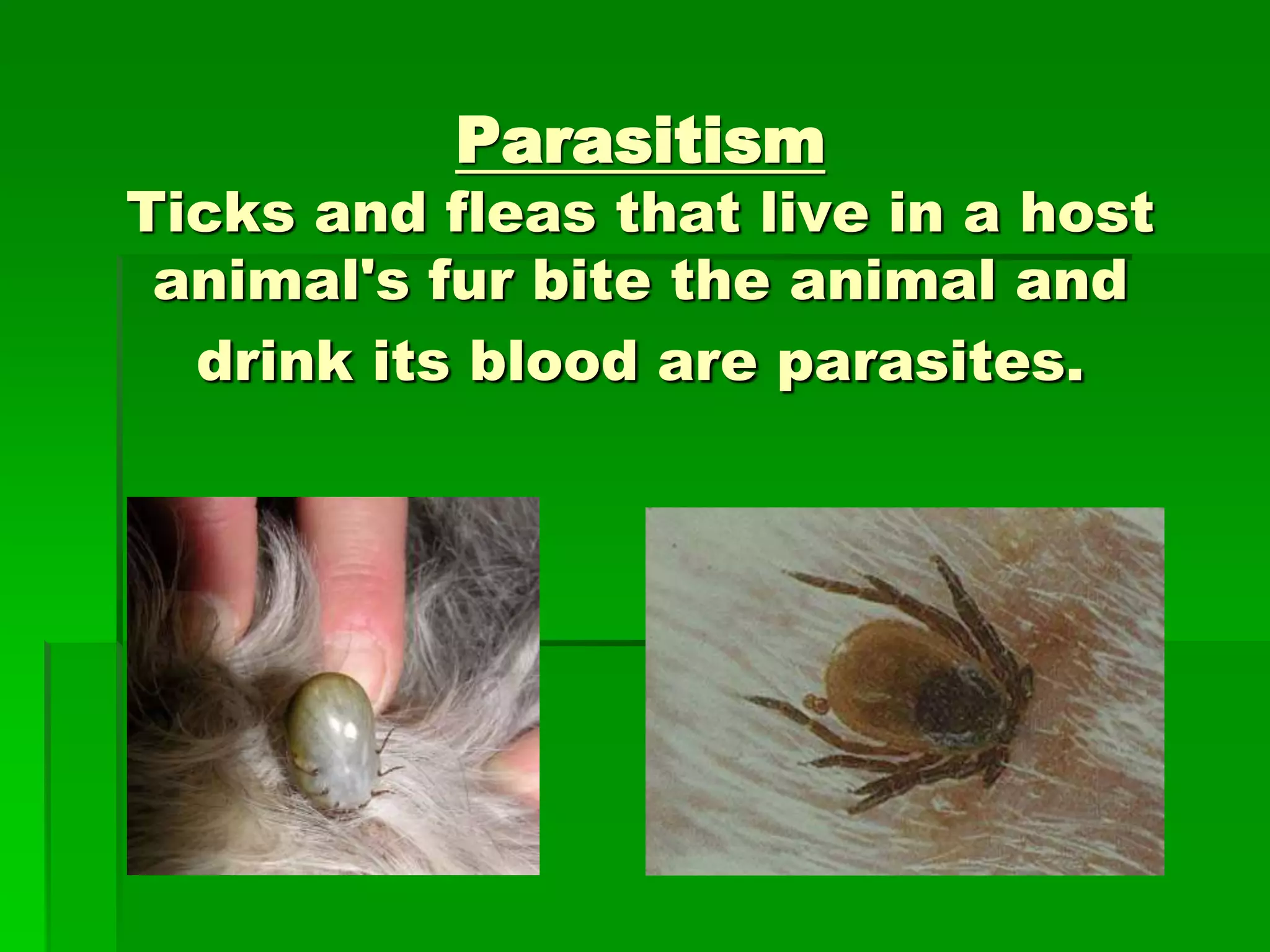
There are three main types of symbiotic relationships: mutualism, in which both organisms benefit; commensalism, where one benefits and the other is not affected; and parasitism, where one benefits while harming the other. Mutualism examples include flowers and pollinators, cleaner fish/moray eels, and lichens. Commensalism examples include barnacles on whales and remoras following sharks. Parasitism examples harm the host, like ticks that transmit Lyme disease and tapeworms in dog intestines.