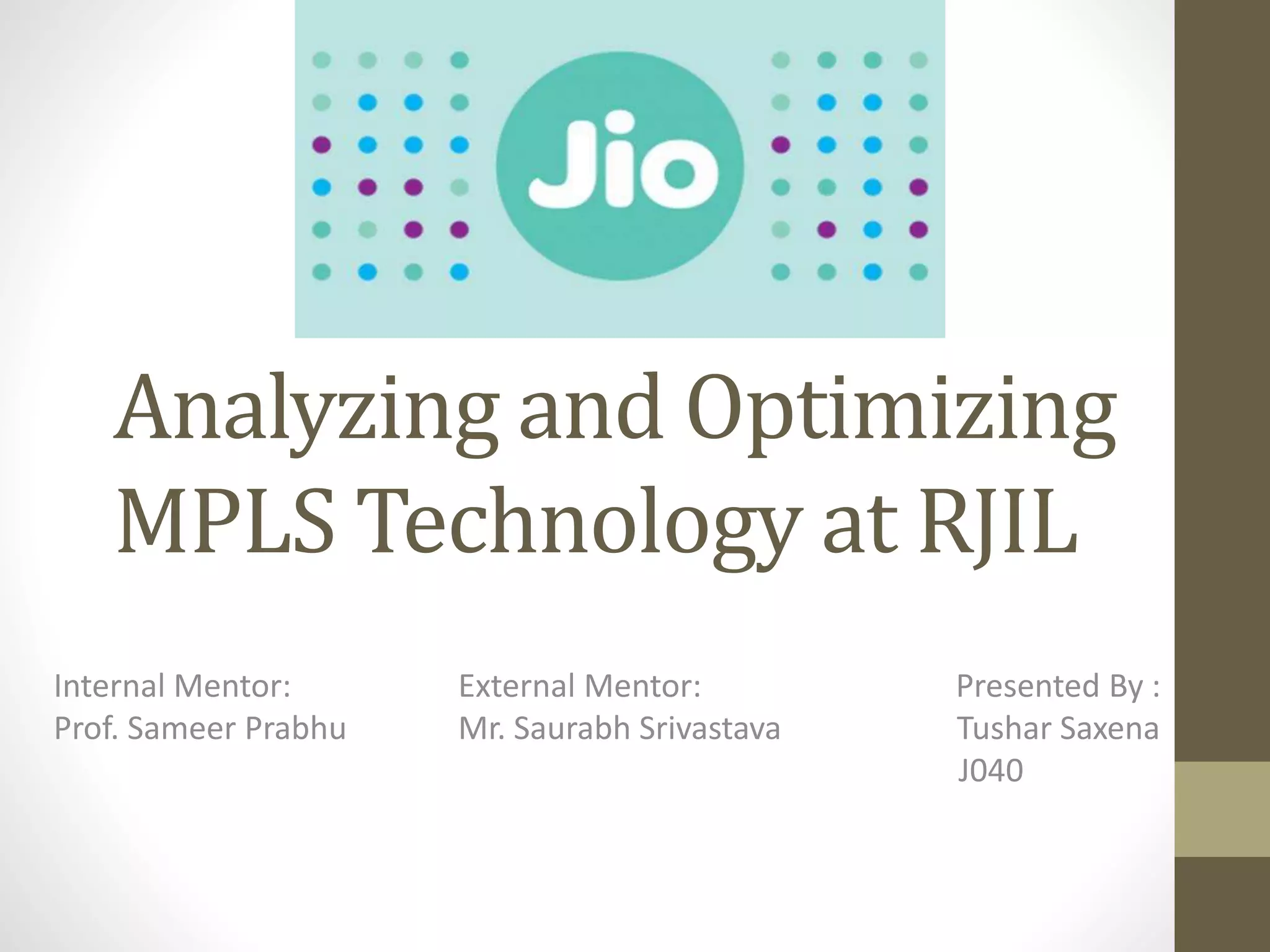
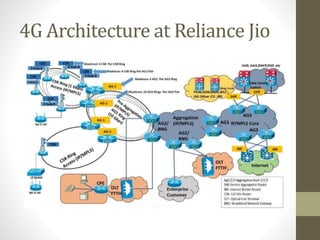
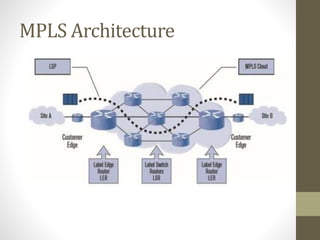
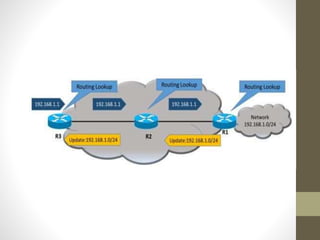
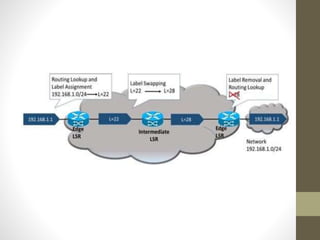
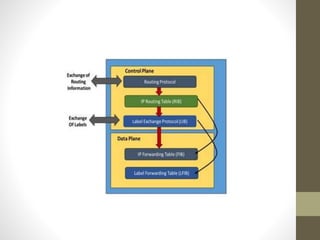
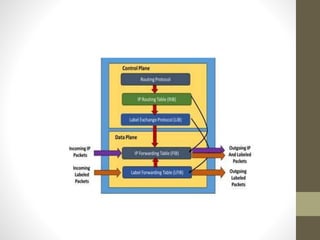
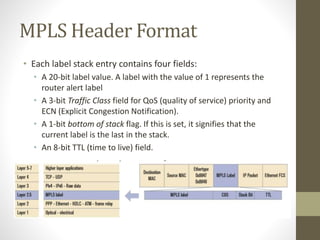
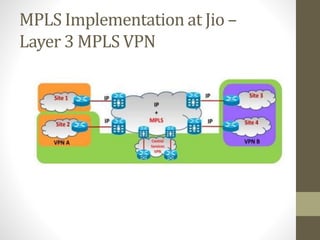
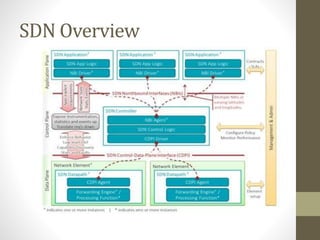
The document discusses the analysis and optimization of MPLS technology implemented by RJIL, a growing telecom provider in India aiming to deliver comprehensive 4G services. It outlines the MPLS architecture, control and forwarding planes, and the advantages of MPLS over traditional routing methodologies, particularly in handling real-time multimedia applications. Additionally, it highlights the implementation of Layer 3 MPLS VPNs for efficient customer connectivity, along with the scalability benefits of SDN as compared to MPLS VPN.