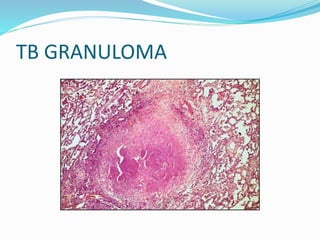
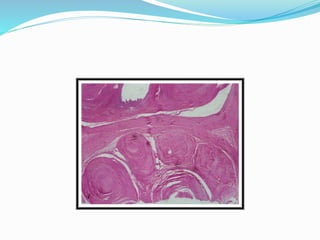
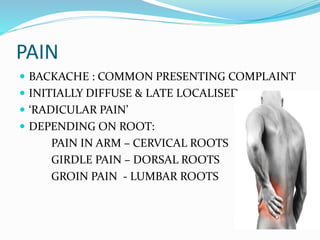
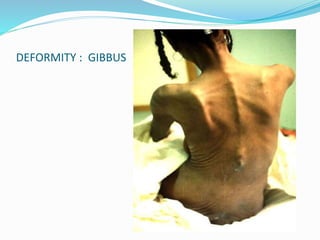
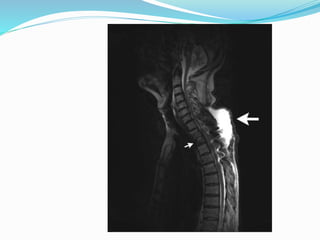
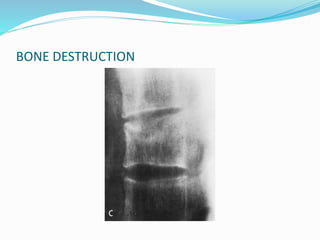
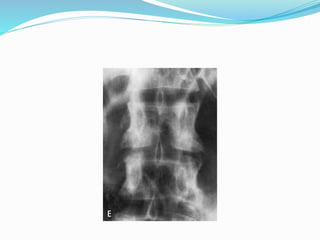
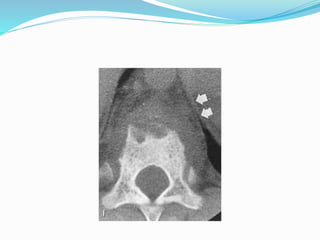
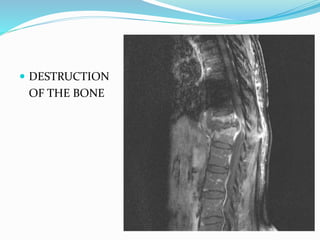
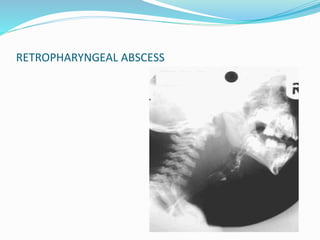
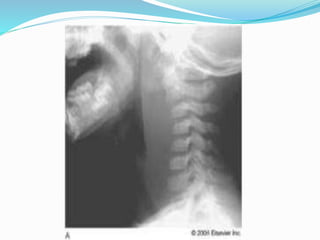
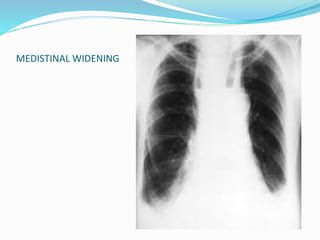
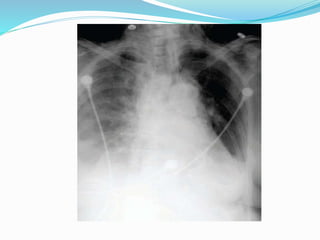
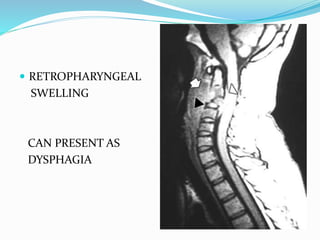
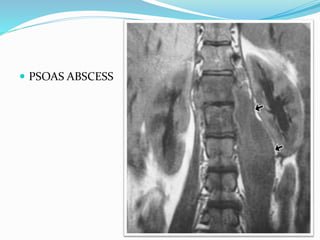
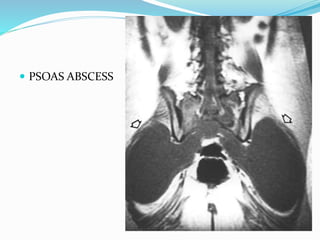
TB of the spine commonly affects the thoracic and lumbar regions. It spreads hematogenously and causes destruction of vertebral bodies. Common presentations include chronic back pain and deformities. Advanced cases may involve neurological deficits due to spinal cord compression. Diagnosis involves imaging tests like x-rays and MRI. Treatment is with anti-TB medications along with rest. Surgery is indicated for complications like paraplegia. Prognosis depends on factors like age, duration of symptoms and severity of neurological involvement.