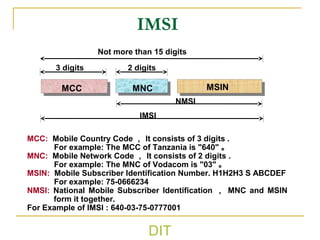
The document provides an overview of GSM system components and protocols. It discusses key aspects of GSM including that it uses TDMA and FDD, describes the development of GSM standards over time, and outlines the main network components like the BTS, BSC, MSC, HLR, VLR, and interfaces between them. It also discusses protocols like IMSI, TMSI, IMEI, LAI and their roles in the GSM network.