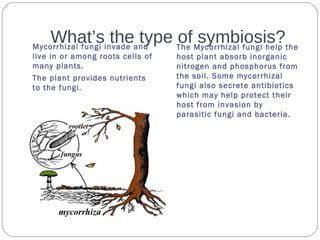
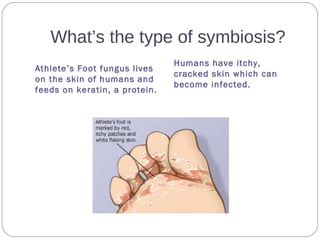
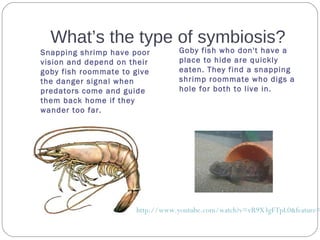
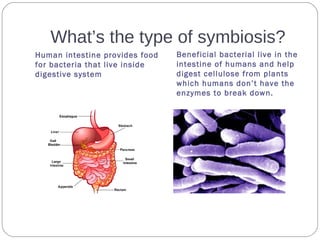
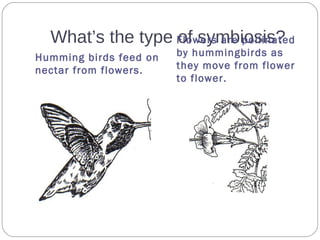
The document describes various examples of symbiotic relationships between different organisms, and asks the reader to identify the type of symbiosis in each case. The three main types are defined as mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. Mutualism benefits both organisms, commensalism benefits one without affecting the other, and parasitism benefits one organism at the expense of the other.