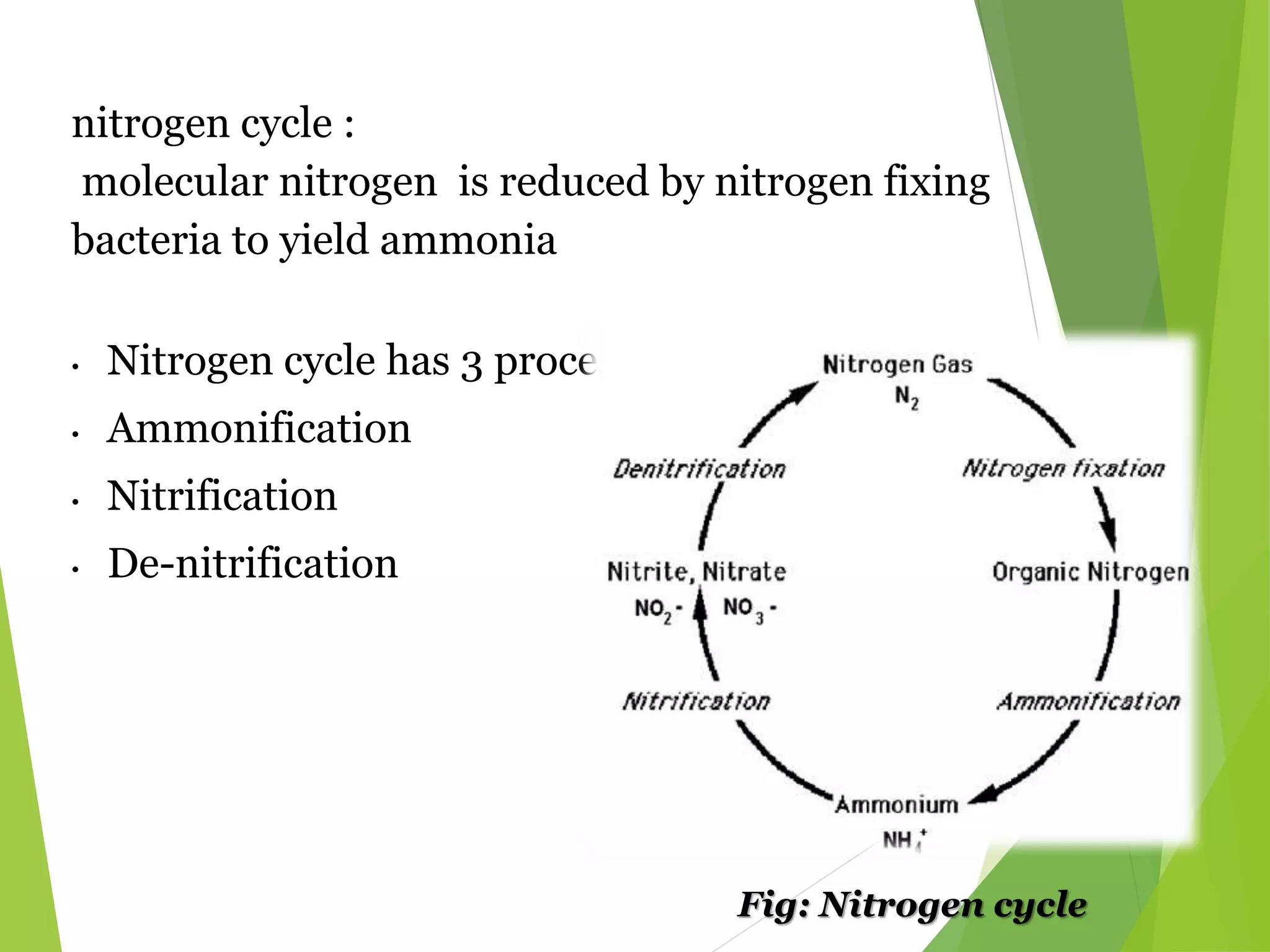
The document explains nitrogen fixation as the process of converting atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into a useful form for plants, primarily facilitated by nitrogen-fixing bacteria through the enzyme nitrogenase. It details both symbiotic and asymbiotic nitrogen fixation, with symbiotic bacteria, such as those from the genus Rhizobium, forming root nodules with legumes while free-living organisms also contribute to nitrogen fixation in various environments. Key mechanisms, requirements, and cycles involved in biological nitrogen fixation are discussed, emphasizing the importance of specific enzymes and environmental conditions.













![• Dinitrogenase reductase – is a dimer of 2
identical subunits
• It contains a single 4Fe – 4S redox center
bound between the subunits
• This can be oxidized and reduced by 1 electron
• Also it has 2 binding sites for ATP or ADP
• Dinitrogenase – is a tetramer with 2 copies of 2
different subunits (𝜶𝟐 − 𝜷𝟐 heterodimer)
• Contains both iron and molybdenum
• Its redox centres has 2 MO, 32 Fe and 30 S per
tetramer
• And it has 2 binding site for reductase
• About half of the iron and sulphur is present as
2 bridged pairs of 4Fe – 4S centres called as P
• P cluster – consists 2[ 4Fe – 4S] clusters linked
through additional sulphide ion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nitrogenfixationreal-200610150715/75/Nitrogen-fixation-in-plants-15-2048.jpg)


