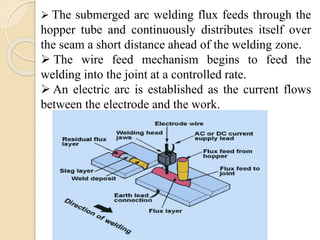
Submerged arc welding (SAW) is a process where the arc and molten pool are concealed under a layer of granular flux. An electric current is passed between the continuously fed electrode wire and workpiece, heating them to fuse the metals. Key advantages include high quality welds, high deposition rates, and the ability to weld thick plates. Applications include boilers, pressure vessels, ships, and structural fabrication.