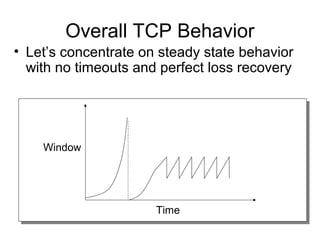
TCP uses congestion control to prevent network congestion collapse. It uses additive increase multiplicative decrease (AIMD) where the sending rate is increased slowly but cut in half after a loss. TCP paces packets using a congestion window that limits unacknowledged data. It uses slow start to quickly reach bandwidth and congestion avoidance to increase the window by 1 packet per RTT. This models TCP behavior and shows throughput is related to window size, loss rate, and RTT.