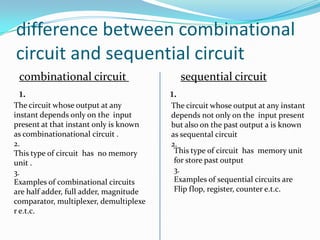
Combinational circuits have no memory and their output depends only on the current input. Examples are half adders, full adders, multiplexers. Sequential circuits have memory and their output depends on both the current input and past outputs. Examples are flip-flops, registers, counters. The document provides examples of concepts related to combinational and sequential circuits like exam preparation (no memory vs remembering) and gives circuit examples for each type.