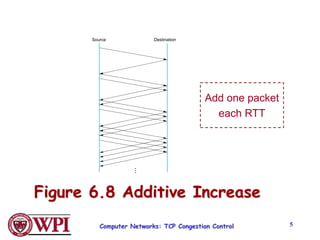
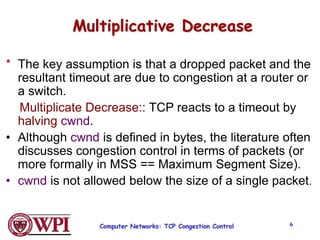
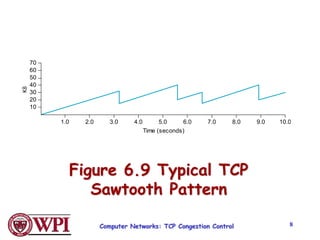
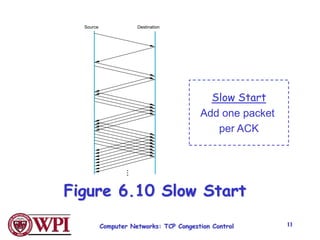
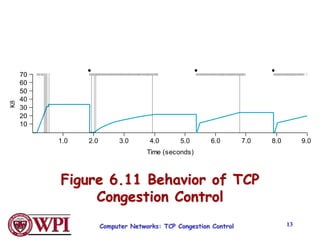
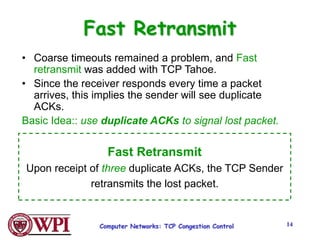
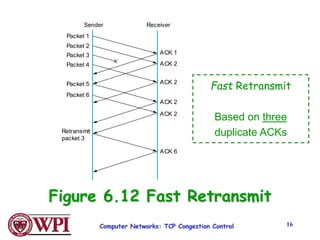
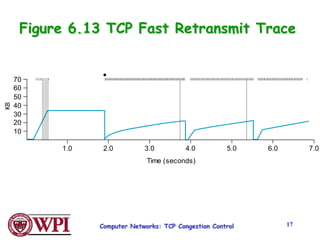
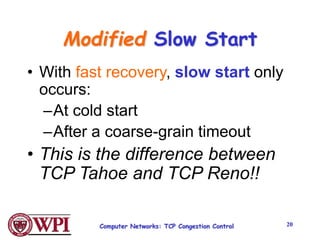
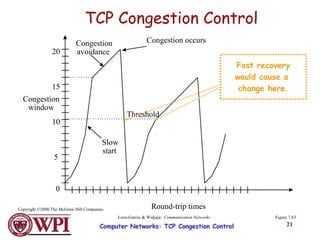
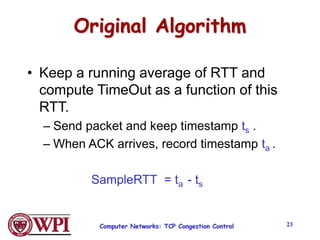
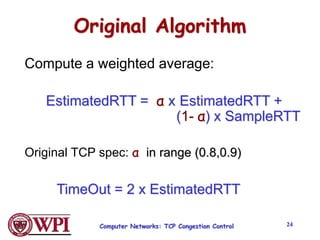
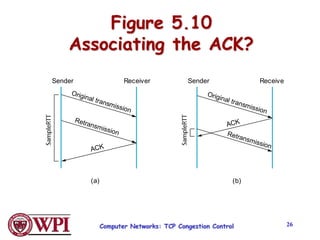
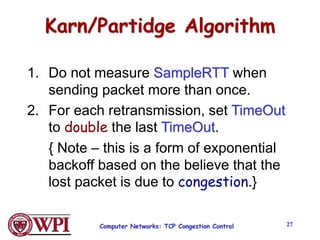
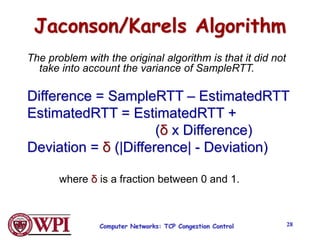
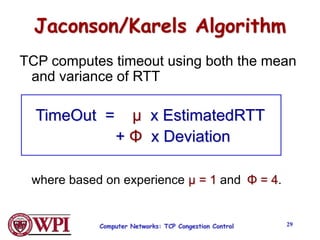
TCP uses congestion control algorithms like AIMD (Additive Increase Multiplicative Decrease) to adjust the congestion window size (cwnd) in response to indications of congestion from dropped or marked packets. Cwnd is increased linearly but decreased multiplicatively in half upon timeouts. Slow start is used initially and after timeouts to exponentially increase cwnd through doubling. Fast retransmit and fast recovery improve on timeouts by using duplicate ACKs to trigger early retransmits. Adaptive retransmission algorithms factor in the variability of measured RTTs.