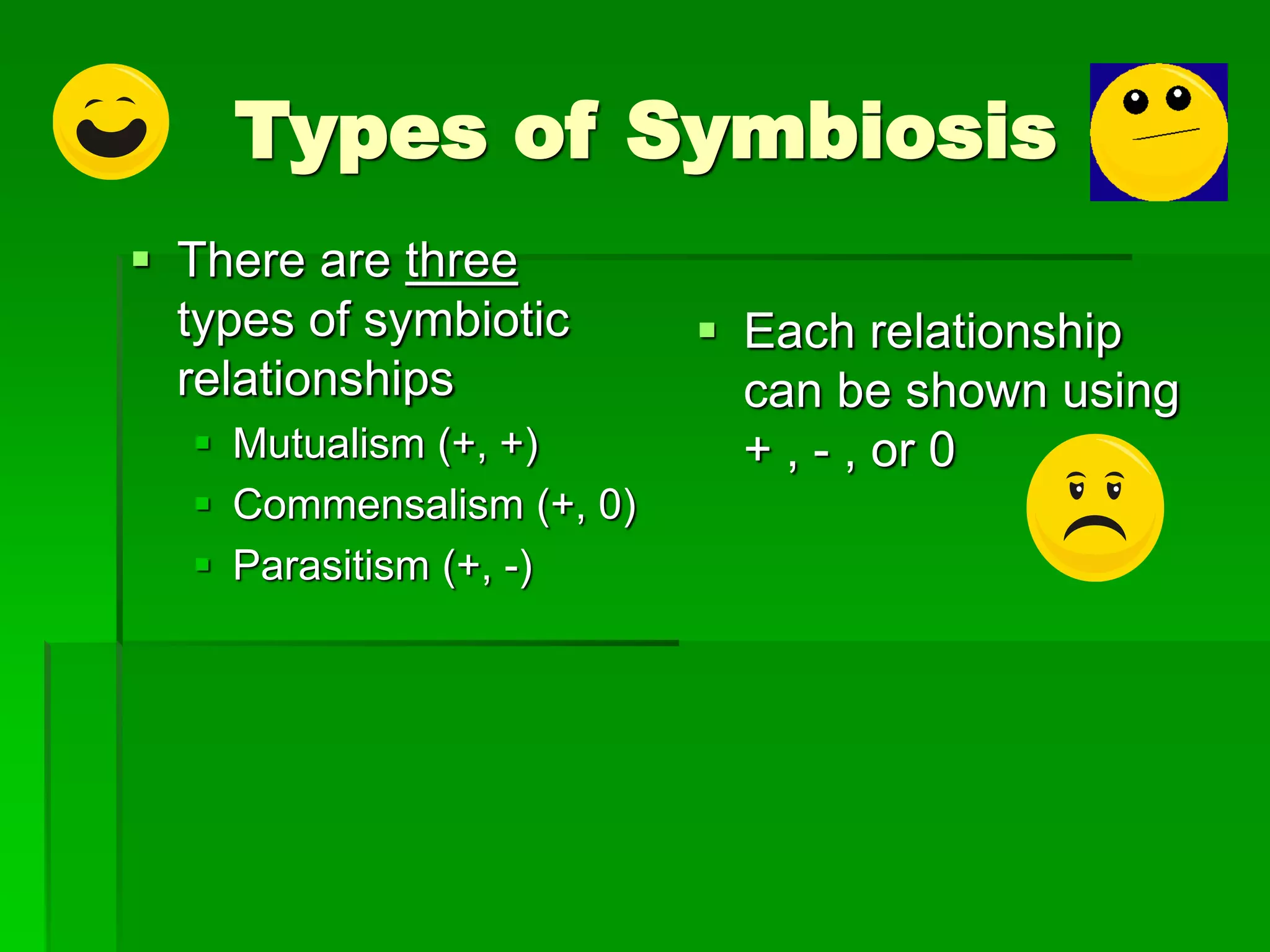
Symbiotic relationships are interactions between two organisms that live together. There are three main types: mutualism, where both species benefit; commensalism, where one benefits and the other is unaffected; and parasitism, where one benefits and the other is harmed. Examples of mutualism include bees pollinating flowers, cleaner fish eating parasites off other fish, and oxpeckers removing ticks from antelopes. Commensalism is seen in remoras attaching to sharks and barnacles attaching to whales. Parasitism includes ticks and mosquitoes feeding on animal blood and mistletoe growing on trees.