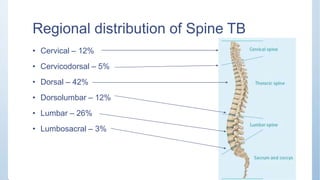
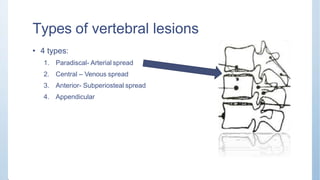
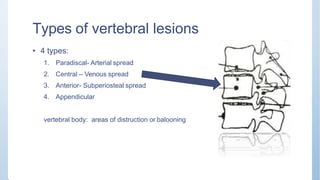
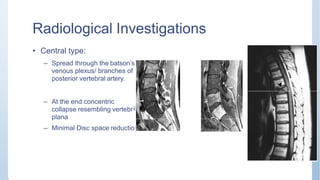
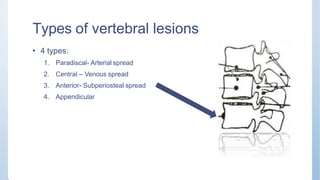
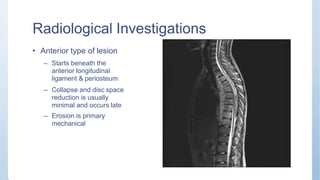
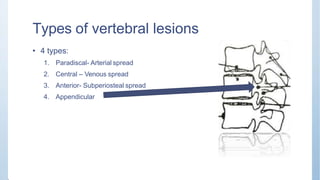
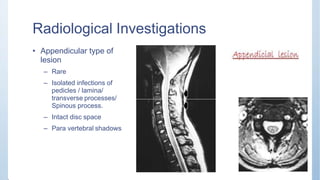
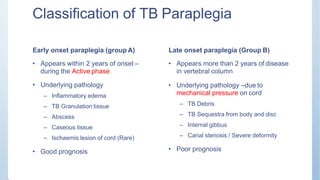
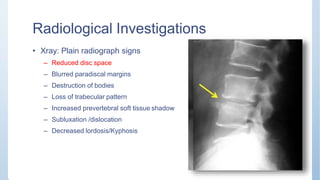
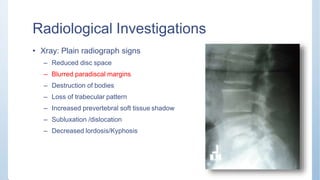
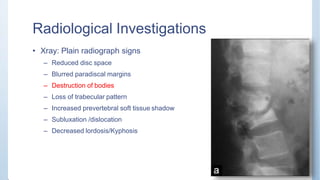
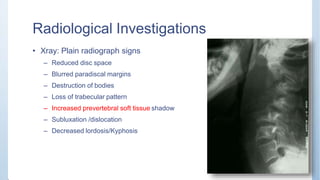
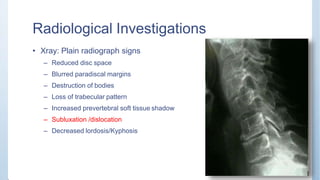
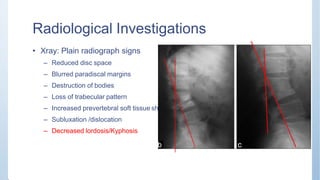
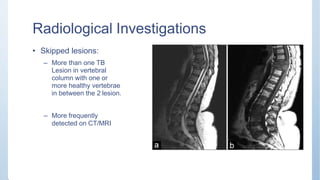
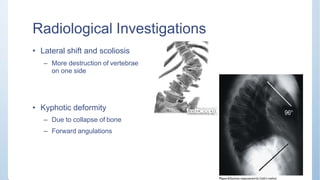
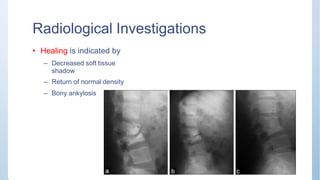
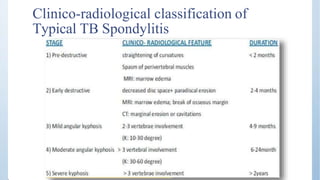
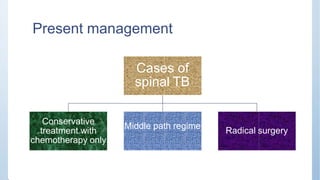
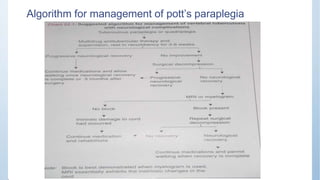
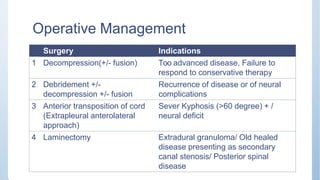
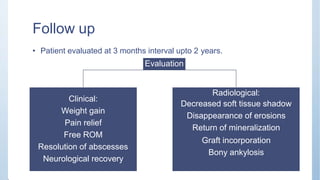
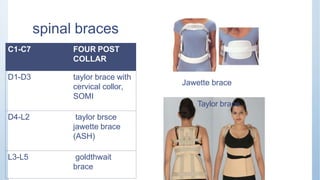
This document discusses Pott's spine and paraplegia caused by spinal tuberculosis. It covers the epidemiology, types of vertebral lesions, clinical features, investigations including radiological findings, classification of tuberculosis-related paraplegia, management using a middle path regime involving both chemotherapy and surgery, and outcomes including recovery and recurrence. The key points are that spinal tuberculosis commonly affects the lower thoracic region and can cause paraplegia, investigations include x-rays and MRI to identify lesions and involvement of the spinal cord, and treatment involves a combination of anti-tuberculosis drugs and surgery if needed to decompress the spinal cord and stabilize the spine.