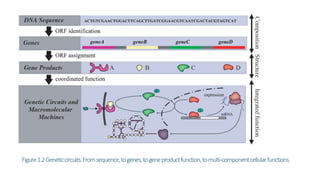
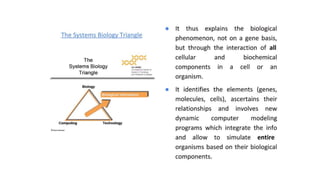
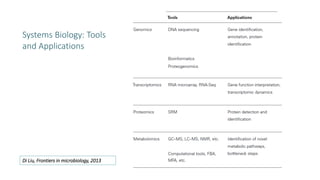
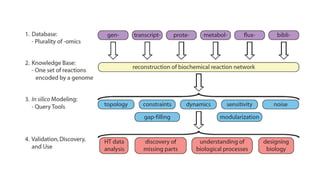
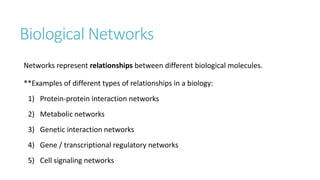
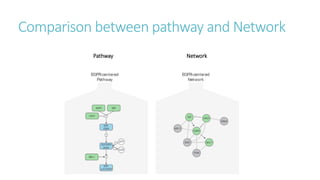
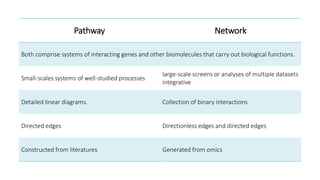
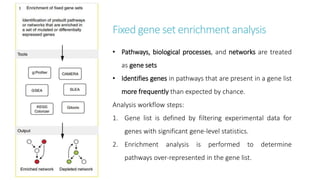
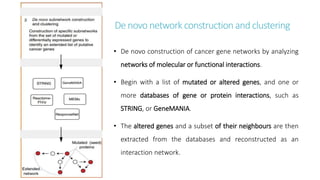
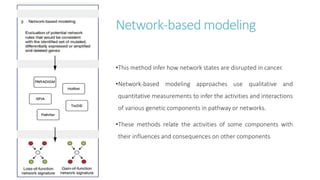
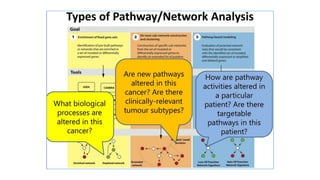
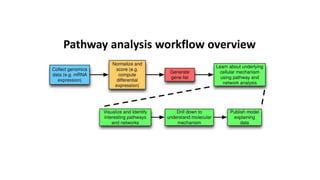
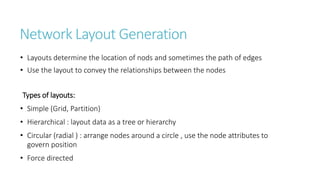
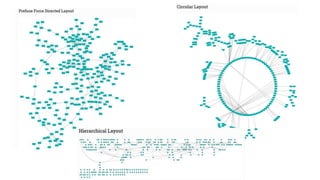
Systems biology aims to understand biological systems as complex networks of interacting components. It combines experimental and computational approaches to analyze biological processes at multiple scales. The genotype-phenotype relationship involves coordinated functions of multiple gene products, creating challenges in understanding complex interactions. Historical developments led to a systems approach applying principles of systems analysis to biochemistry. Pathway and network analysis provide integrated views of biological systems and have benefits like improved statistical power and identification of causal mechanisms. Key analysis types include gene set enrichment analysis of fixed pathways, de novo network construction and clustering, and network-based modeling. Network visualization represents relationships to enable discovery of subnetworks and integration of data types.