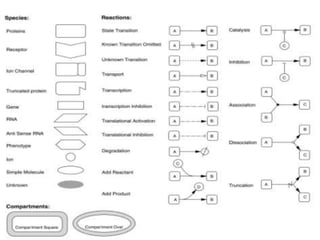
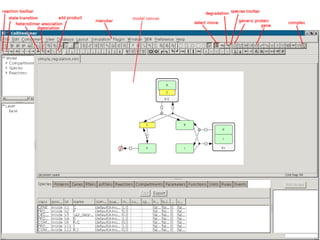
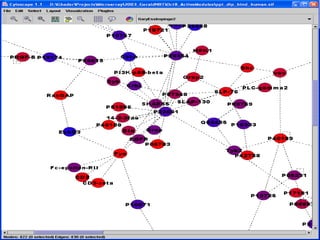
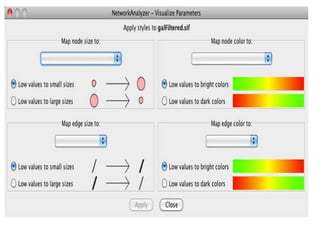
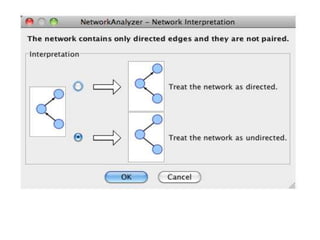
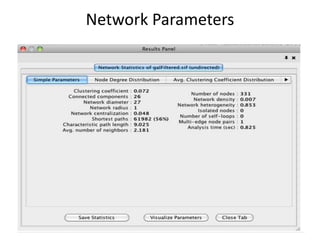
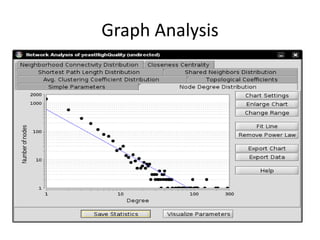
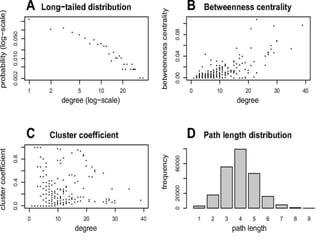
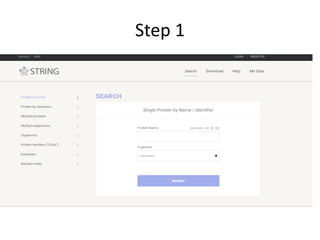
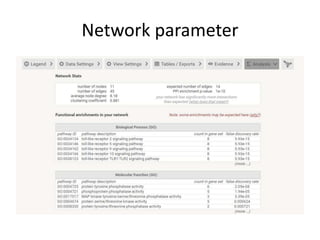
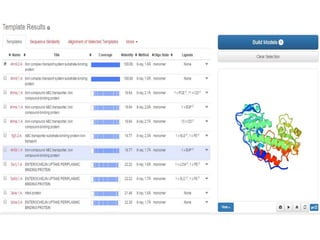
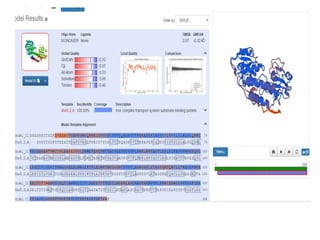
This document discusses systems biology and some of its tools. It defines systems biology as the study of interactions between parts of biological systems to understand how they function. Biological networks involve interactions between pathways. Networks can be modeled as nodes and edges. Tools described for modeling and analyzing networks include Cytoscape for visualization, CellDesigner for drawing networks, and STRING for protein-protein interaction data. Databases of pathways, interactions and models are also listed.