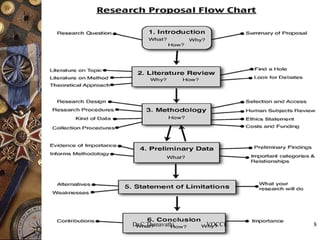
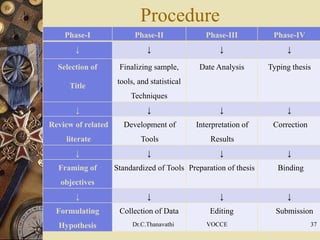
This document provides guidance on writing a research proposal. It begins by defining what a research proposal is and its purpose. It then discusses the key components of a research proposal such as the problem statement, objectives, hypotheses, research methodology, time schedule and expected outcomes. Examples of different types of research proposals and their formats are also provided. Overall, the document serves as a comprehensive guide for developing an effective research proposal.