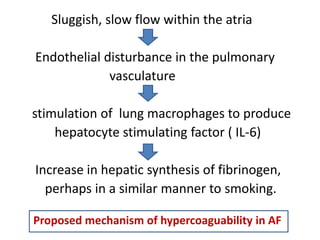
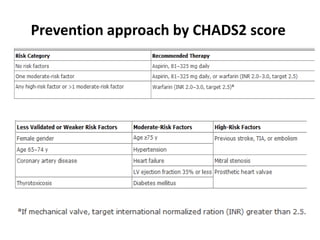
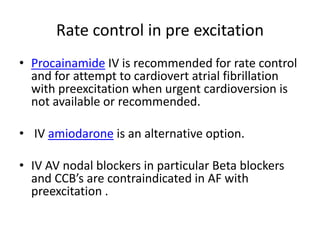
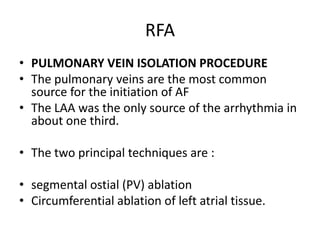
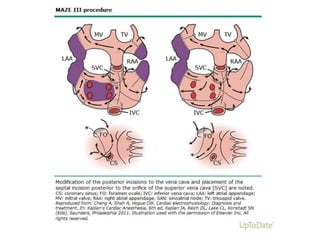
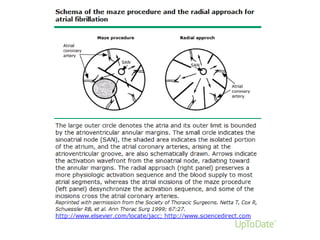
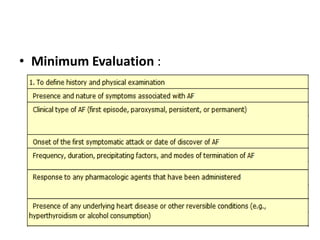
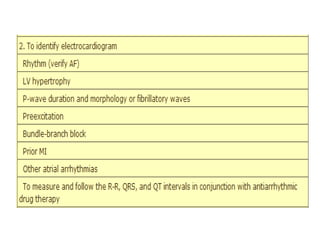
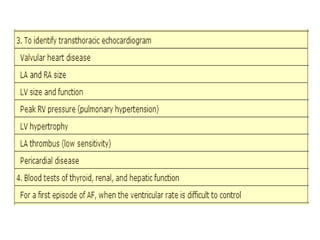
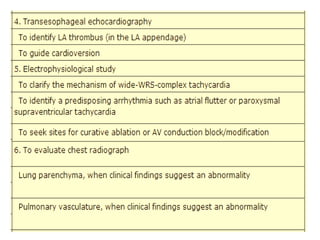
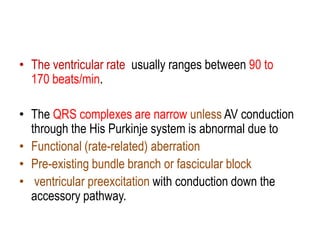
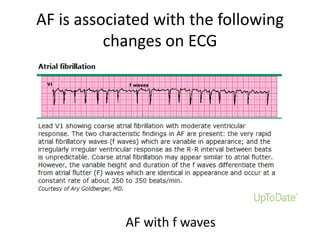
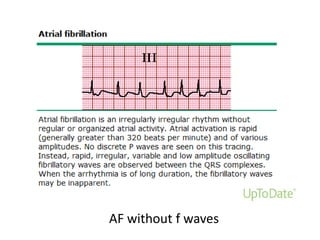
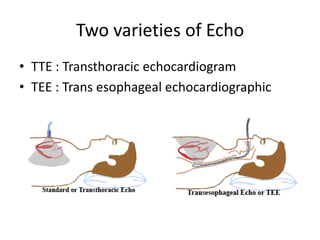
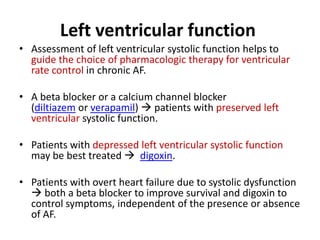
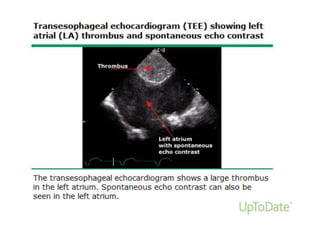
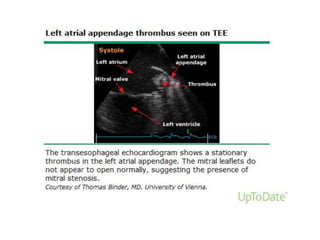
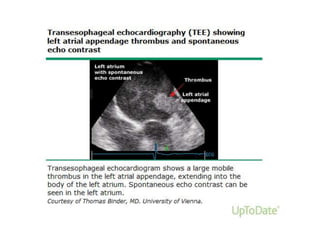
Transthoracic echocardiography is useful for evaluating left atrial size, left ventricular systolic function, and mitral valve morphology in patients with atrial fibrillation. Larger left atrial size is associated with worse prognosis and lower chance of maintaining sinus rhythm. Left ventricular dysfunction predicts increased risk of stroke. Transesophageal echocardiography can more accurately identify left atrial thrombi and help determine stroke risk in patients needing cardioversion.




















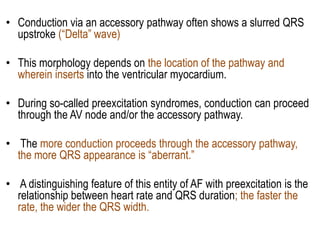




































![FACTORS PROMOTING
THROMBOEMBOLISM in AF
Almost 150 years ago, Virchow proposed that three
conditions should be present for development of
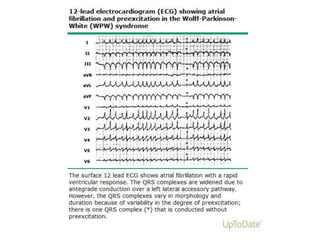
thrombosis [1]:
• Abnormalities in blood flow
• Abnormalities in the blood vessel wall
• Interaction with blood constituents
• Abnormalities in blood flow and vessels (the first two
components of Virchow's triad) can be related to the
presence of structural heart disease or extrinsic
interventions such as cardioversion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atrialfibrillationgood-140106101128-phpapp01/85/Atrial-fibrillation-good-89-320.jpg)


![In a substudy from the AFASAK trial
• 100 patients with chronic AF were randomized to
treatment with
fixed minidose warfarin 1.25 mg daily alone
combination with aspirin 300 mg/day and conventional
warfarin therapy with dose adjusted to maintain an
International Normalized Ratio (INR) between 2.0 and
3.0
Aspirin 300 mg daily.
• Patients treated with warfarin at any dose demonstrated
a significant rise in the INR with a corresponding
reduction in prothrombin fragment F1 + 2 [52].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atrialfibrillationgood-140106101128-phpapp01/85/Atrial-fibrillation-good-93-320.jpg)