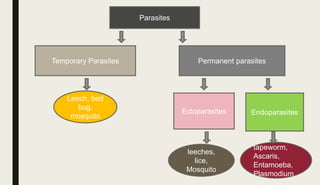
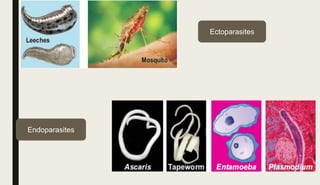
The document discusses different types of symbiotic relationships:
- Parasitism involves a parasite harming its host for food and shelter. Examples include mosquitoes and tapeworms.
- Mutualism benefits both species, like the relationship between termites and protozoa in the termite's gut.
- Commensalism helps one species without affecting the other, such as epiphytic plants growing on trees or suckerfish attaching to sharks.