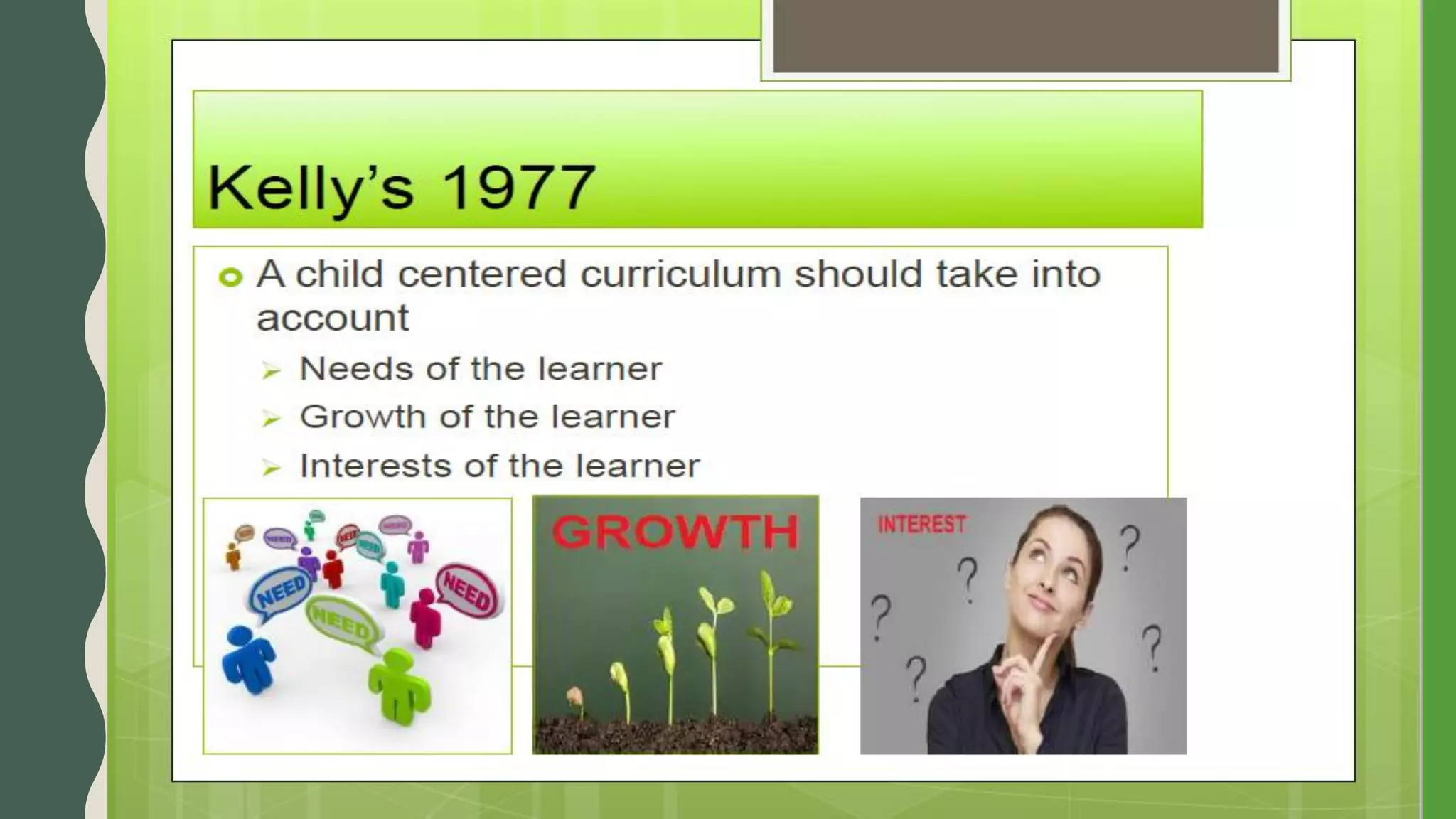
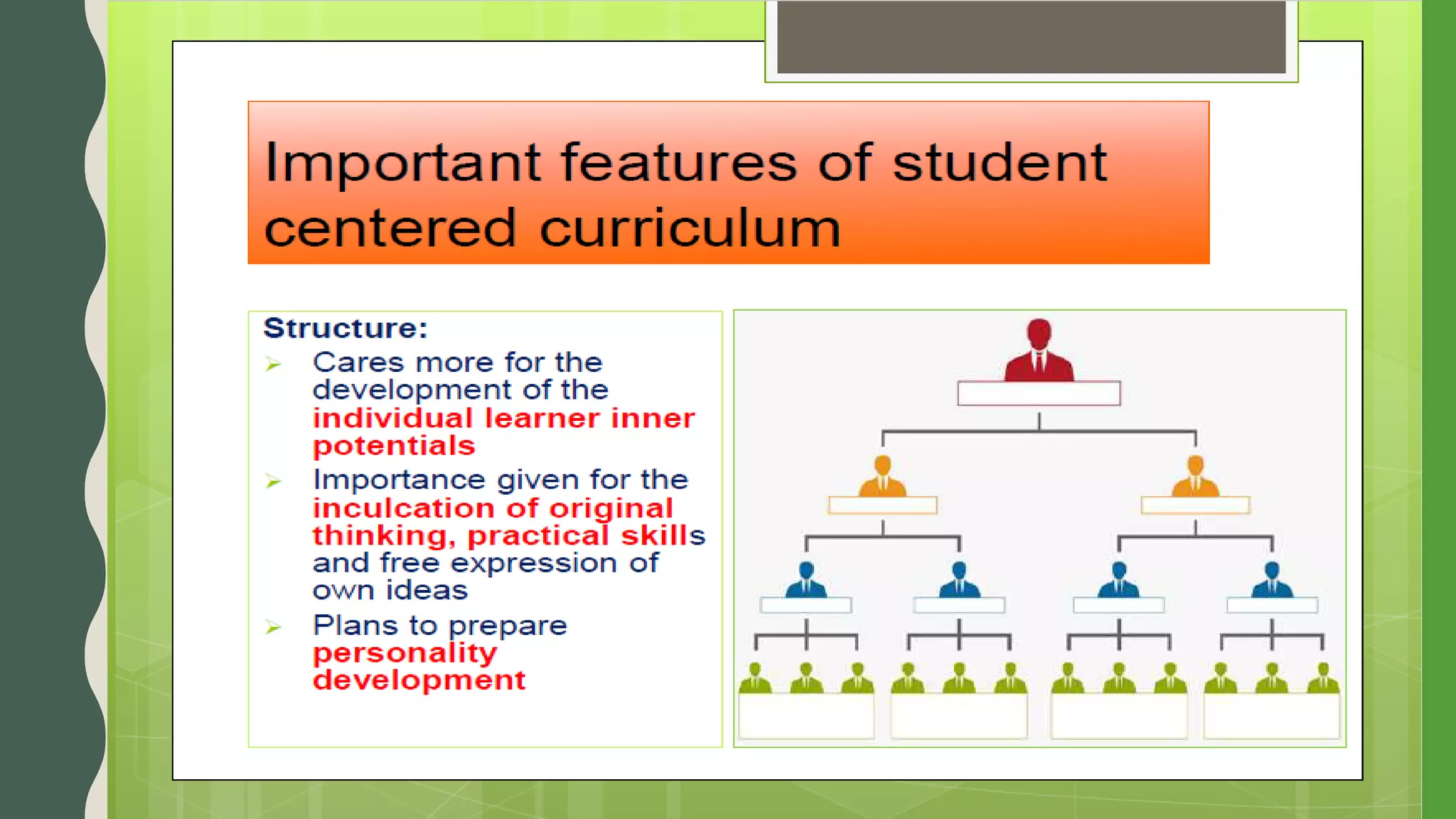
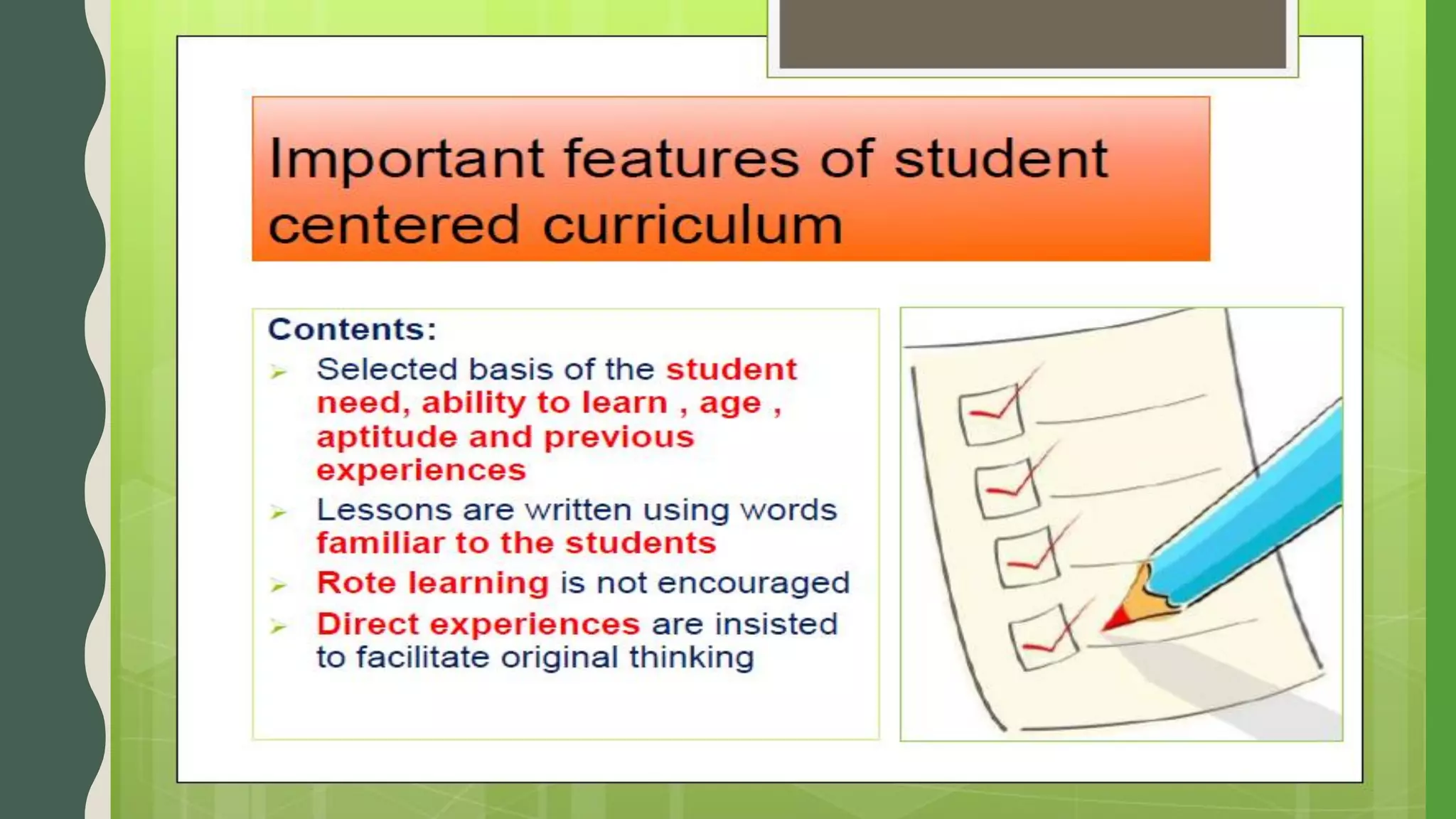
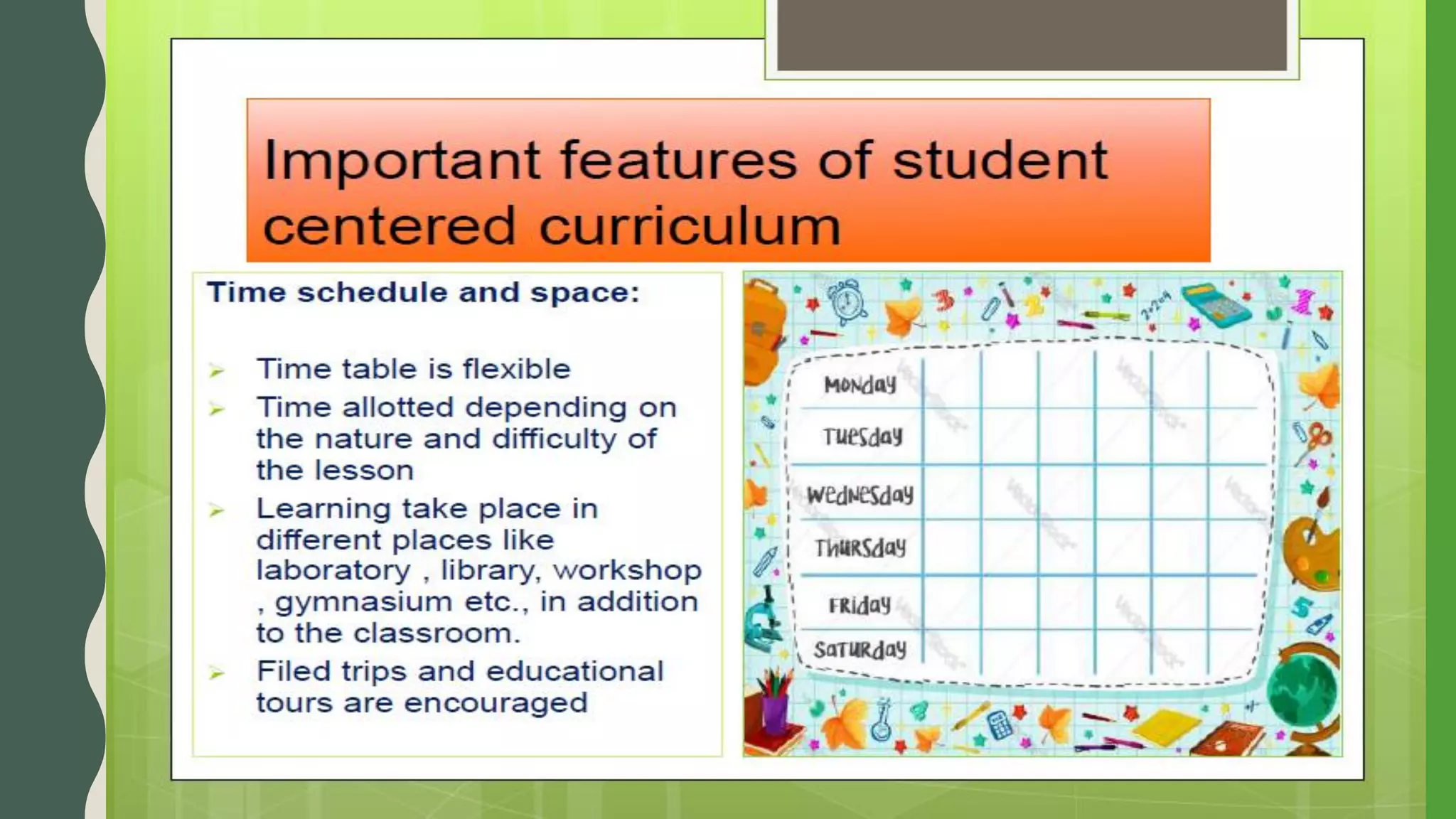
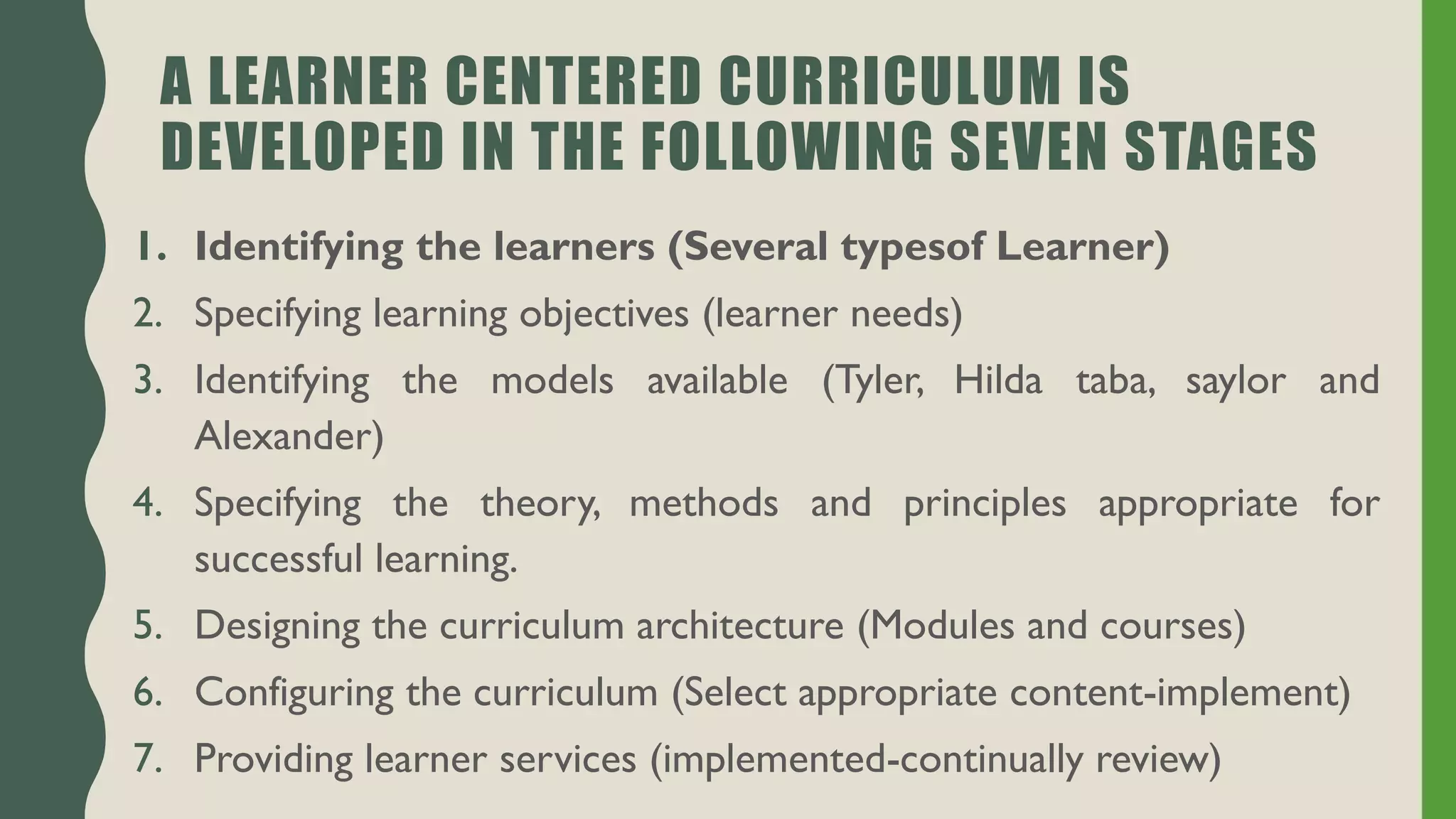
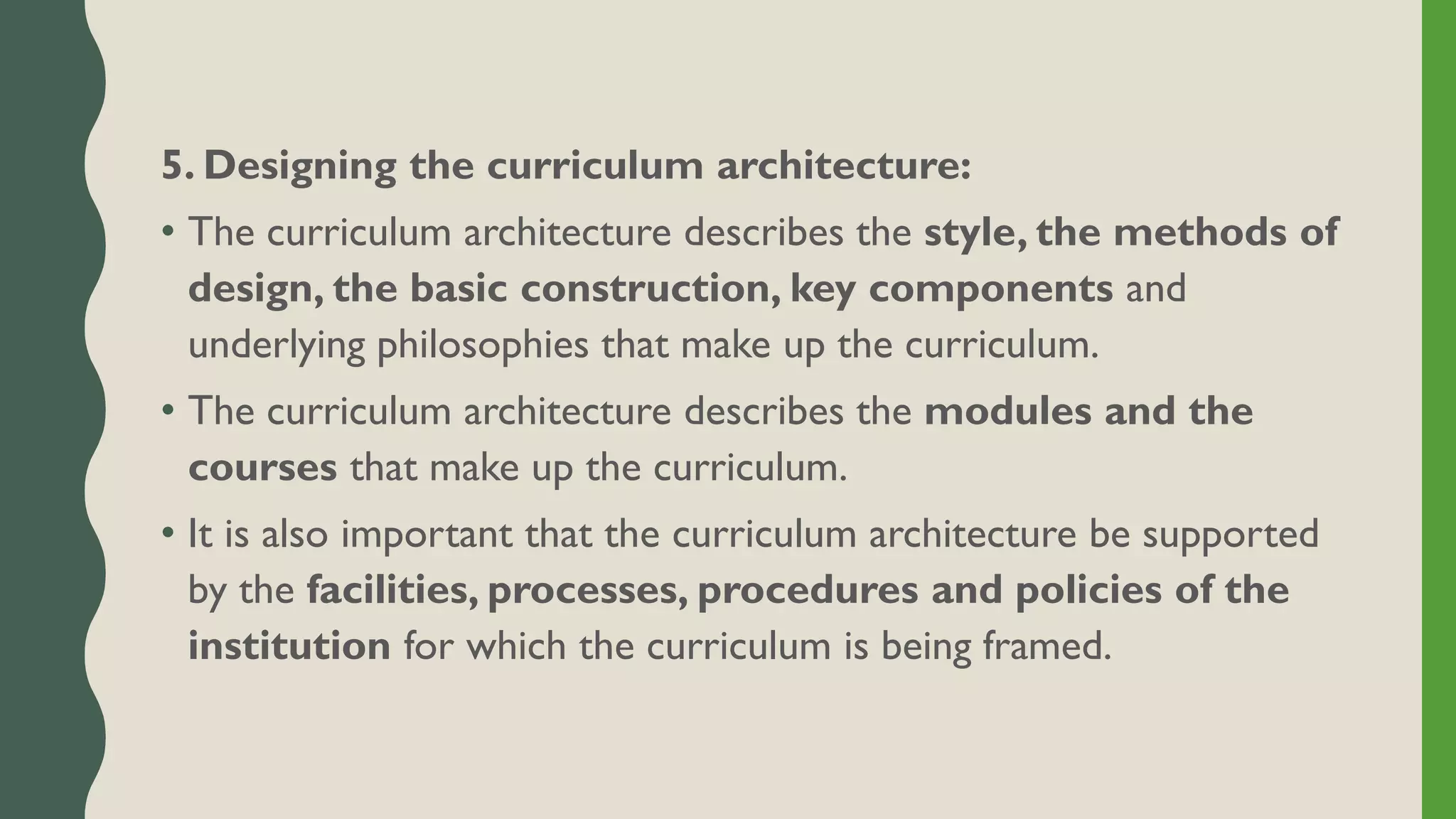
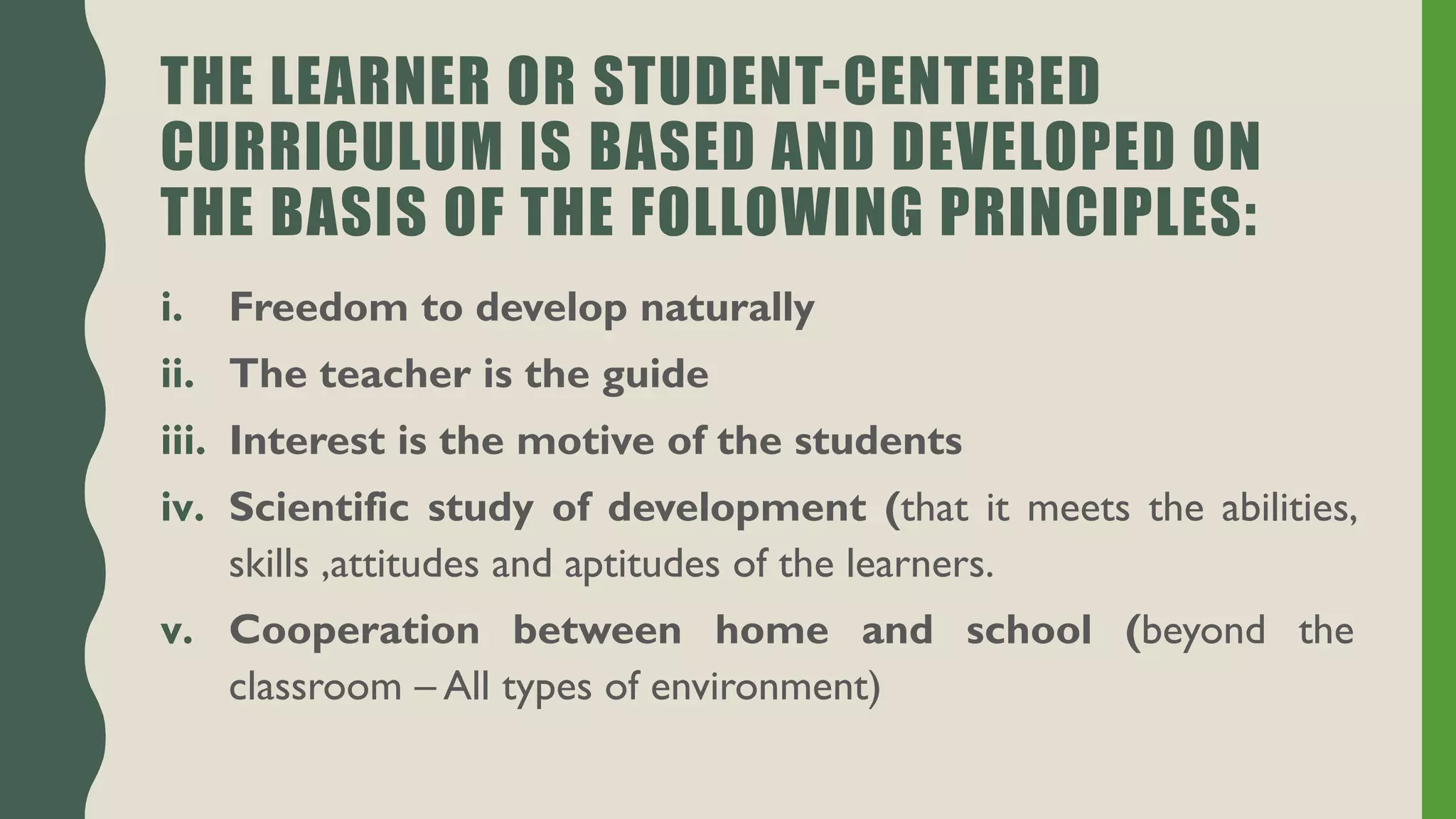
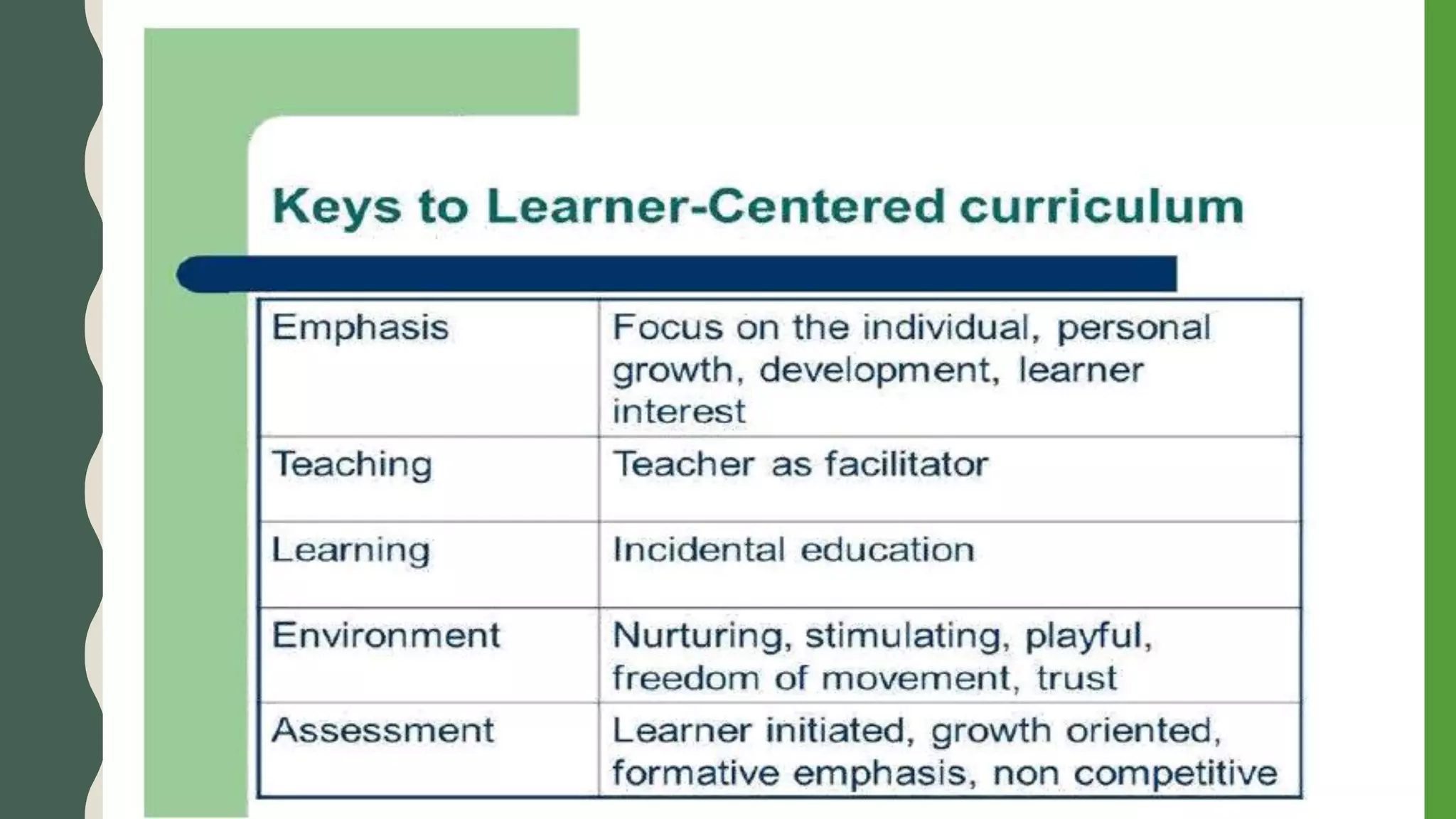
The document discusses student-centered curriculum. It states that in this type of curriculum, students are given more importance compared to subjects or teachers. The curriculum is framed based on the needs, skills, abilities and aptitudes of learners. The goal is to ensure overall development of students. Students influence content, activities, materials and pace of learning. The teacher provides opportunities for independent learning and coaches students in skills. A learner-centered curriculum is developed in 7 stages: identifying learners, learning objectives, models, theories, curriculum architecture, content selection, and learner services. The curriculum focuses on freedom to develop naturally, teacher as guide, learner interest, development study, and home-school cooperation.