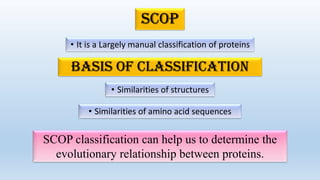
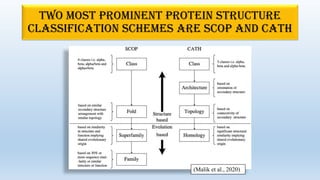
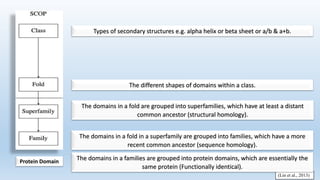
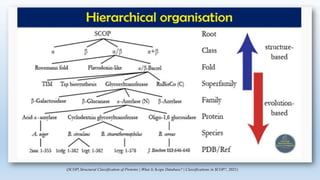
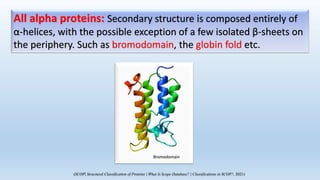
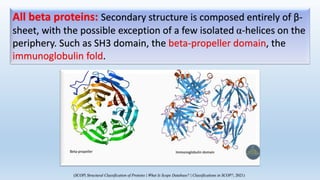
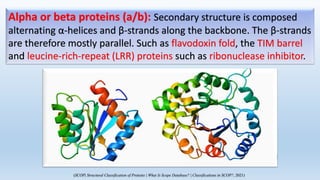
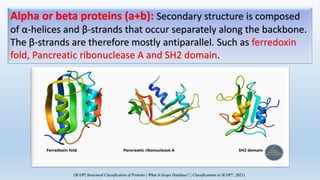
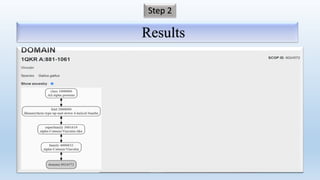
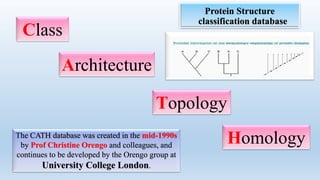
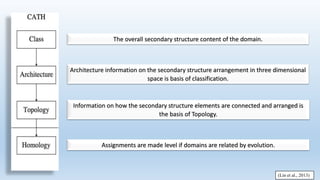
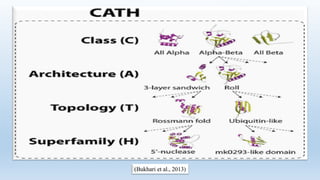
The document provides an overview of two prominent protein structure classification schemes, SCOP and CATH, detailing their methodologies for categorizing proteins based on structural and sequence similarities. It explains the classification hierarchy from domains to superfamilies and families, highlighting various secondary structural types like alpha helices and beta sheets. Additionally, it cites relevant literature and provides links to databases for further information.