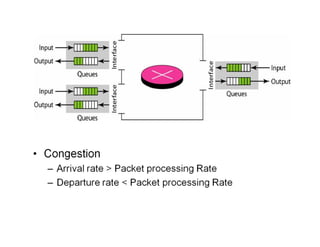
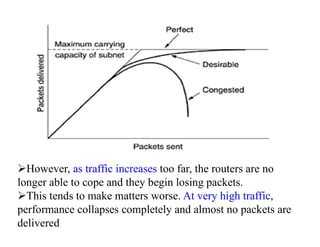
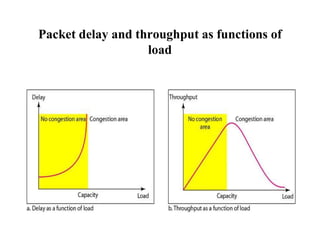
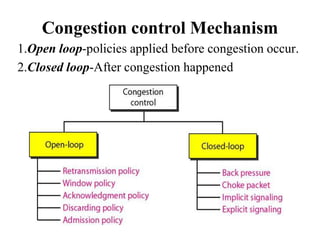
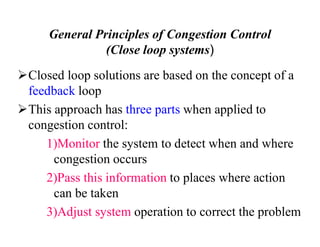
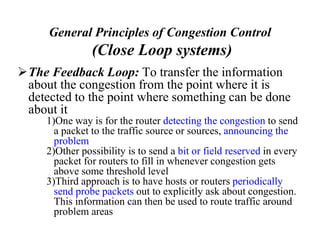
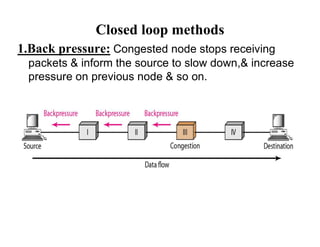
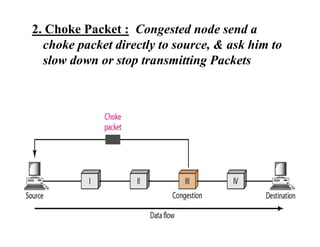
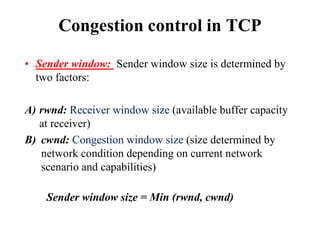
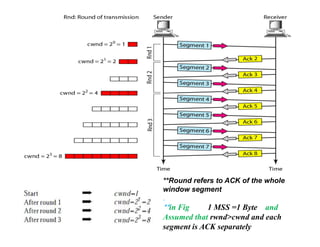
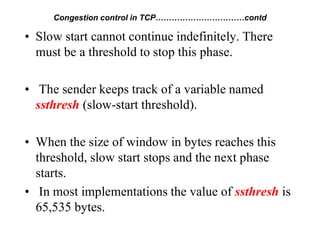
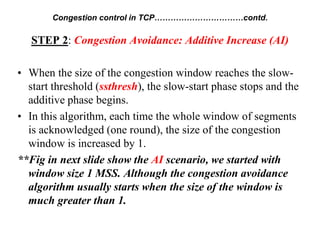
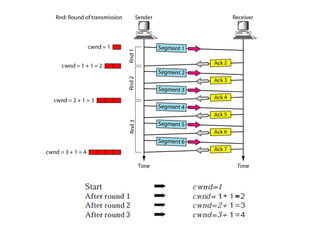
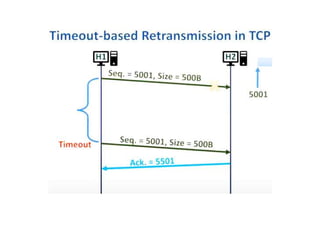
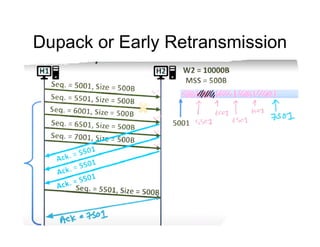
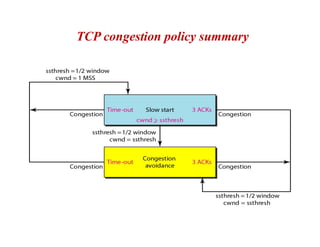
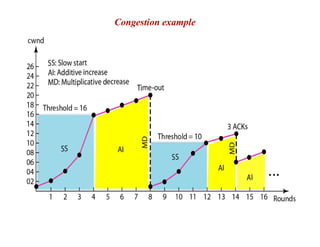
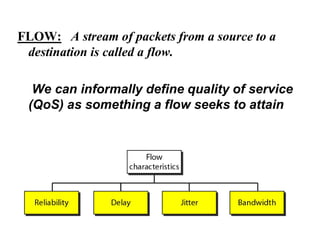
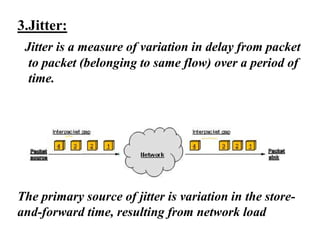
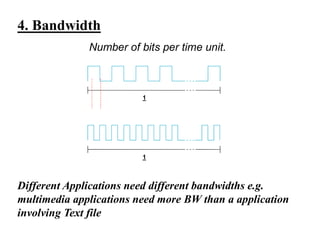
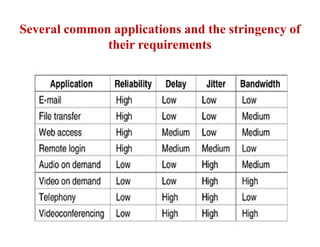
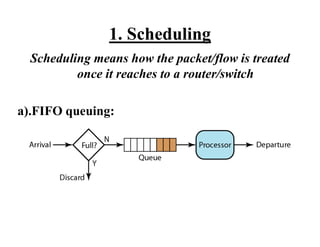
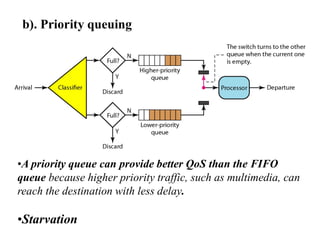
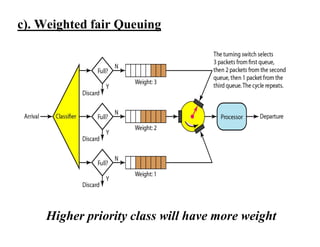
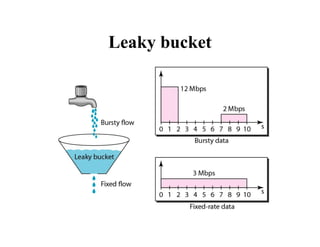
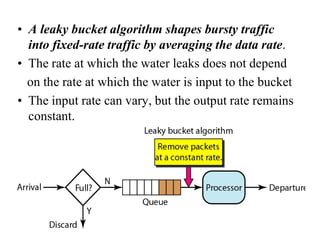
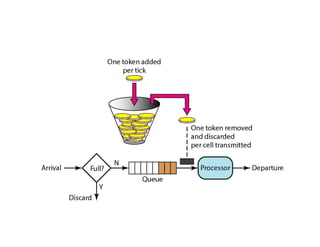
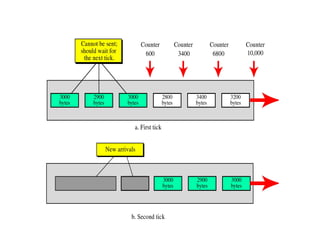
Congestion occurs when there are too many packets in a part of the network, degrading performance as routers cannot clear traffic quickly enough. It results from traffic exceeding network capacity. High traffic leads to routers losing packets, worsening matters. Congestion control aims to minimize congestion proactively through policies like admission control, while flow control relates to point-to-point traffic to prevent fast senders overwhelming receivers. TCP uses congestion windows and thresholds to gradually increase traffic while avoiding congestion through additive increase and multiplicative decrease responses to packet loss.