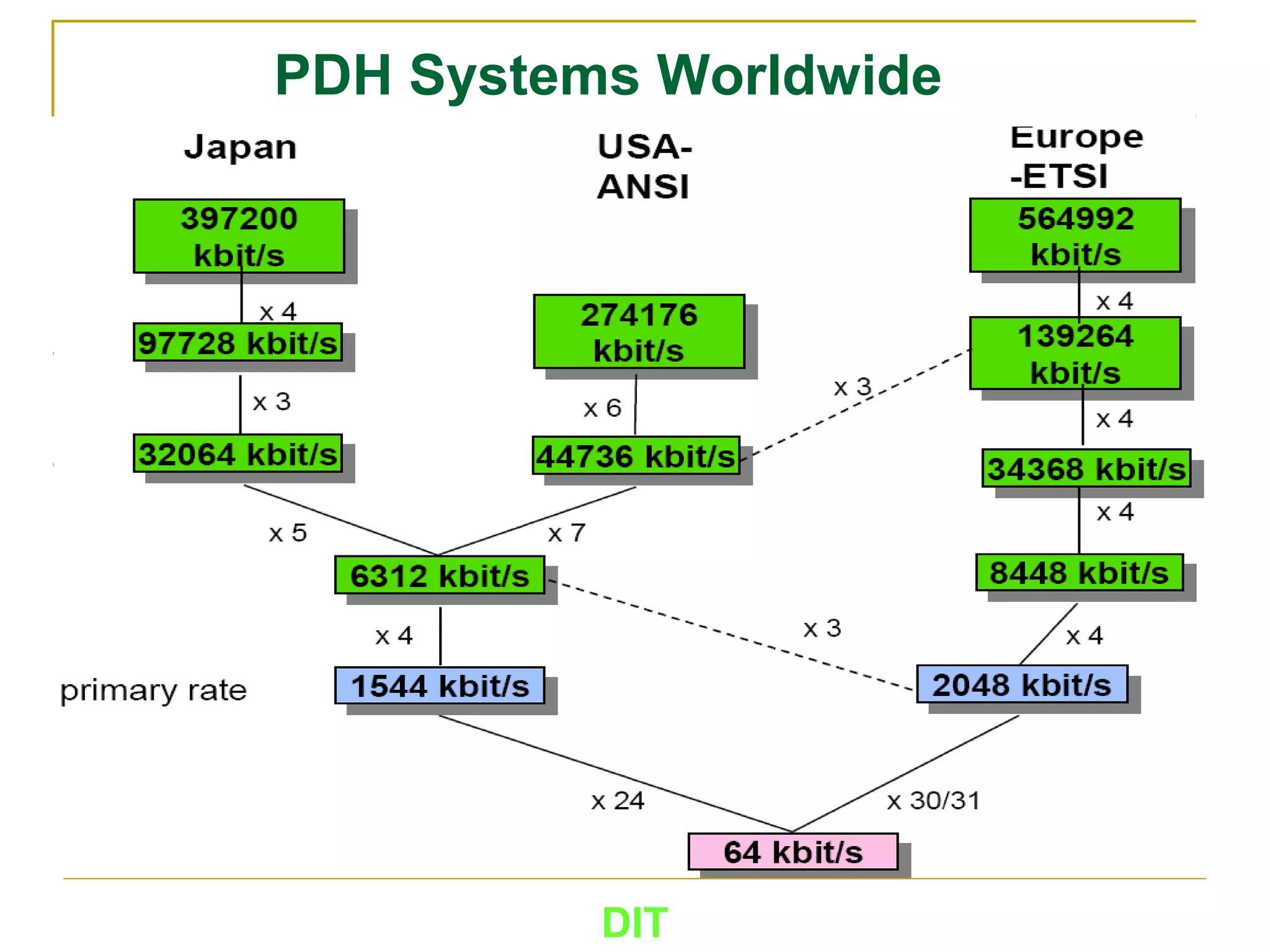
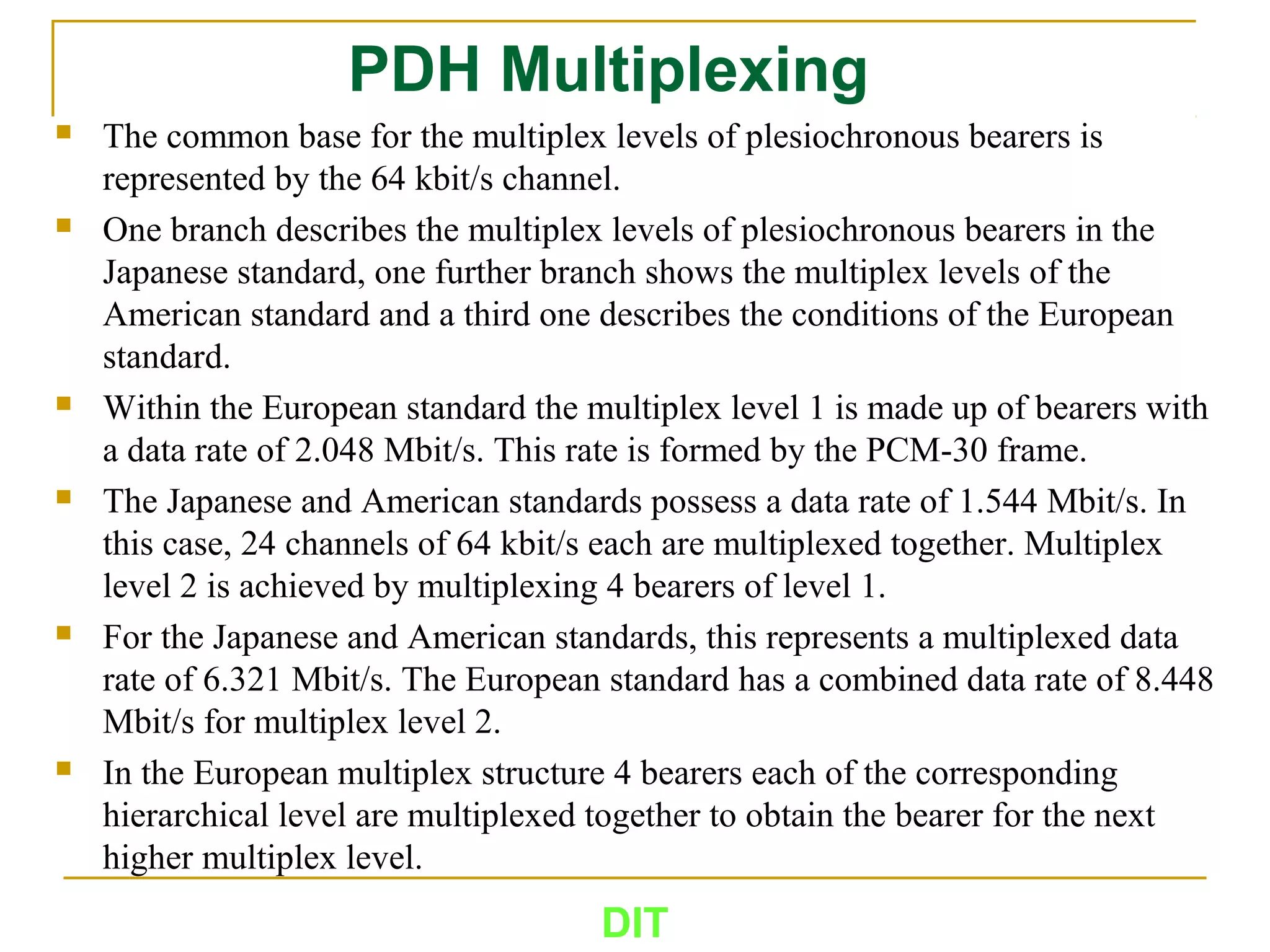
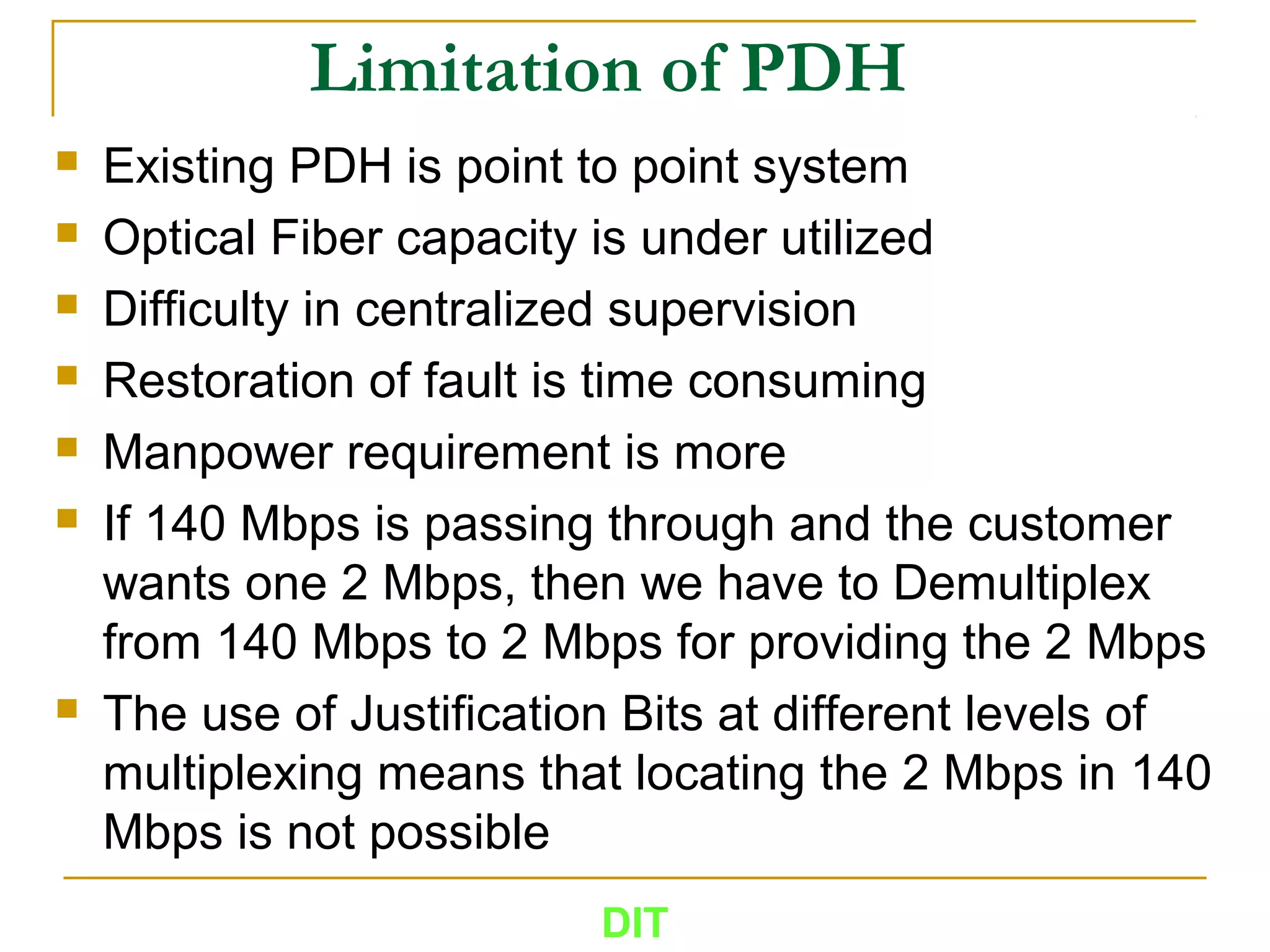
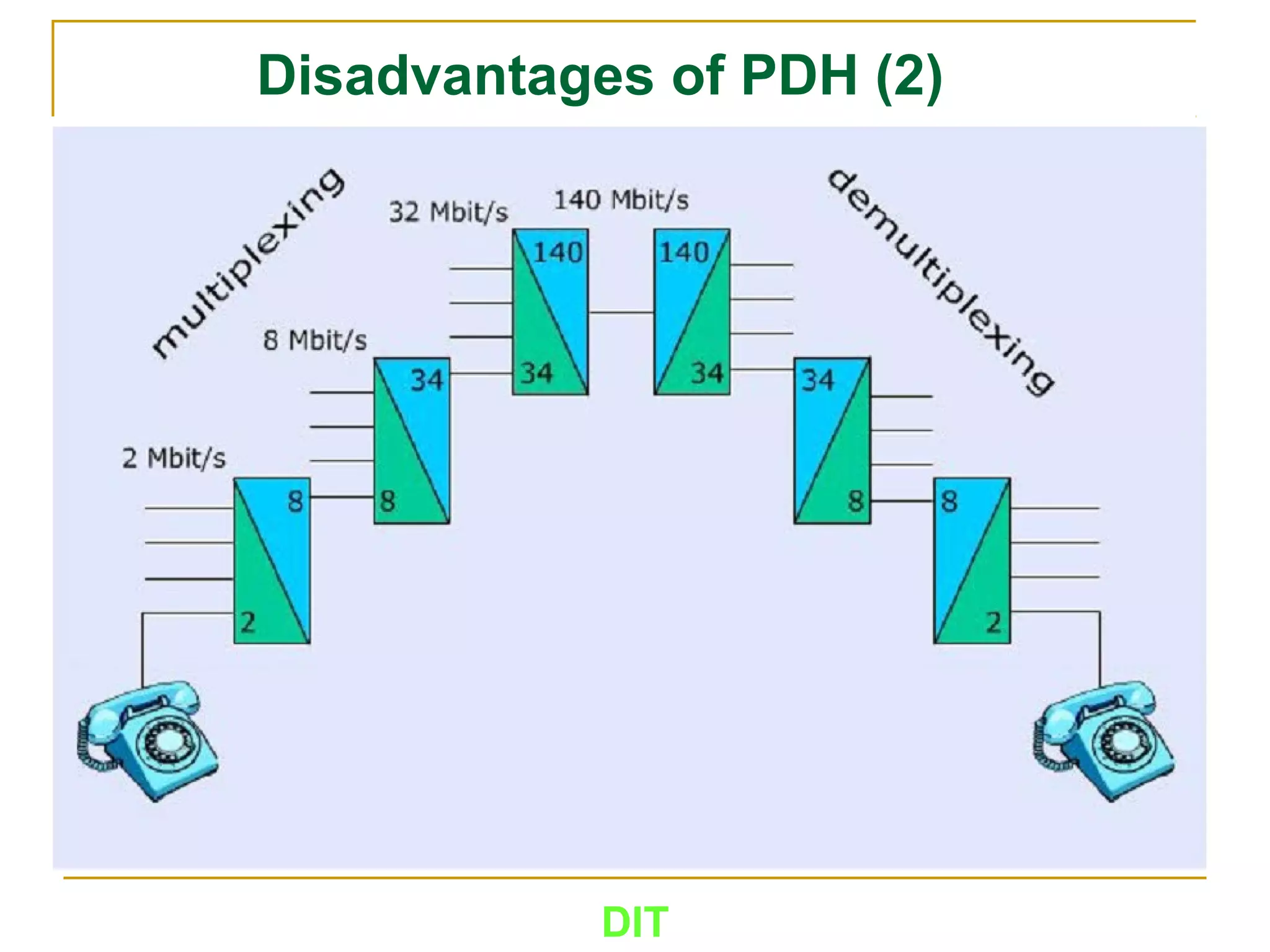
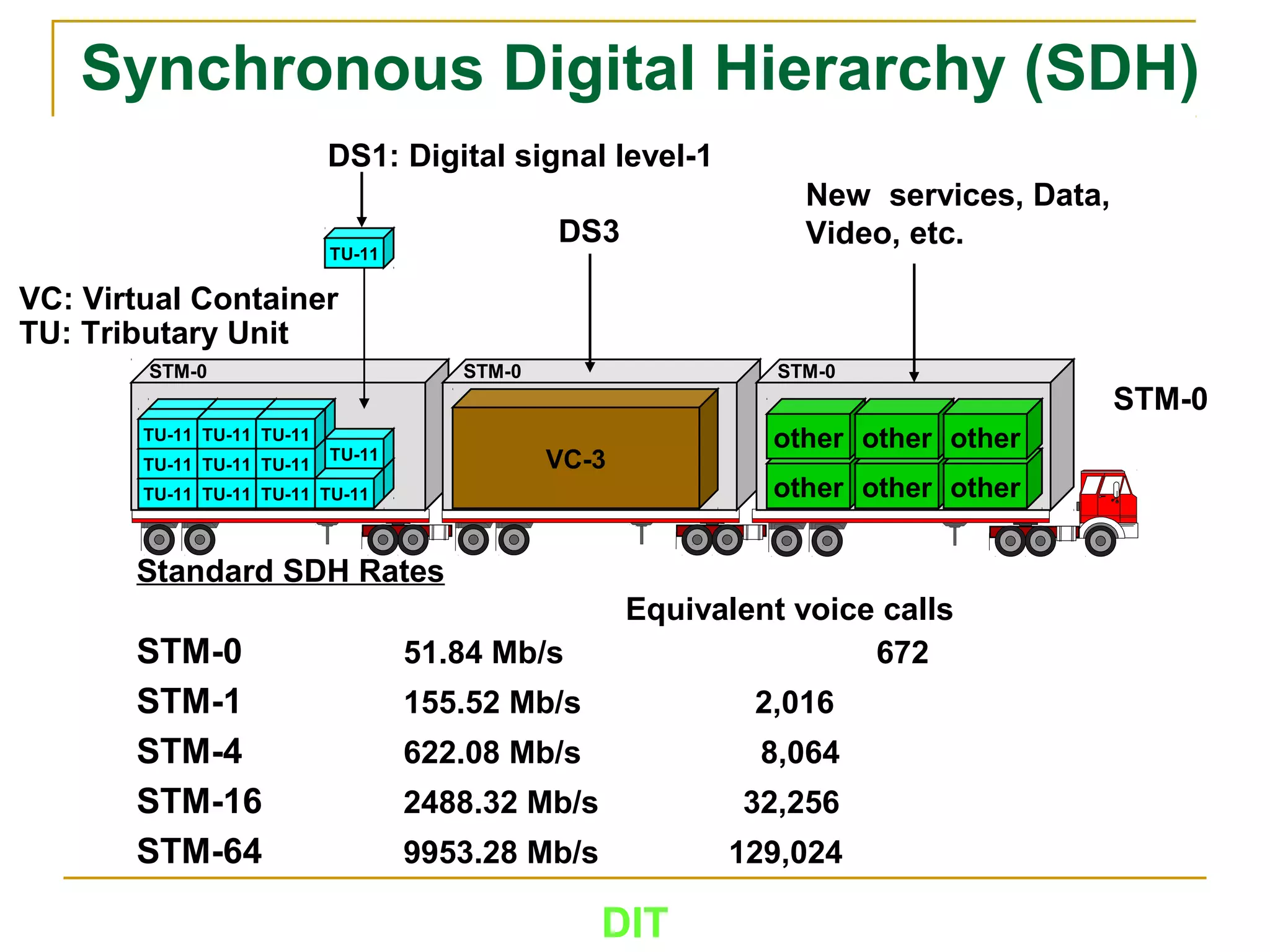
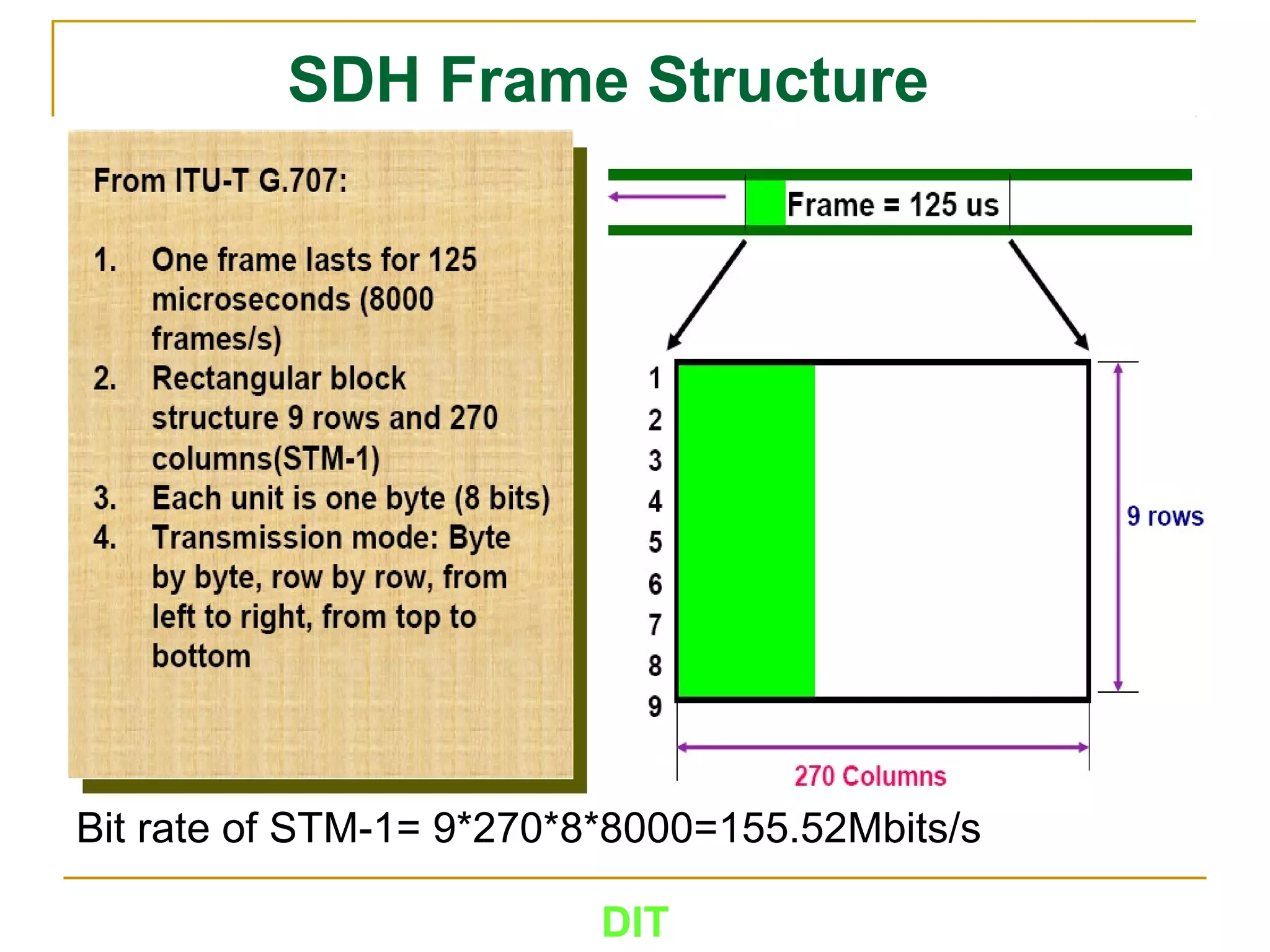
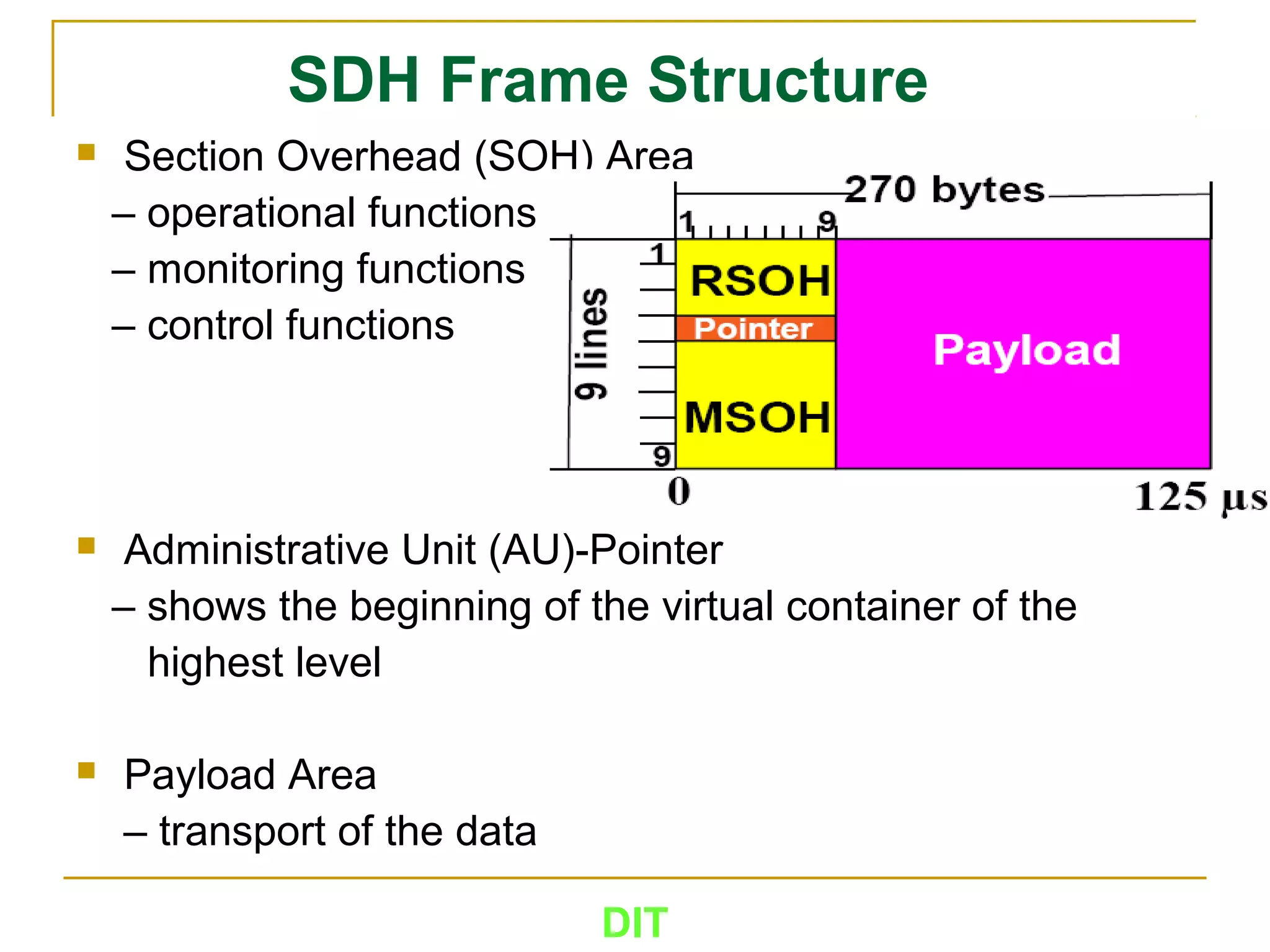
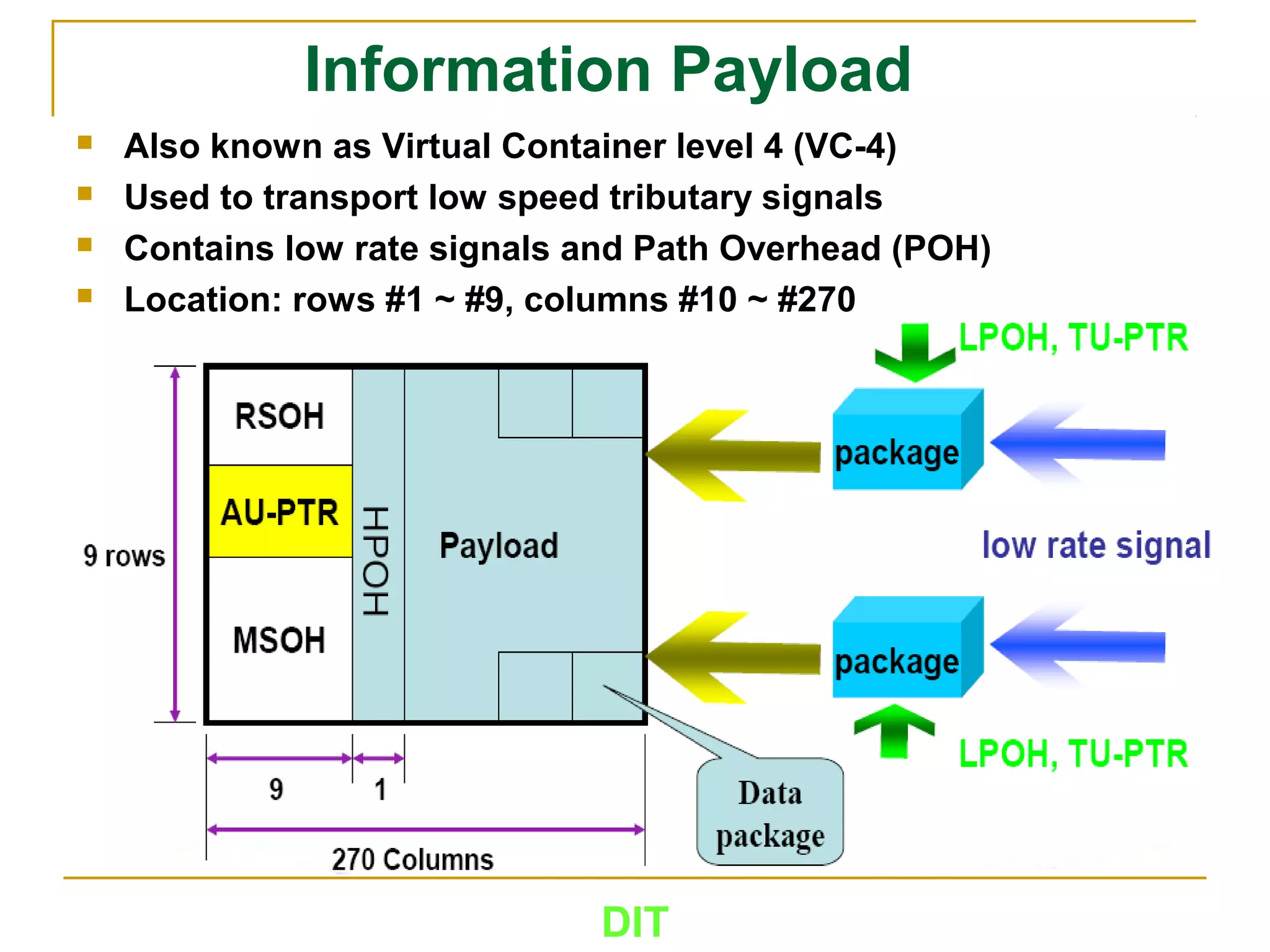
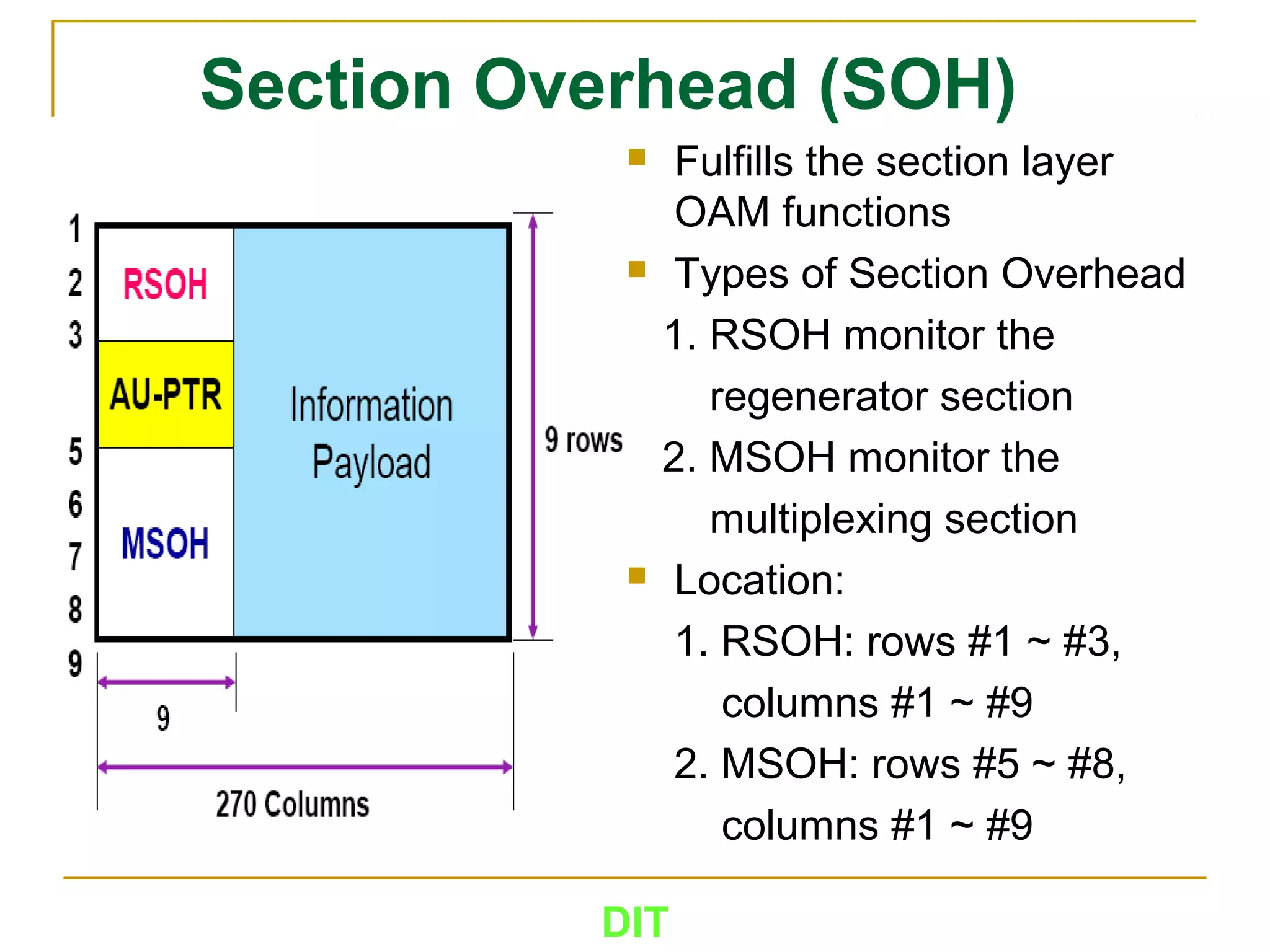
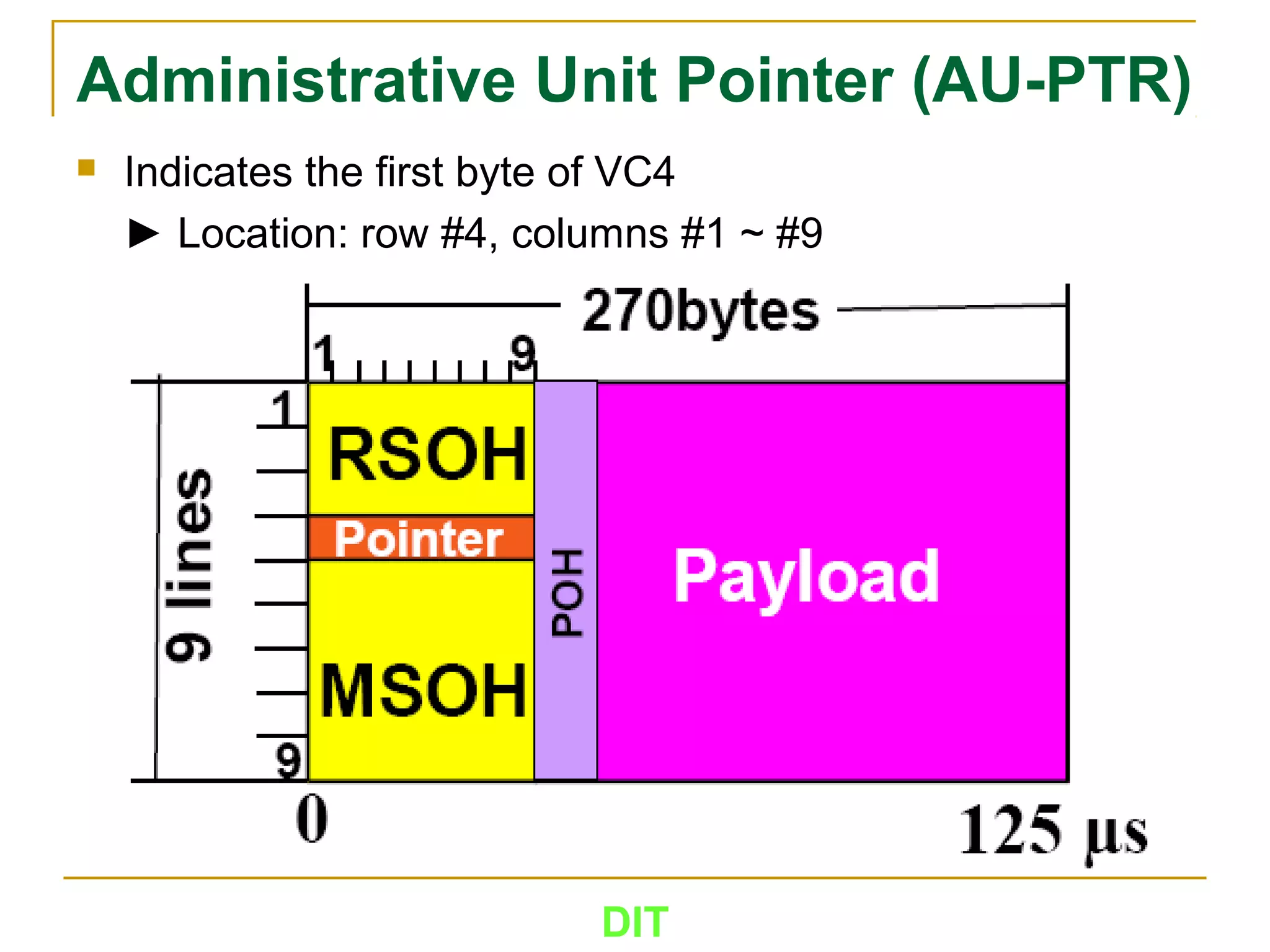
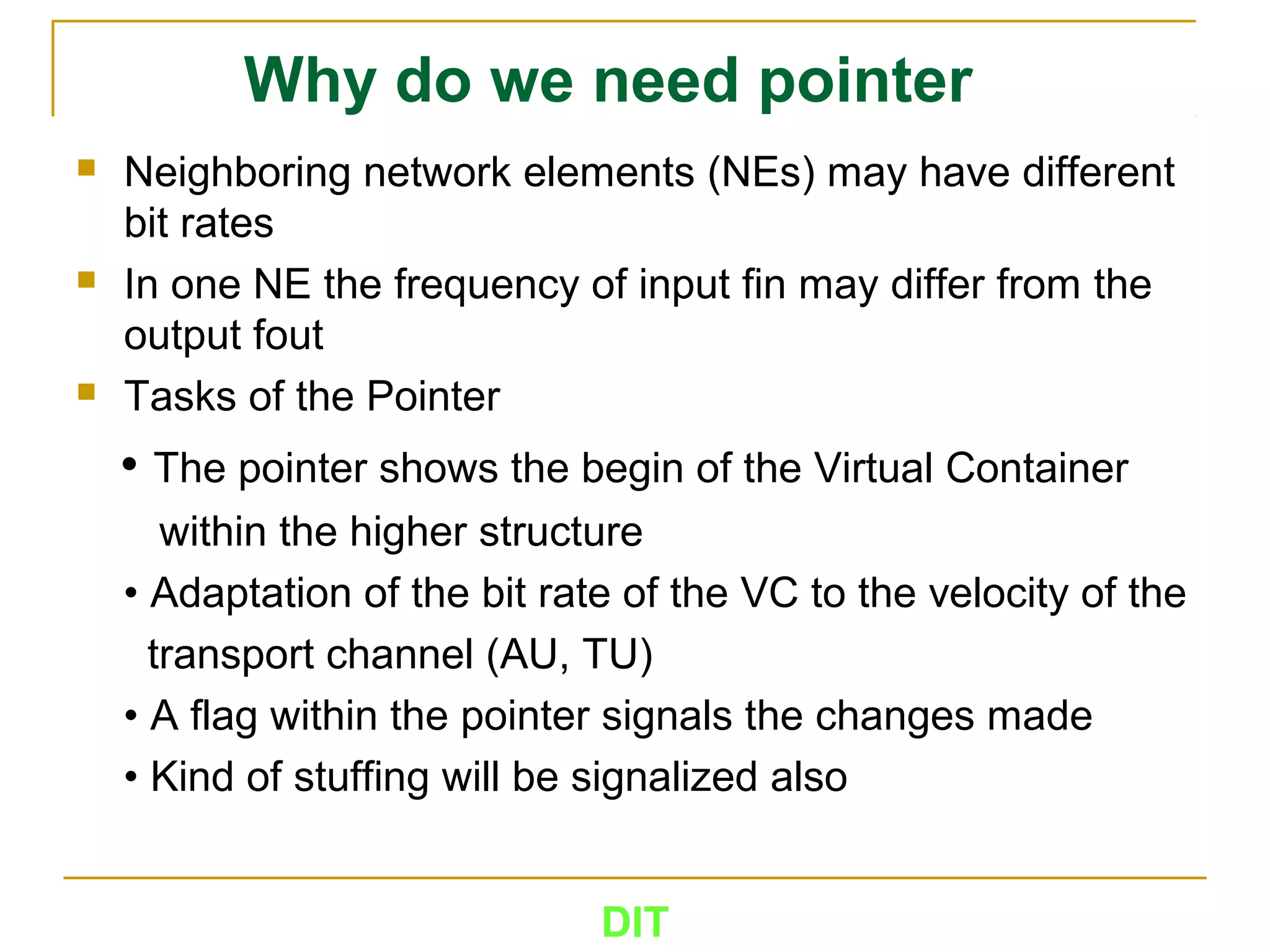
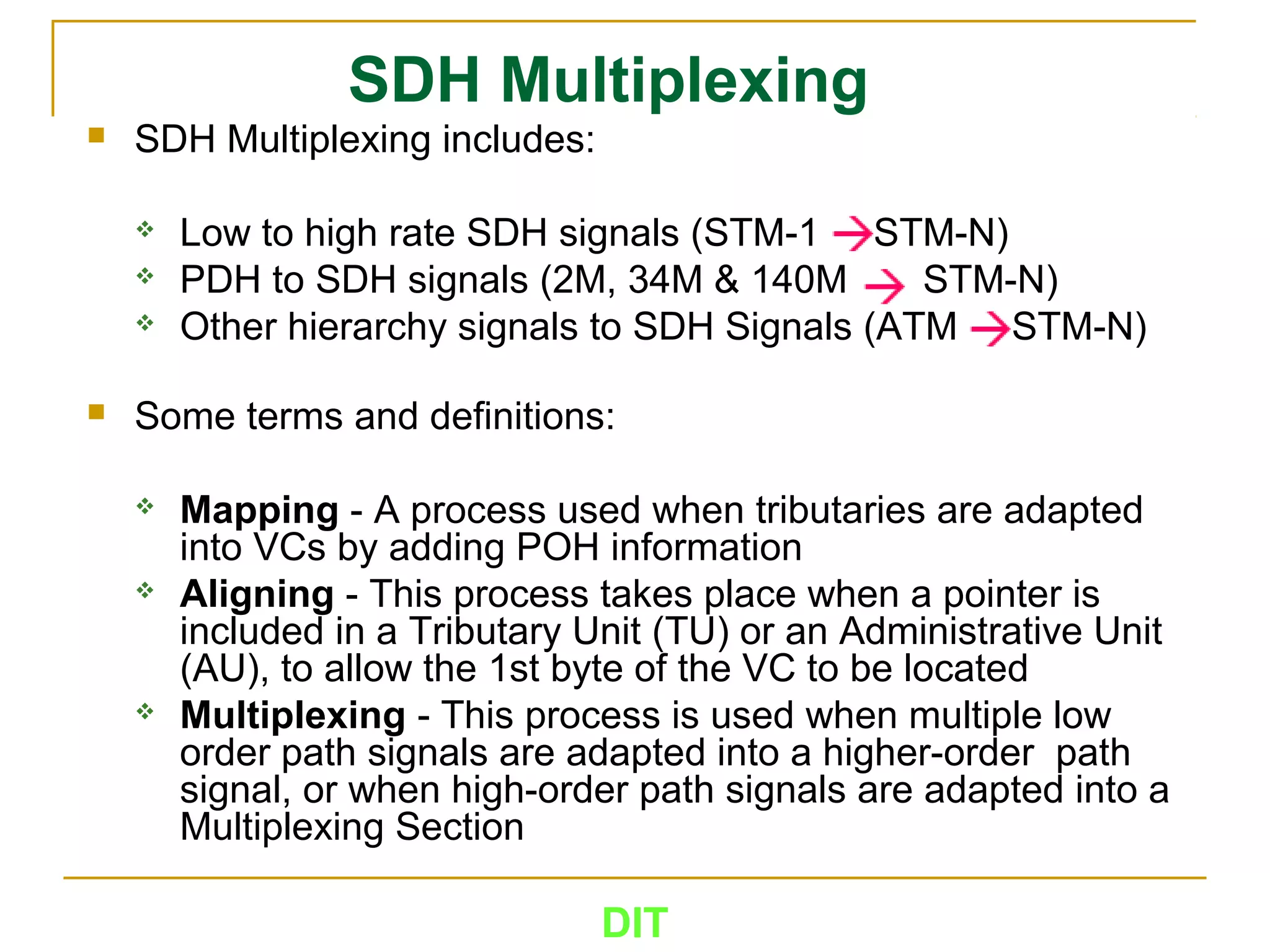
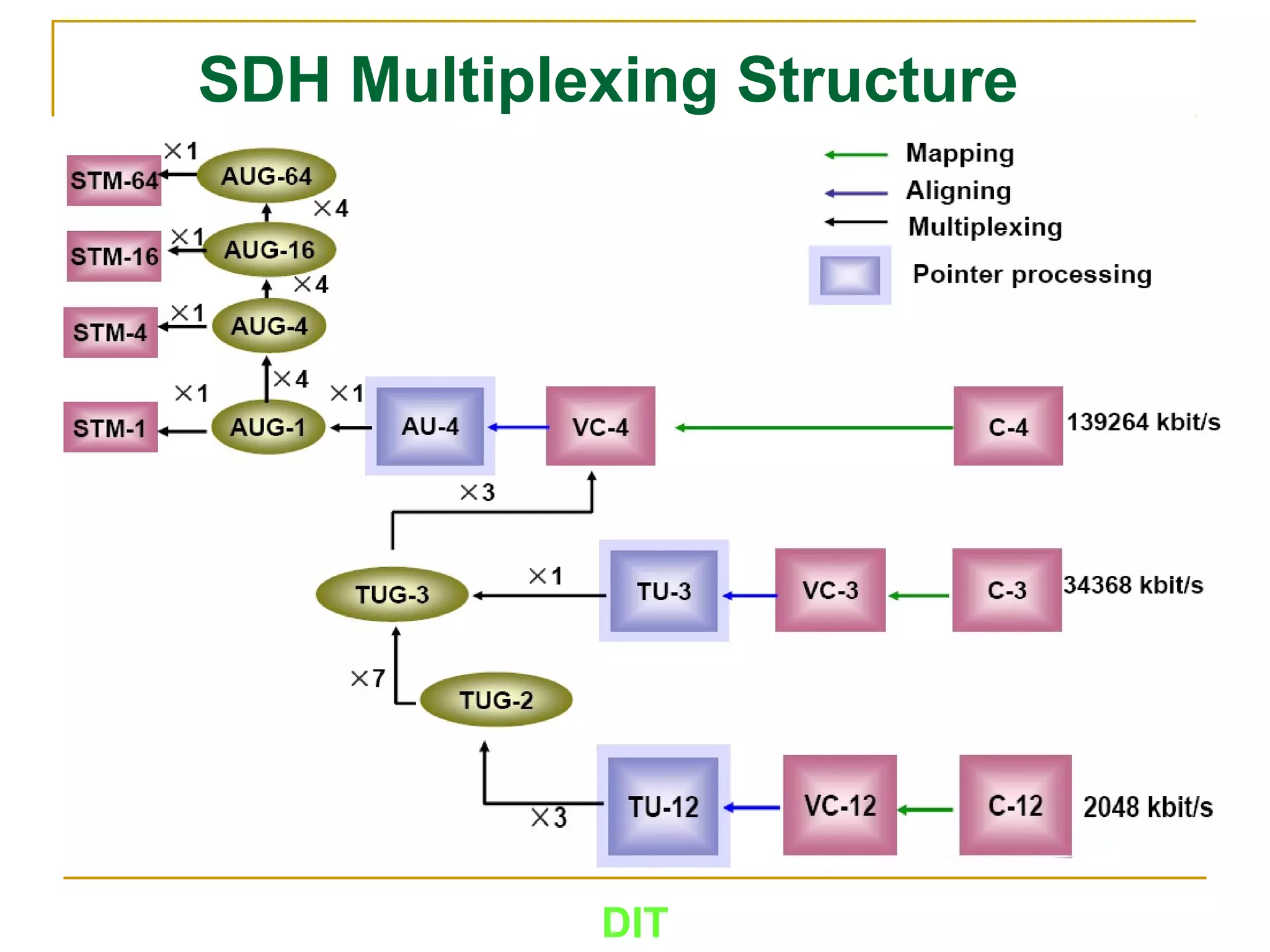
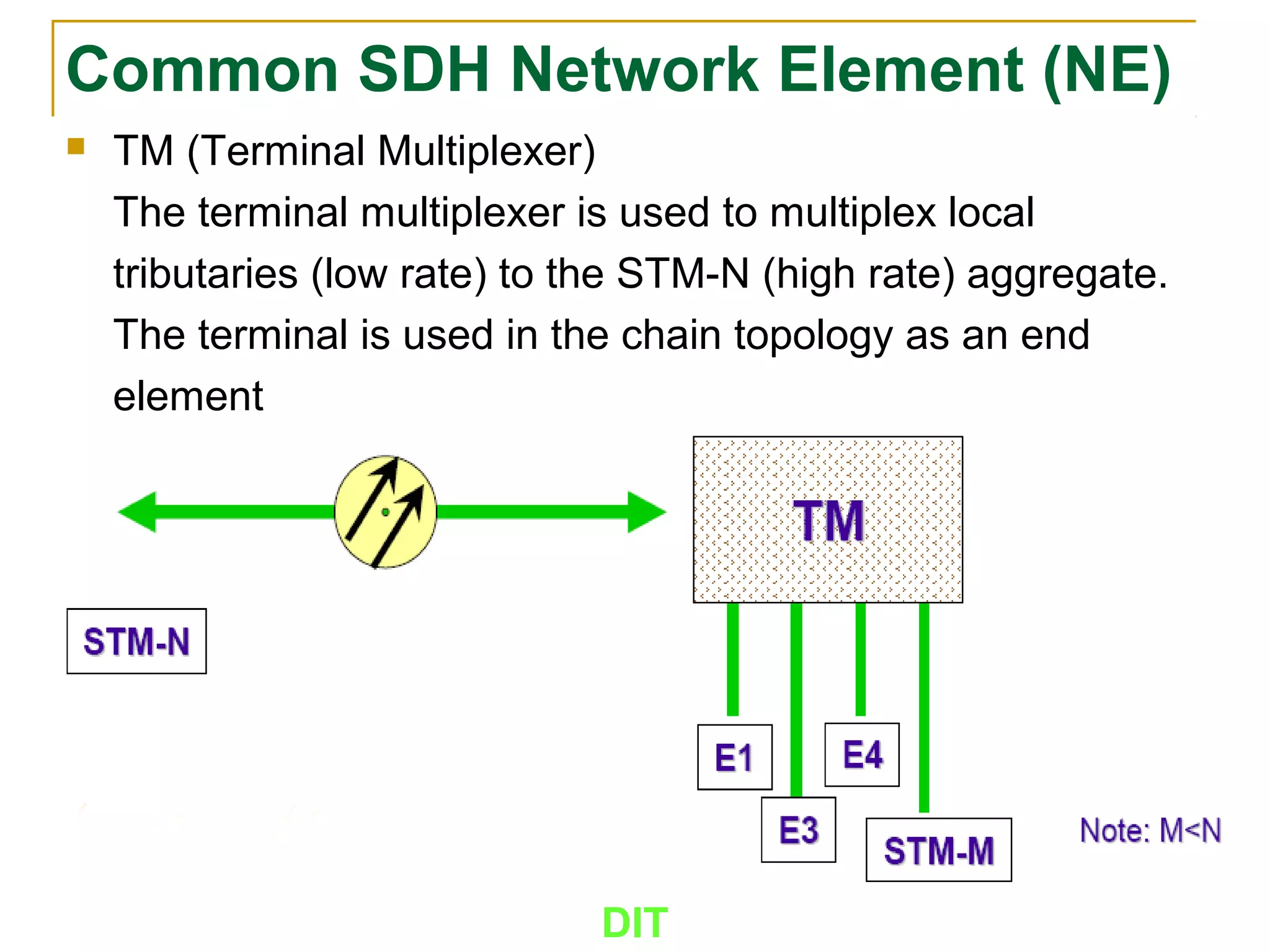
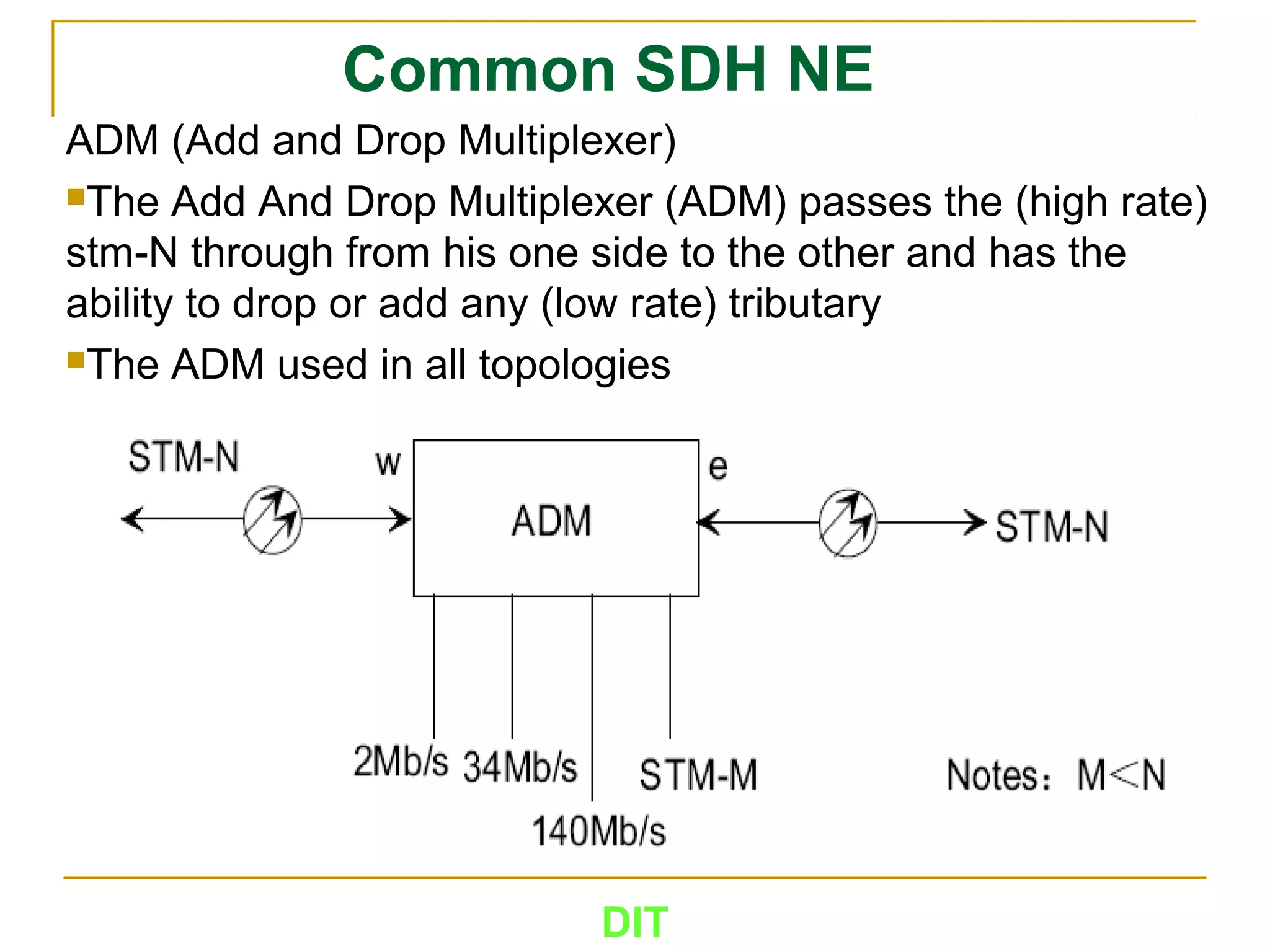
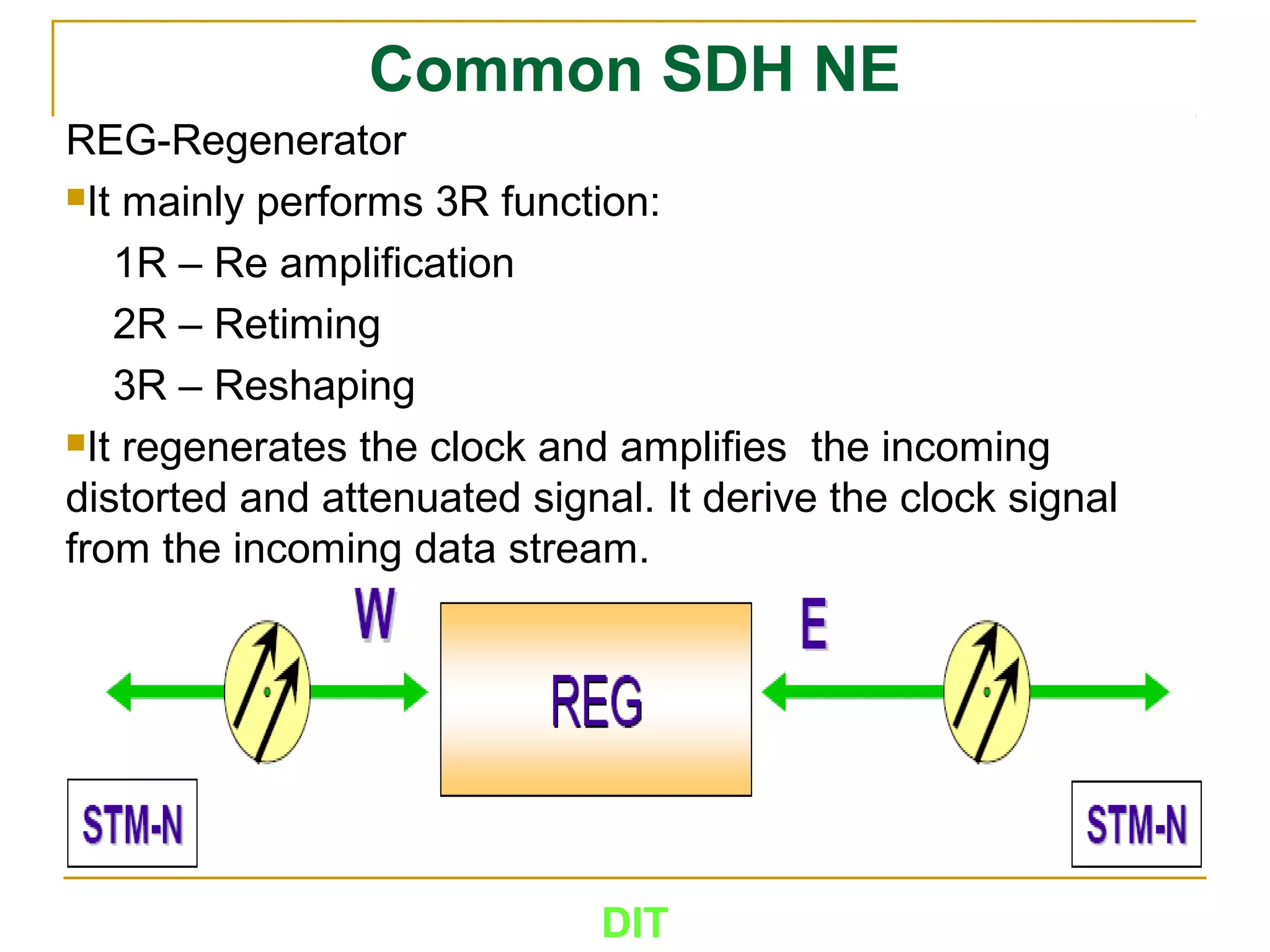
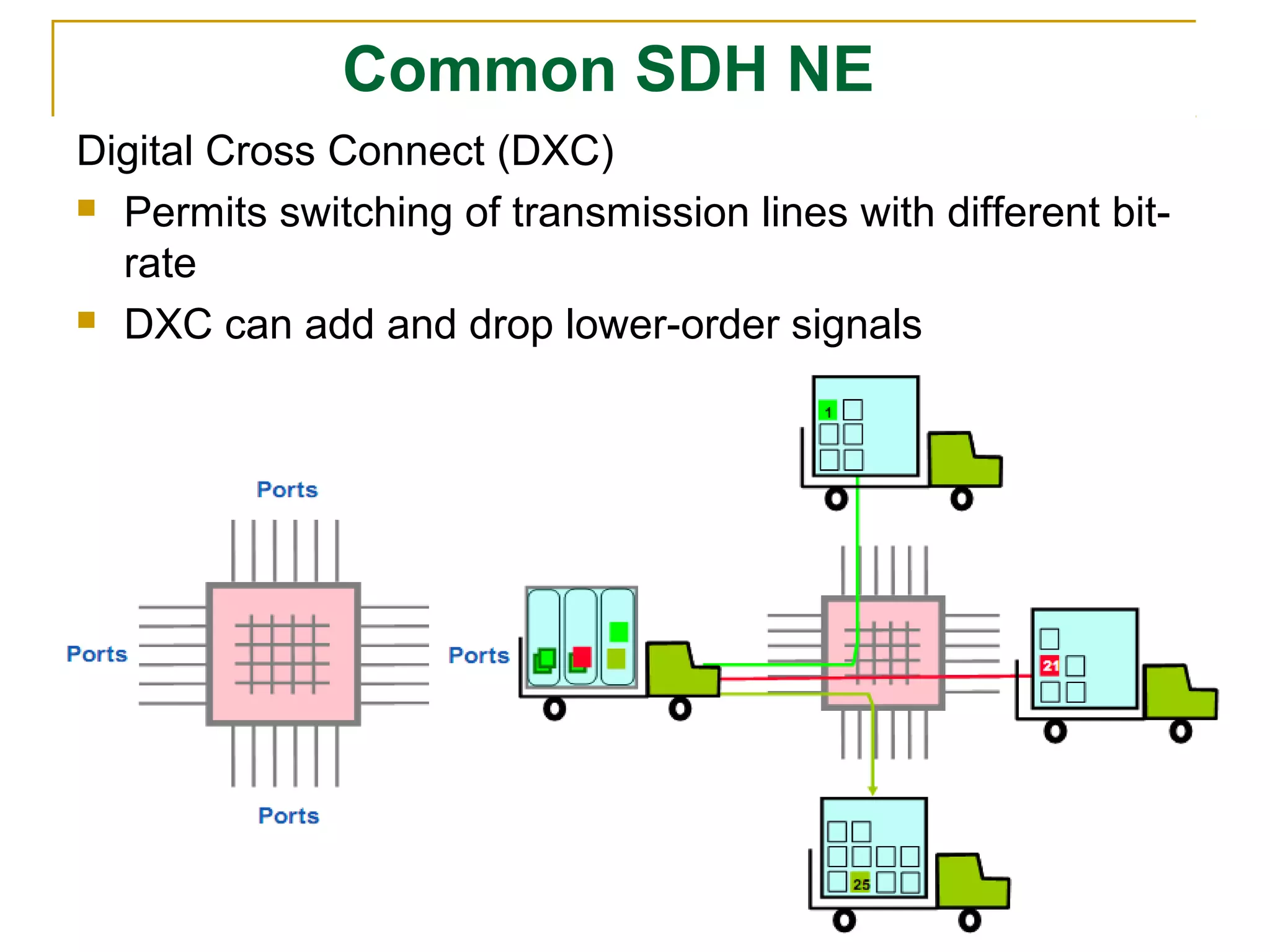
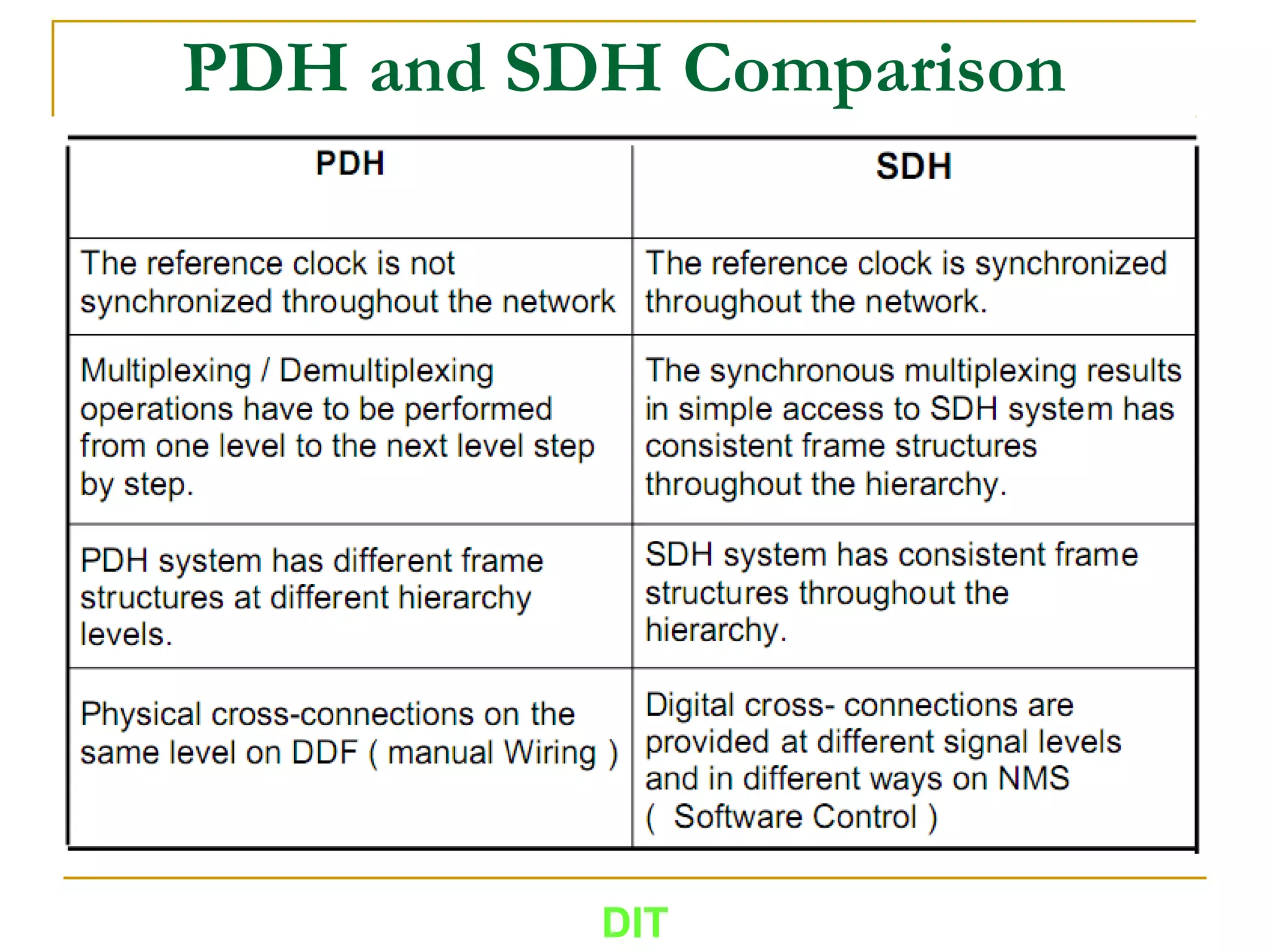
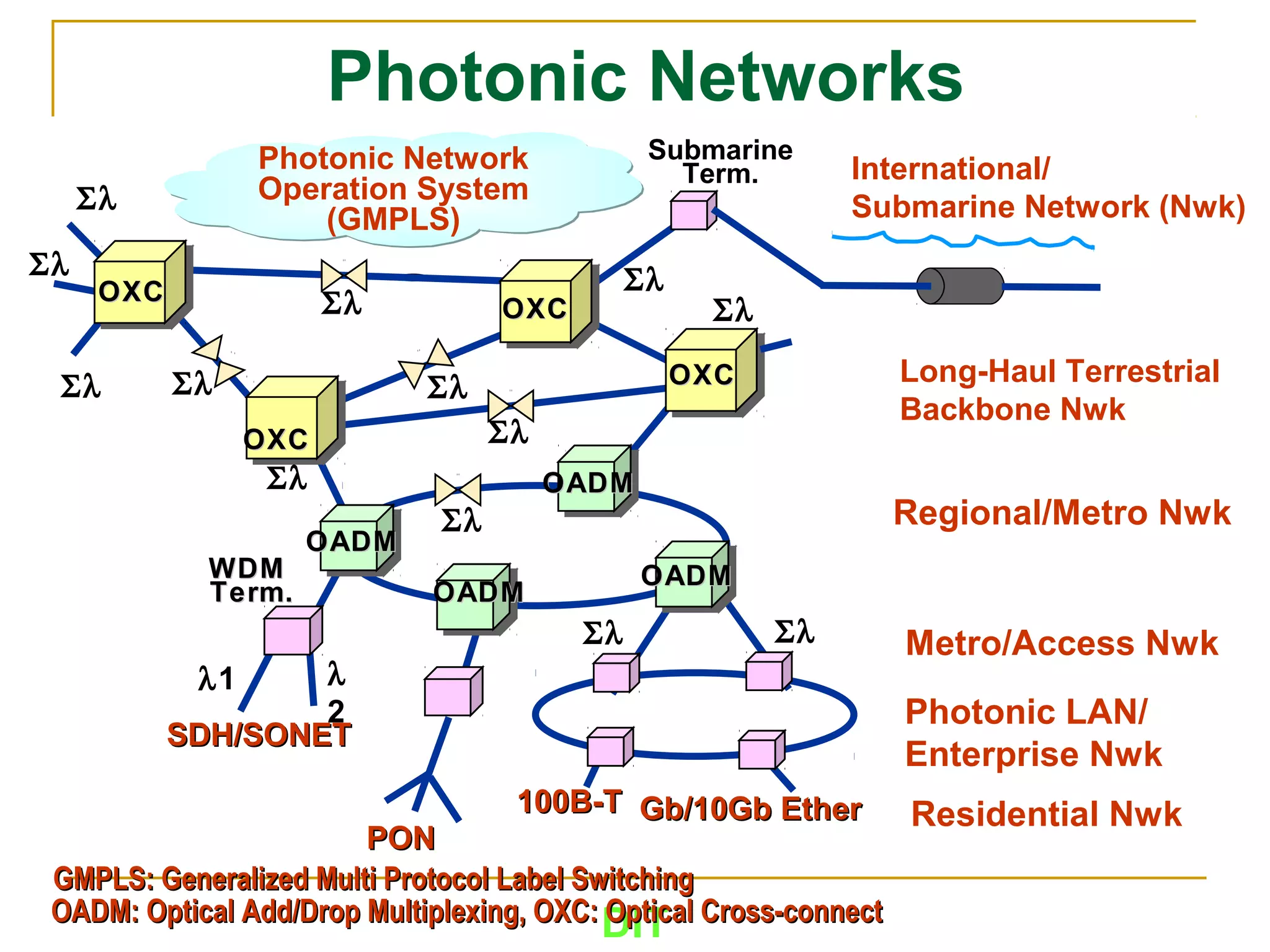
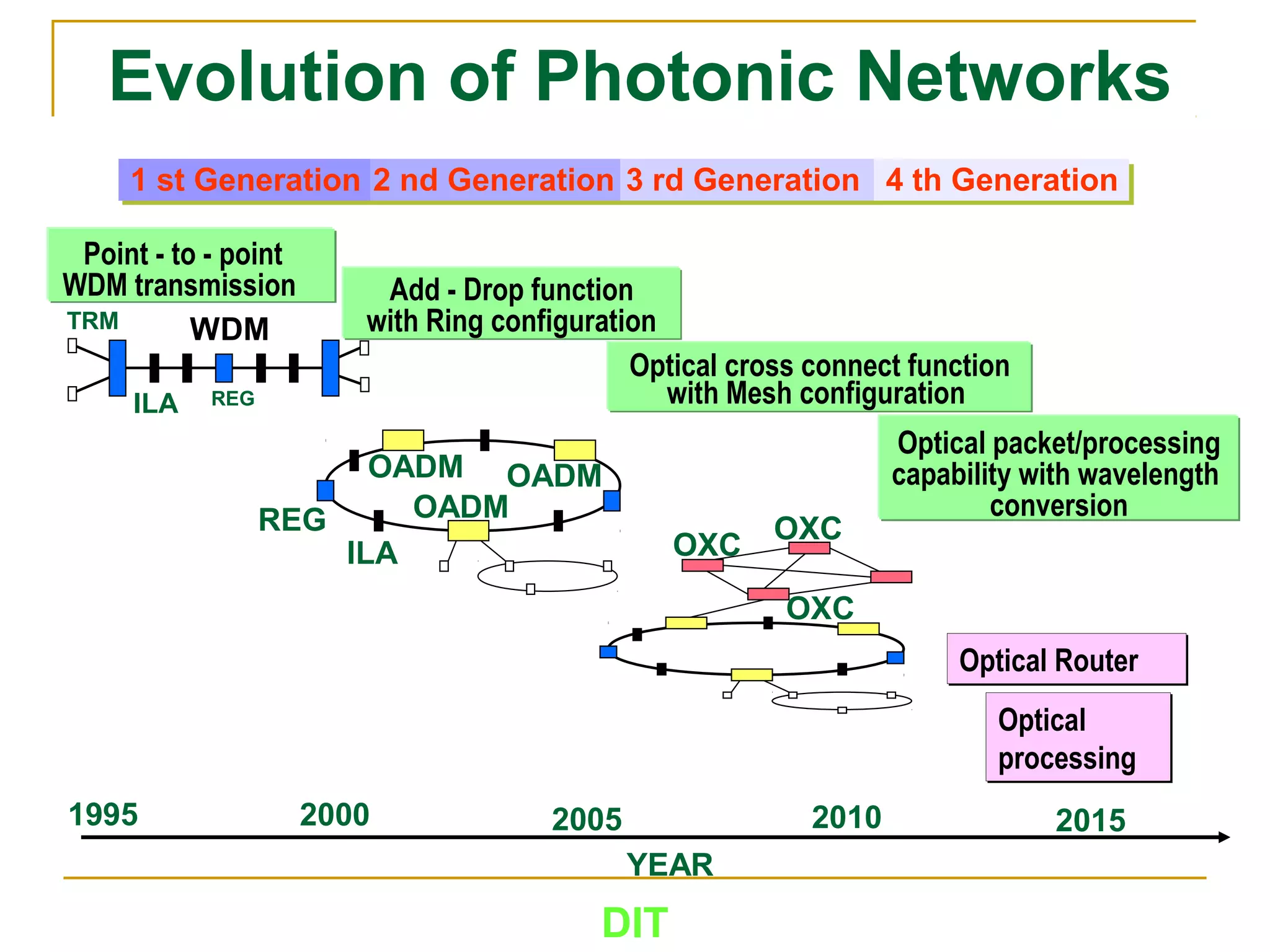
The document is a course outline for a Digital Networks course at Dar es Salaam Institute of Technology (DIT). The outline covers the following topics: SDH Network, IP Networks, MPLS Fundamentals, IMS, GSM Network, UMTS/HSPA Networks, LTE Network, and WLAN Network.