This document provides an overview of MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) including:
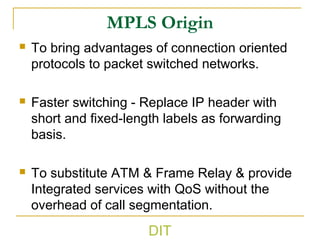
1) It describes the need for MPLS arising from limitations in traditional IP forwarding and issues running one statmux technology over another.
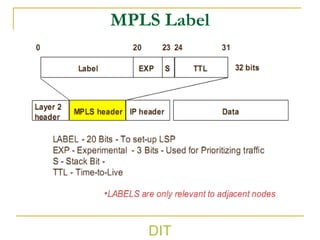
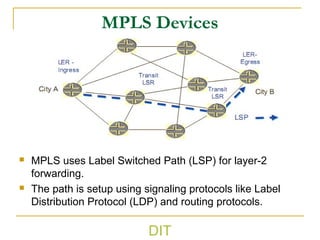
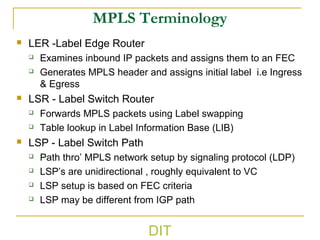
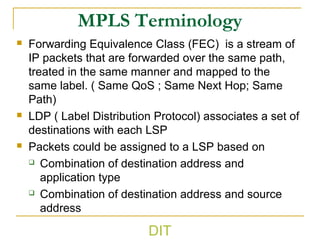
2) It explains basic MPLS concepts like label switching, label distribution protocols, label edge and switch routers, label switching paths, and forwarding equivalence classes.
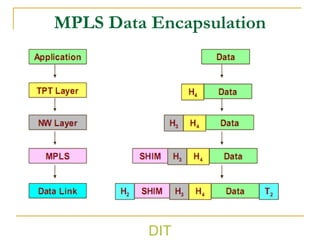
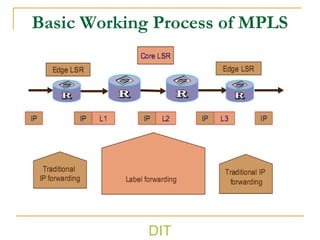
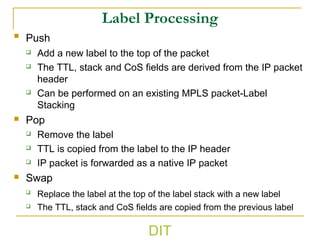
3) It outlines the basic working process of MPLS including label encapsulation, lookup, and processing functions like push, pop and swap.