Embed presentation
Downloaded 60 times




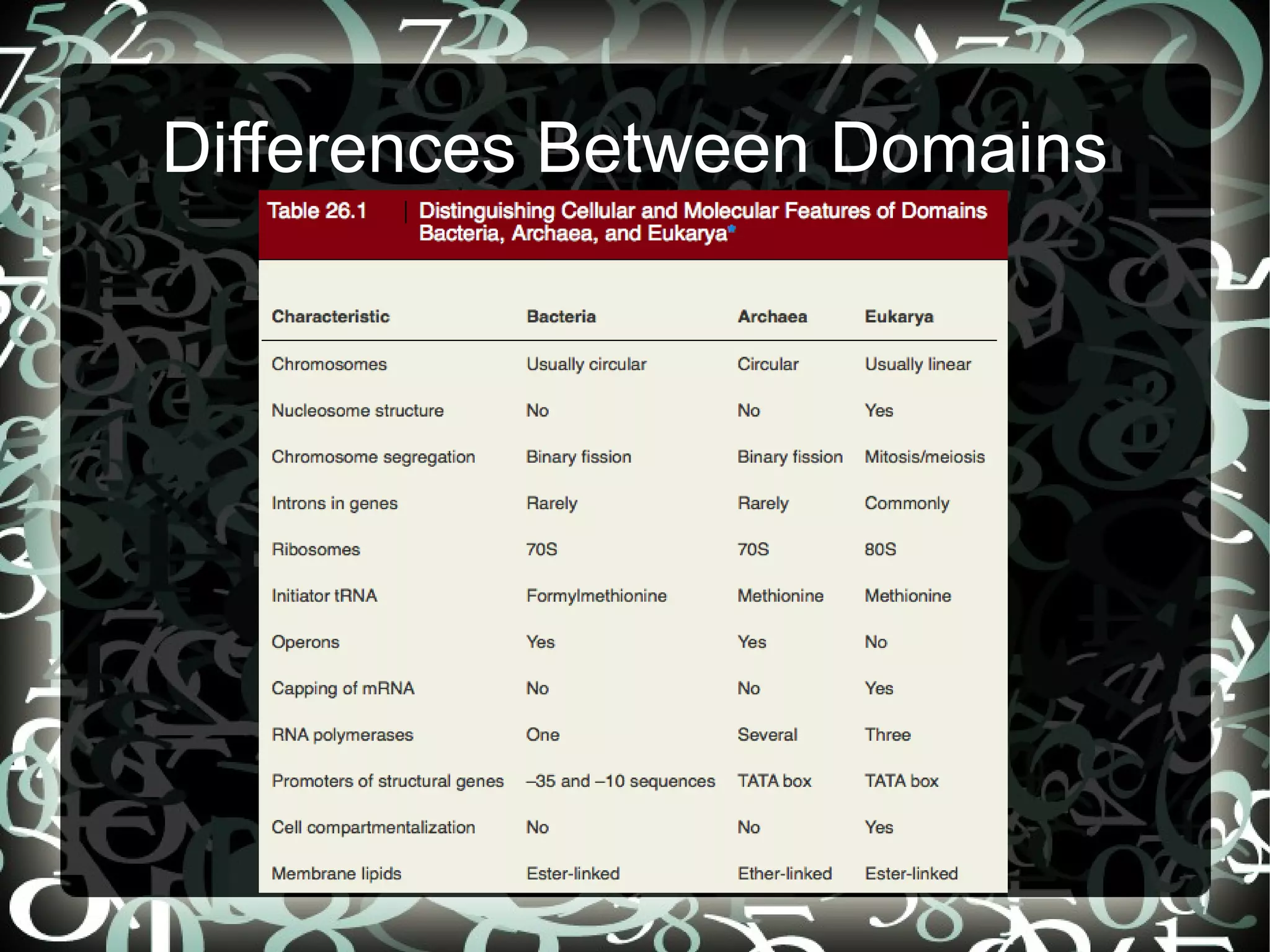
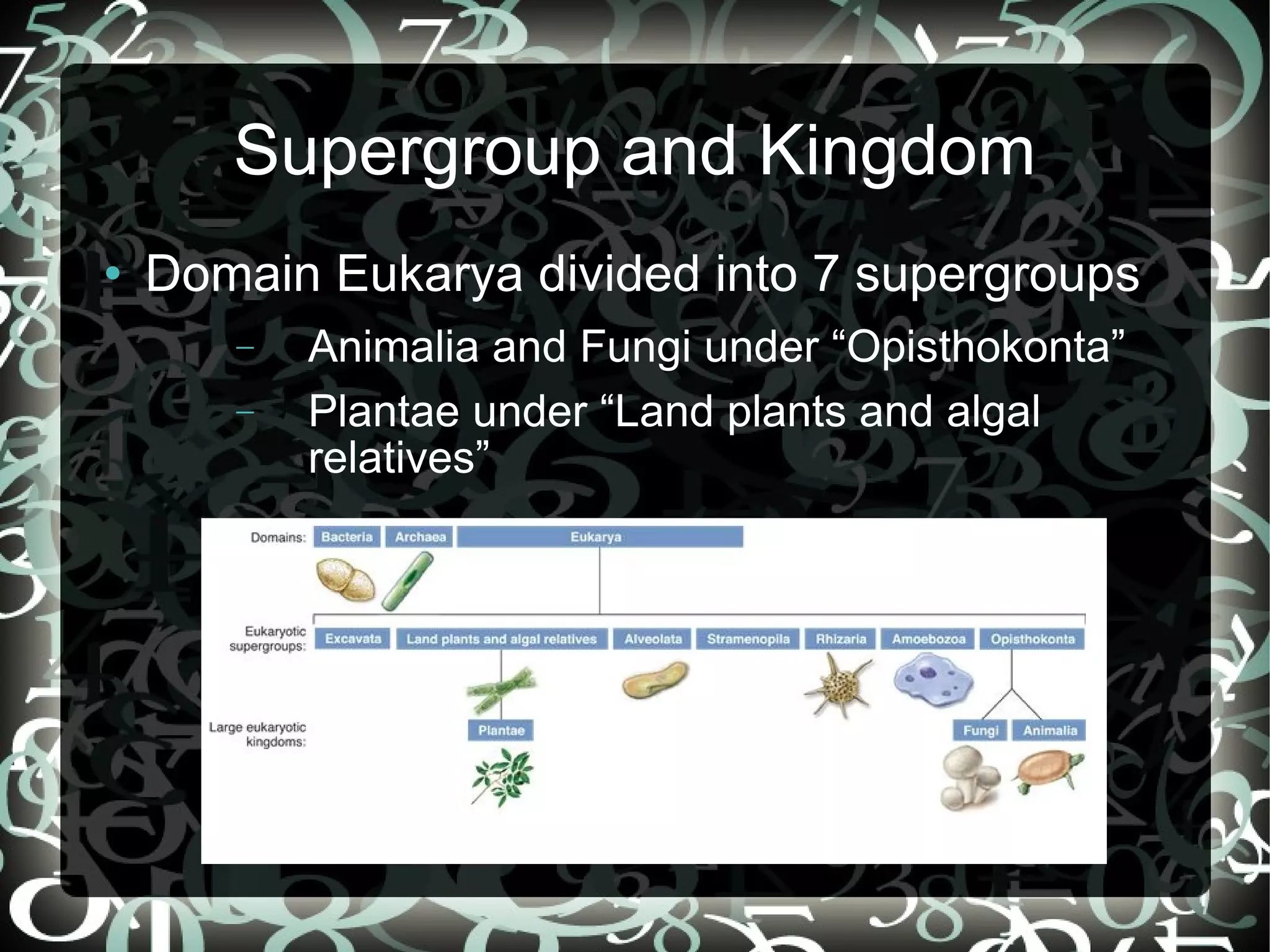



This document provides an overview of taxonomy and how organisms are classified. It explains that taxonomy involves classifying organisms into a hierarchical system of groups from the broadest domain to the most specific species level. The key groups are domains, supergroups, kingdoms, phyla, classes, orders, families, genera and species. It also describes binomial nomenclature, the standard scientific naming convention where each species is identified by its genus and specific epithet.








