1. Taxonomy is the science of classifying organisms based on similarities. It involves assigning organisms unique scientific names and grouping them in a hierarchical system from the most general domains to the most specific species level.
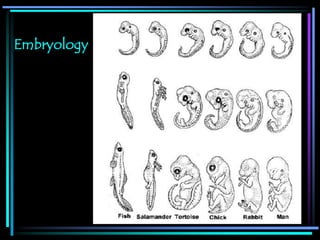
2. Phylogeny refers to the evolutionary history and relationships between organisms as depicted in phylogenetic trees, which are hypotheses based on evidence from fossils, morphology, DNA, and other sources.
3. Organisms are classified into taxonomic ranks including domains, kingdoms, phyla, classes, orders, families, genera, and species to reflect their evolutionary relationships.