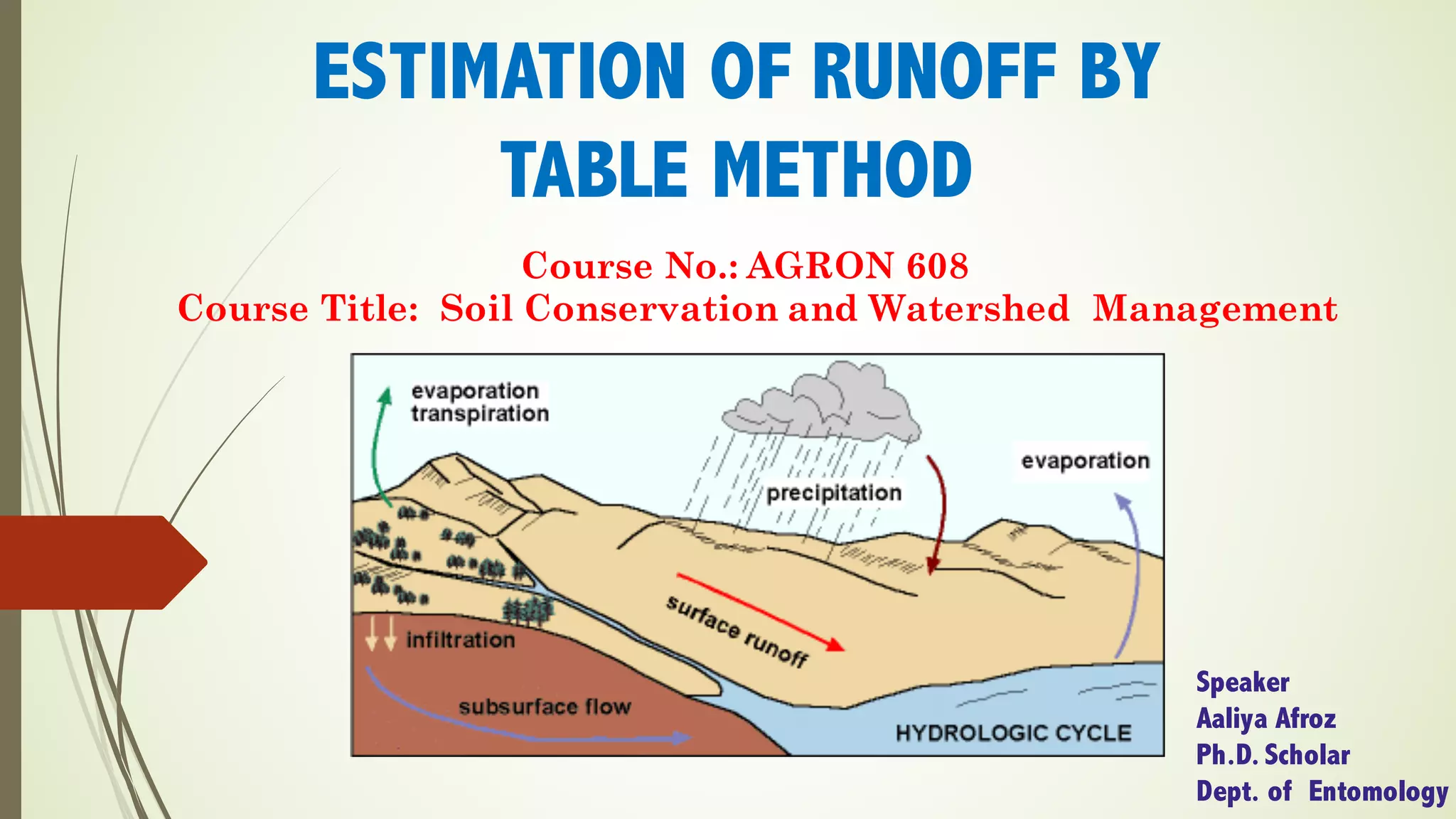
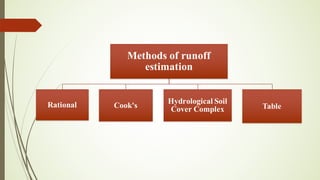
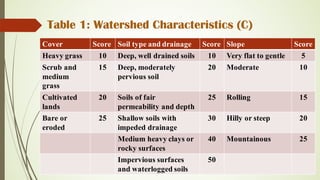
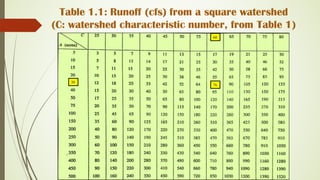
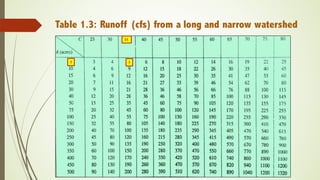
This document describes the table method for estimating runoff. It involves using tables to determine peak runoff rates based on watershed characteristics like soil type, slope, and land cover. The tables are separated based on watershed shape - square, broad and short, or long and narrow. Users first determine the watershed characteristics score from Table 1, then find the peak discharge rate in the appropriate watershed shape table by matching the score and area. Two examples are provided to demonstrate calculating runoff rates using this method.