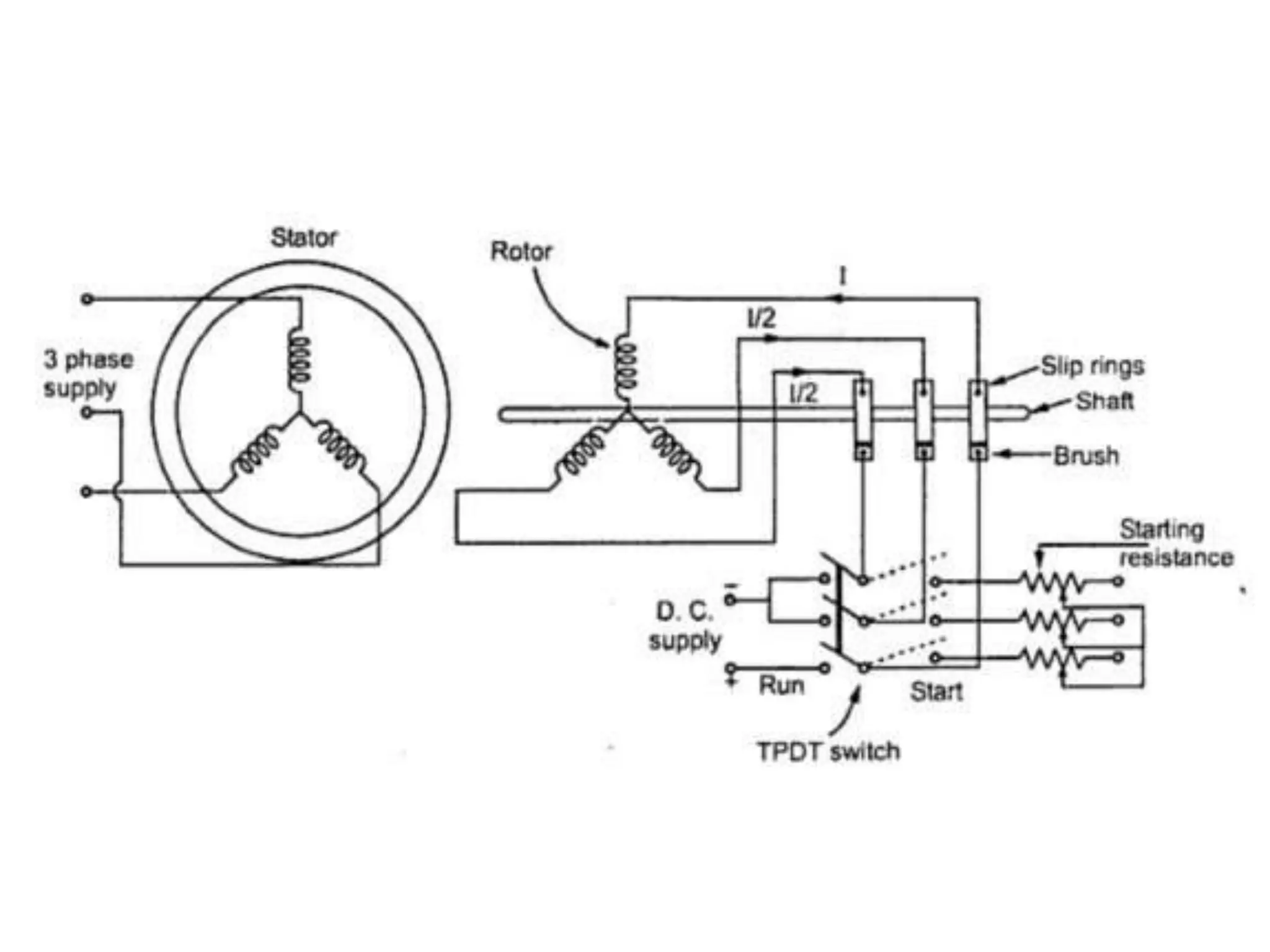
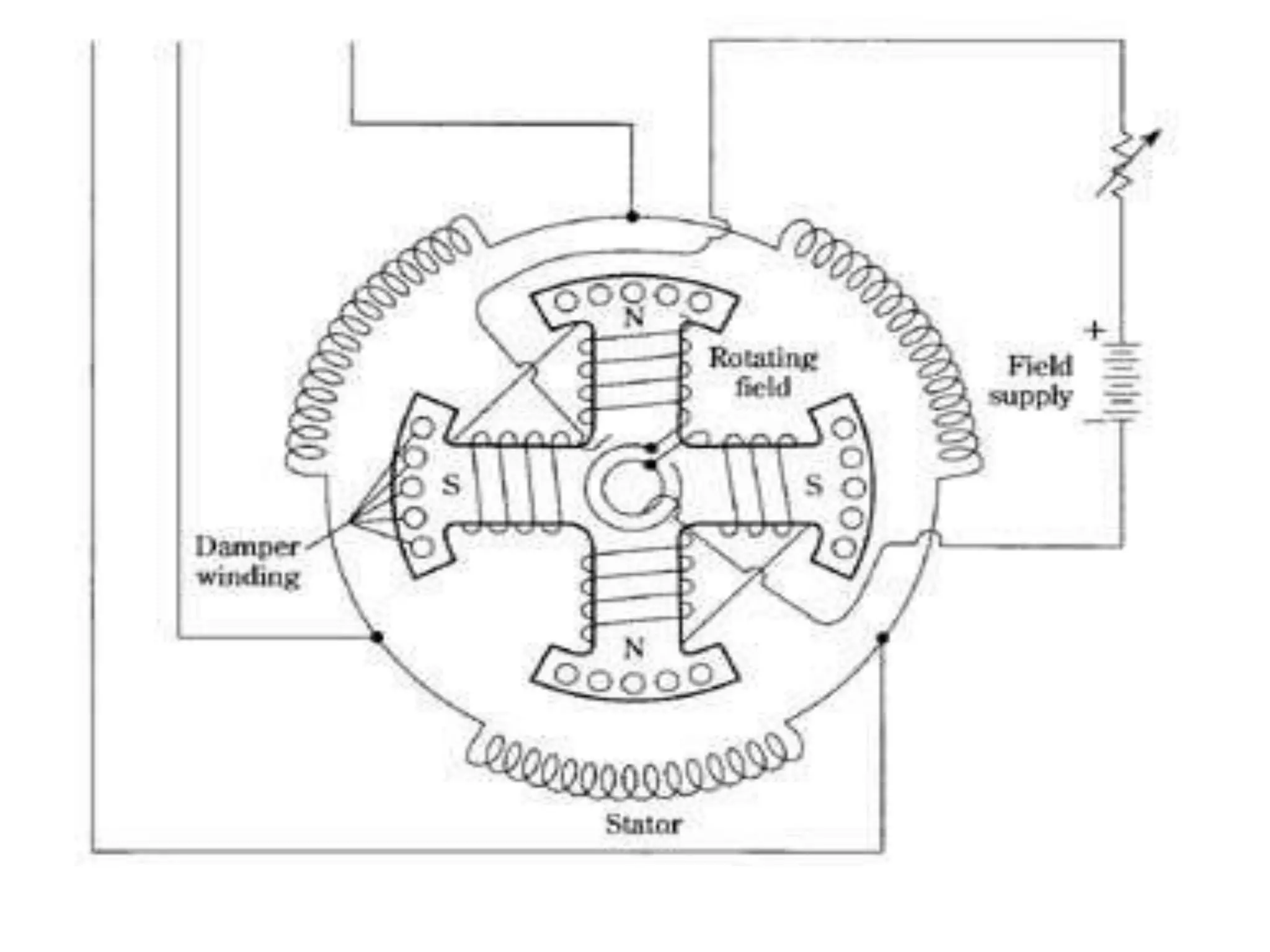
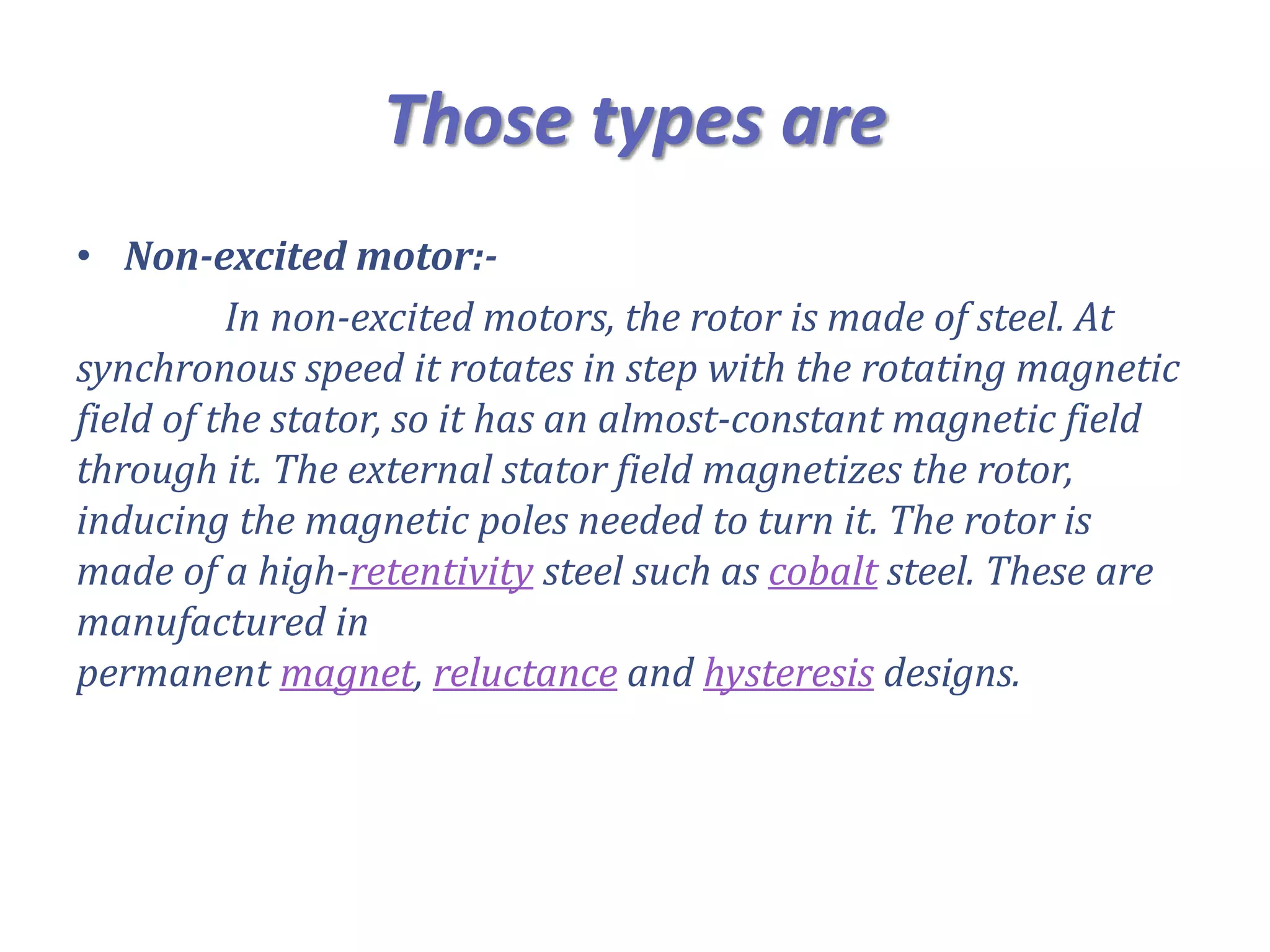
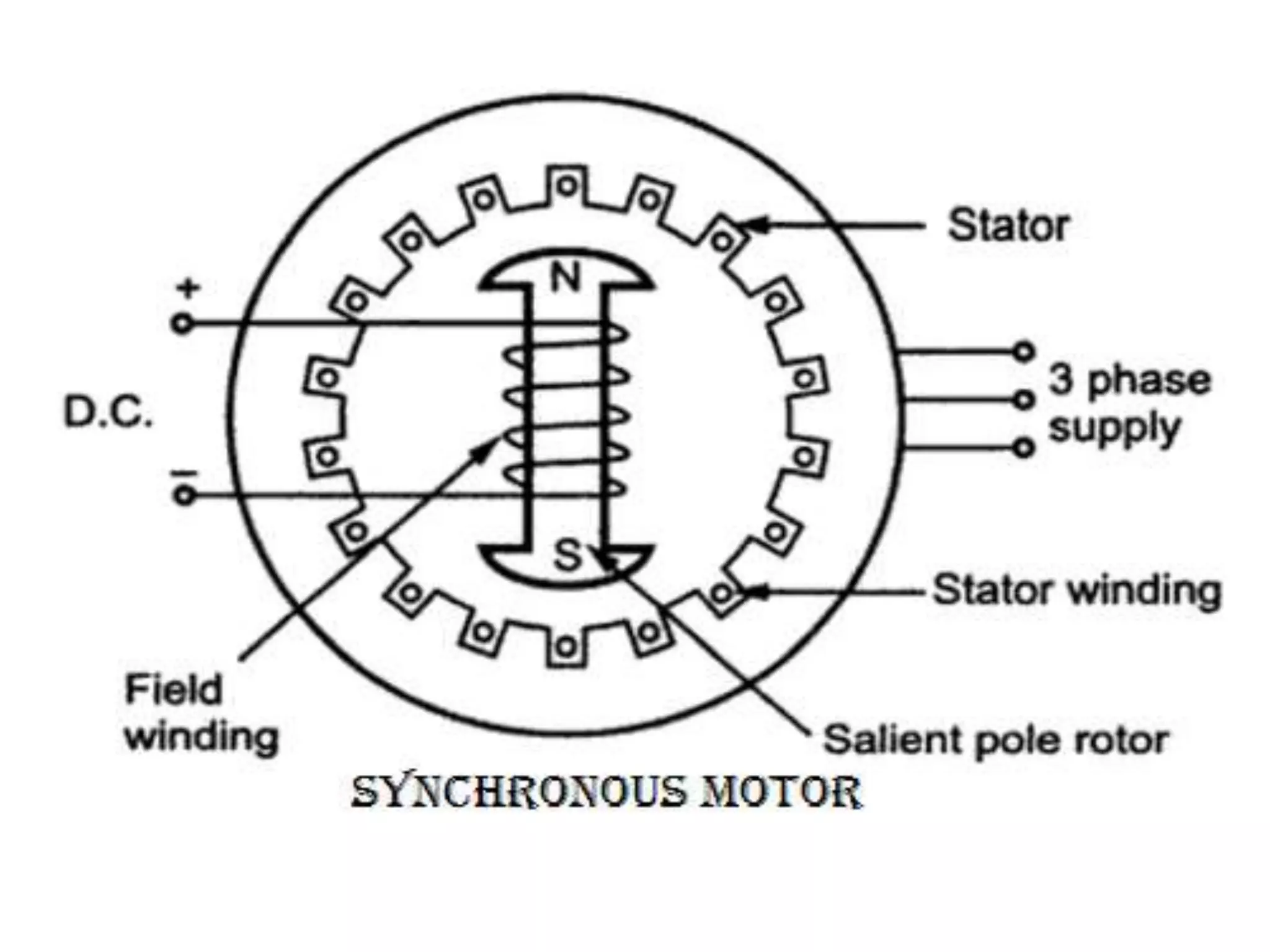
The document summarizes the key aspects of synchronous motors. It describes how synchronous motors synchronize the rotation of their shaft to the frequency of the AC power supply. There are two main types: non-excited motors which use the stator magnetic field to induce poles on the steel rotor, and DC-excited motors which require a separate DC source to excite the rotor. Synchronous motors have advantages over other motors like constant speed operation and unity power factor, and they are commonly used where precise constant speed is required, like in power generation and precision machinery.









![Motors that are electronically controlled can be accelerated from zero
speed by changing the frequency of the stator current.
Very small synchronous motors are commonly used in line-
powered electric mechanical clocks or timers that use the power line
frequency to run the gear mechanism at the correct speed. Such small
synchronous motors are able to start without assistance if the moment
of inertia of the rotor and its mechanical load is sufficiently small
[because the motor] will be accelerated from slip speed up to
synchronous speed during an accelerating half cycle of the reluctance
torque."Single-phase synchronous motors such as in electric wall clocks
can freely rotate in either direction unlike a shaded-pole type.
See Shaded-pole synchronous motor for how consistent starting
direction is obtained.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4thsemsynchronousmotorforpresentation-190527030707/75/synchronous-motor-for-presentation-18-2048.jpg)