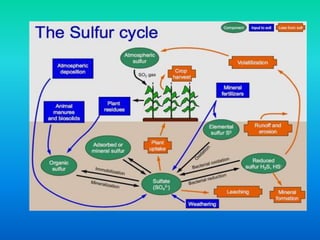
Dr. Vibha Khanna discusses the importance of sulfur as an essential macronutrient for plants. Sulfur plays critical roles as a structural component in amino acids, peptides, vitamins, and secondary products. It is also important for its catalytic functions and participation in redox reactions via thiol groups. Glutathione plays an important role in stress mitigation through antioxidant activity and detoxification of heavy metals and toxins. Sulfur assimilation in plants is part of the global sulfur cycle, with plants fixing inorganic sulfur for use and as a source for animal nutrition.


![WHY IS SULFUR IMPORTANT?
BECAUSE SULFUR NOT ONLY SERVES AS A
STRUCTURAL COMPONENT BUT ALSO PLAYS
CHARACTERISTIC FUNCTIONS IN CELLS
• Sulphur is found in
– amino acids (Cys and Met),
– oligopeptides (glutathione [GSH] and phytochelatins),
– vitamins and cofactors (biotin, thiamine, CoA, andS-
adenosyl-Met), and
– a variety of secondary products (glucosinolates in
Cruciferae and allyl Cys sulfoxides in Allium).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paperviii2ia-200404172938/85/Sulphur-the-macronutrient-4-320.jpg)