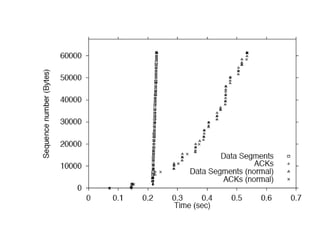
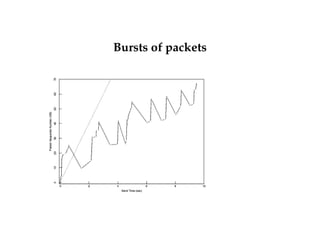
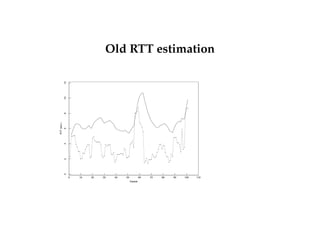
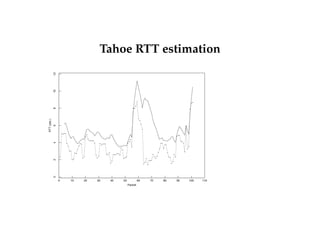
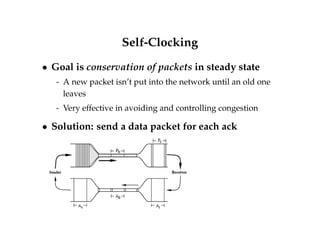
This document summarizes key concepts about congestion control in TCP including:
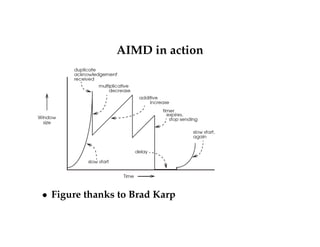
- TCP uses additive increase multiplicative decrease (AIMD) to dynamically adjust the congestion window size and maintain efficiency and fairness.
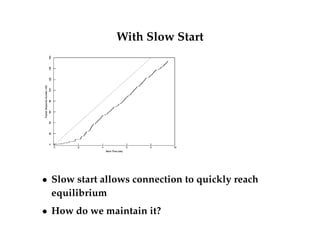
- TCP has slow start and congestion avoidance states that govern how the congestion window is adjusted in response to acknowledgements.
- TCP responds to packet loss through fast retransmit, fast recovery, and halving the congestion window size to reduce congestion according to protocols like Tahoe, Reno, and New Reno.



















![TCP Reno [RFC 2581]
Same as Tahoe on timeout
On triple duplicate ACK
- Set threshold to cwnd
2
- Set cwnd to cwnd
2 (fast recovery)
- Retransmit missing segment (fast retransmit)
- Stays in congestion avoidance state](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computernetwork13-140901161739-phpapp01/85/Computer-network-13-28-320.jpg)
![TCP NewReno [RFC 3782]
Same as Tahoe/Reno on timeout
During fast recovery
- Keep track of last unacknowledged packet on entering fast
recovery
- On every duplicate ACK, inflate congestion window by
MSS
- When last packet is acknowledged, return to congestion
avoidance, set cwnd back to original value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computernetwork13-140901161739-phpapp01/85/Computer-network-13-29-320.jpg)