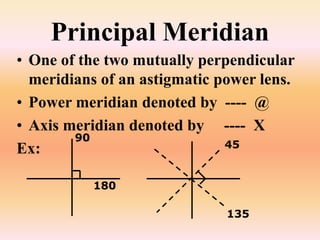
The document describes the process of transposing a lens prescription from plus cylinder notation to minus cylinder notation, detailing the importance and steps involved. It outlines different types of transposition, including simple and toric transpositions, with examples to illustrate algebraic manipulation of sphere and cylinder powers. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of maintaining axes alignment and provides procedures for transforming various lens types.