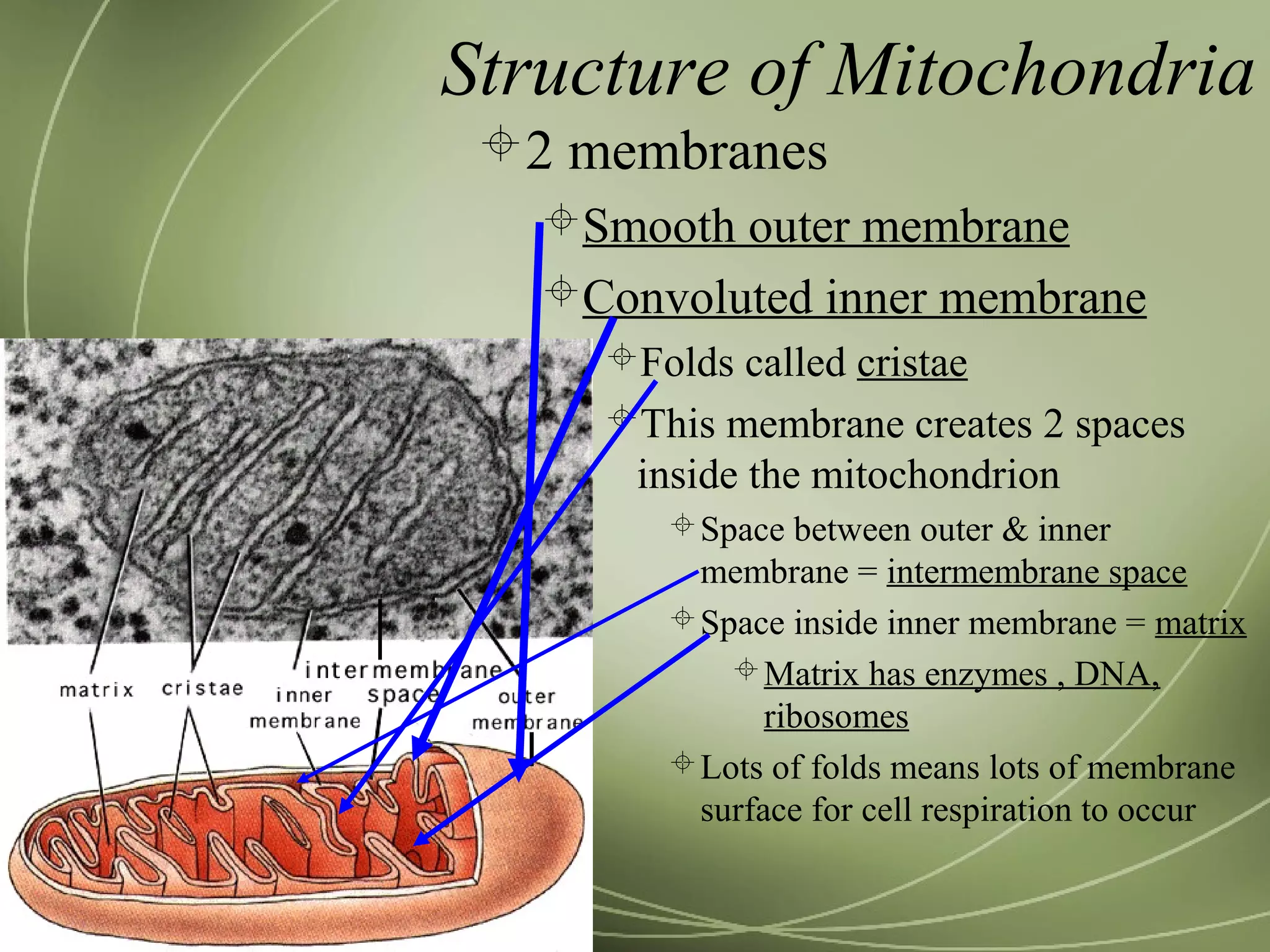
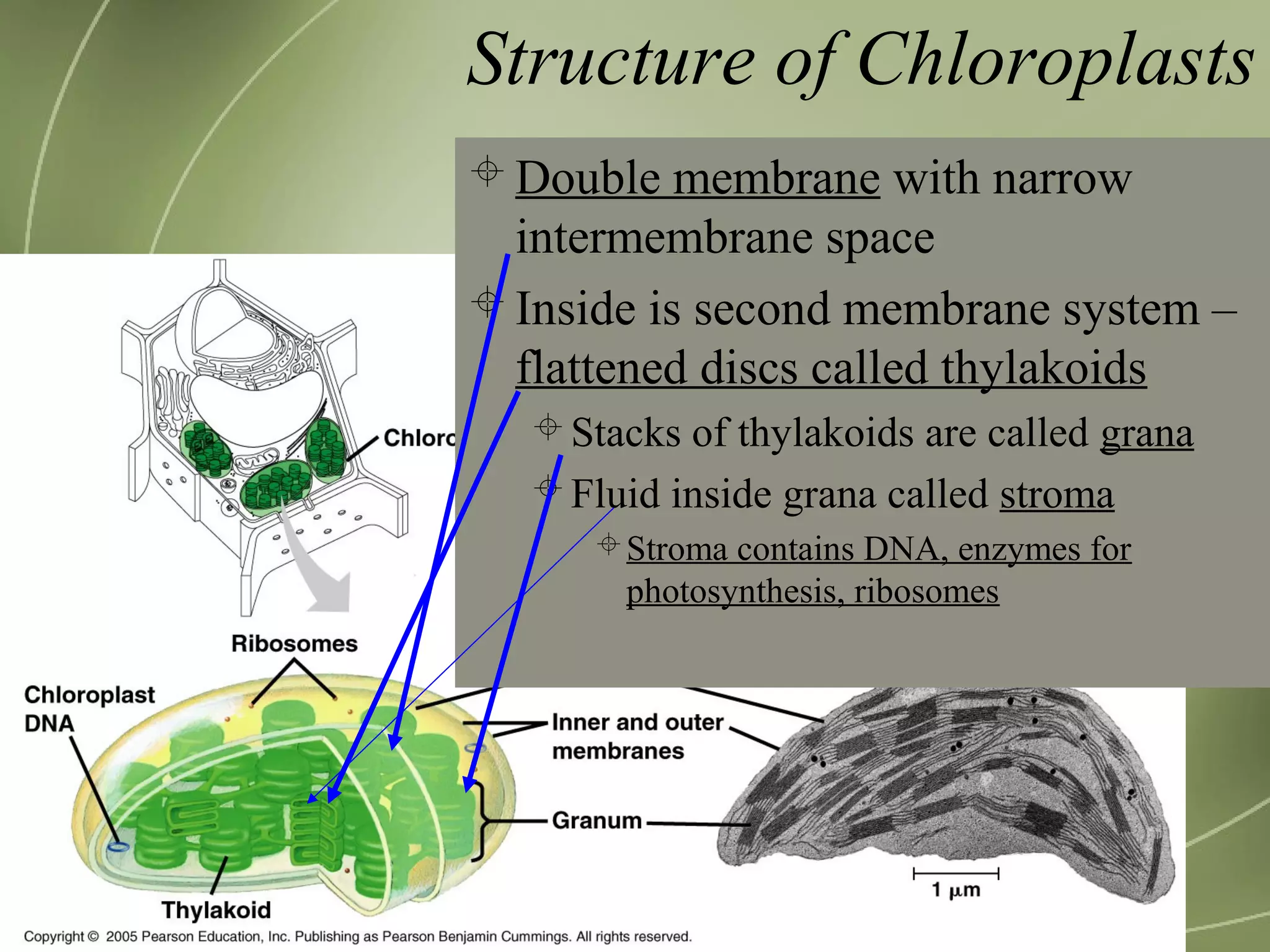
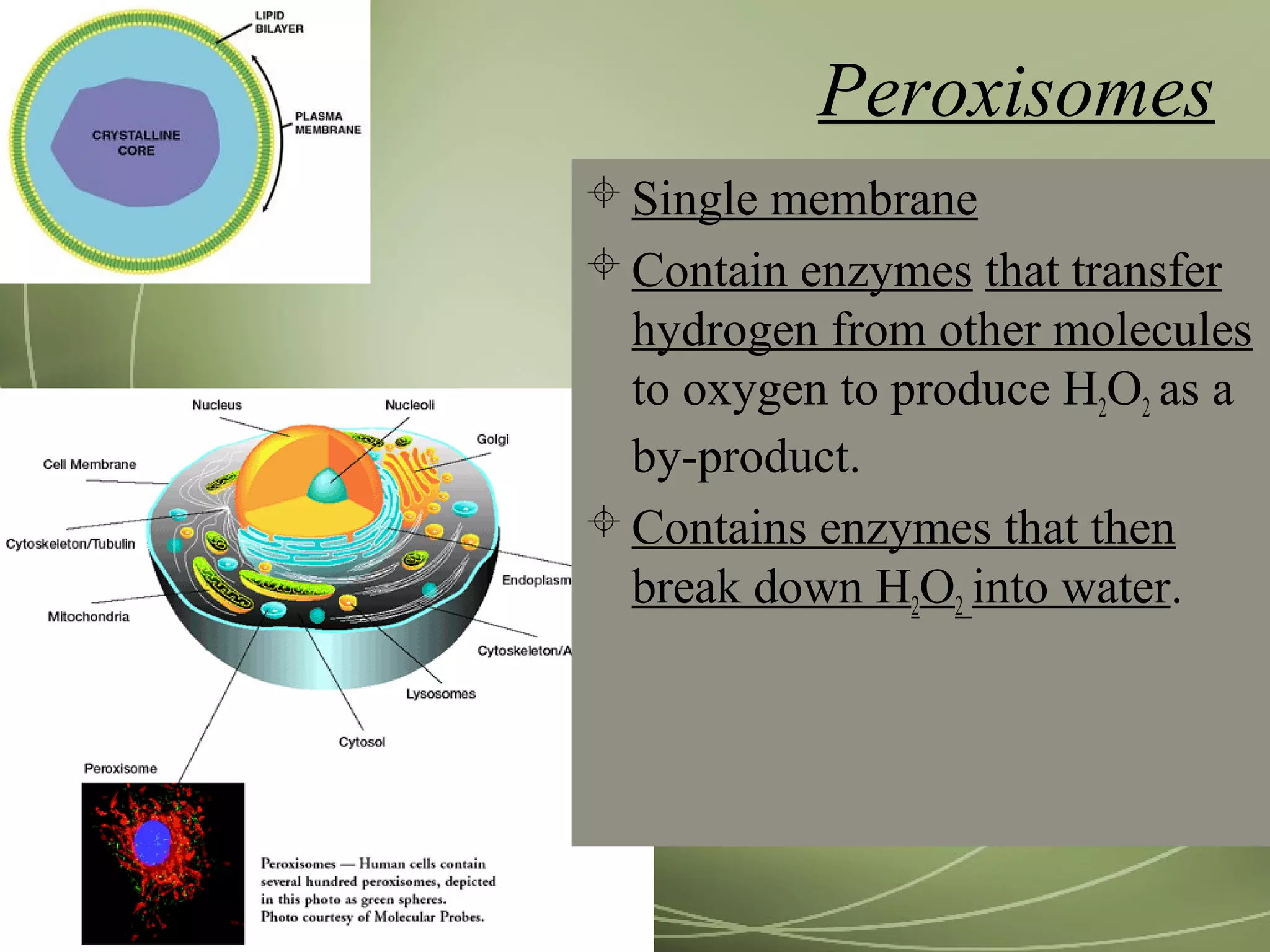
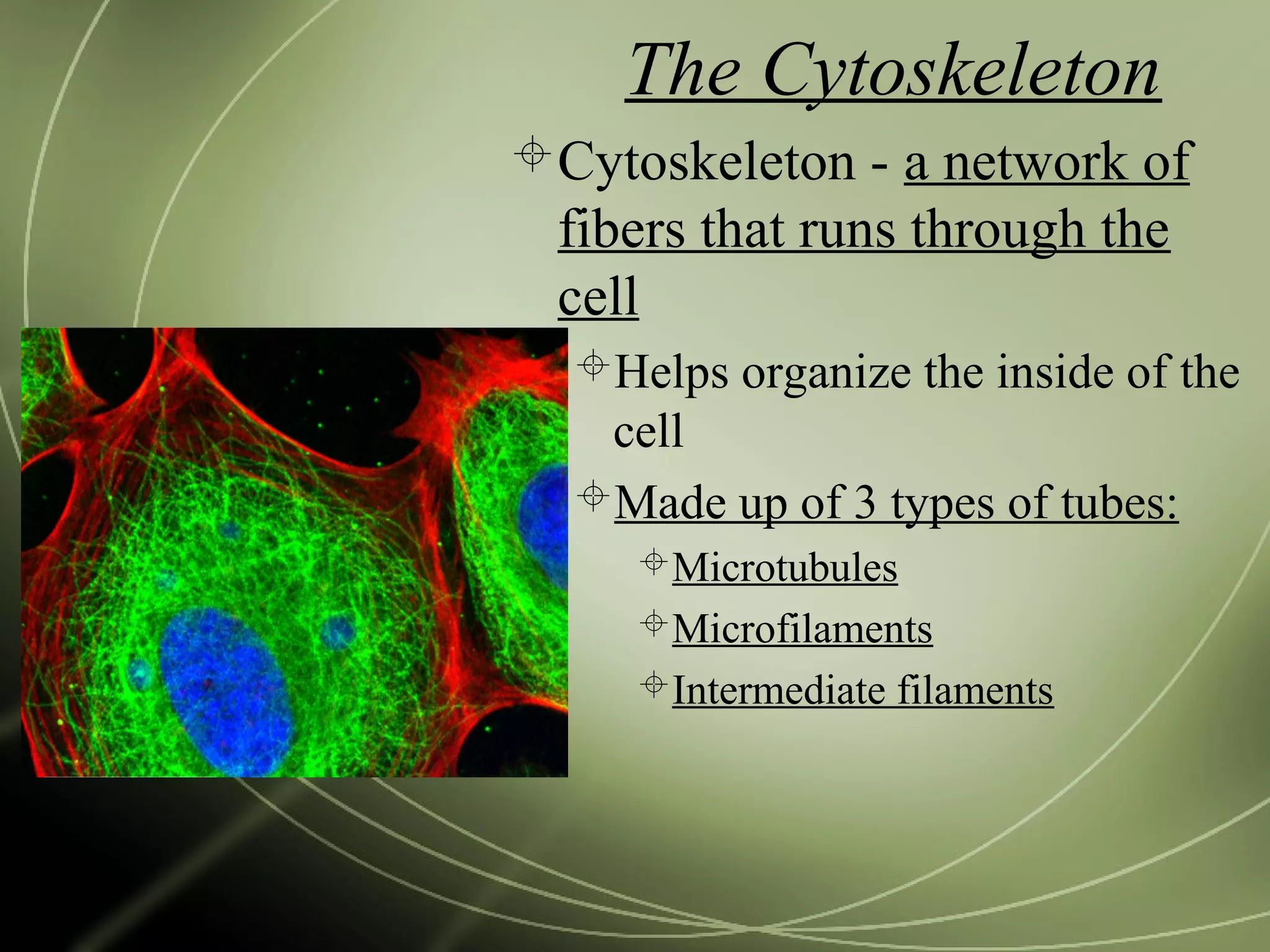
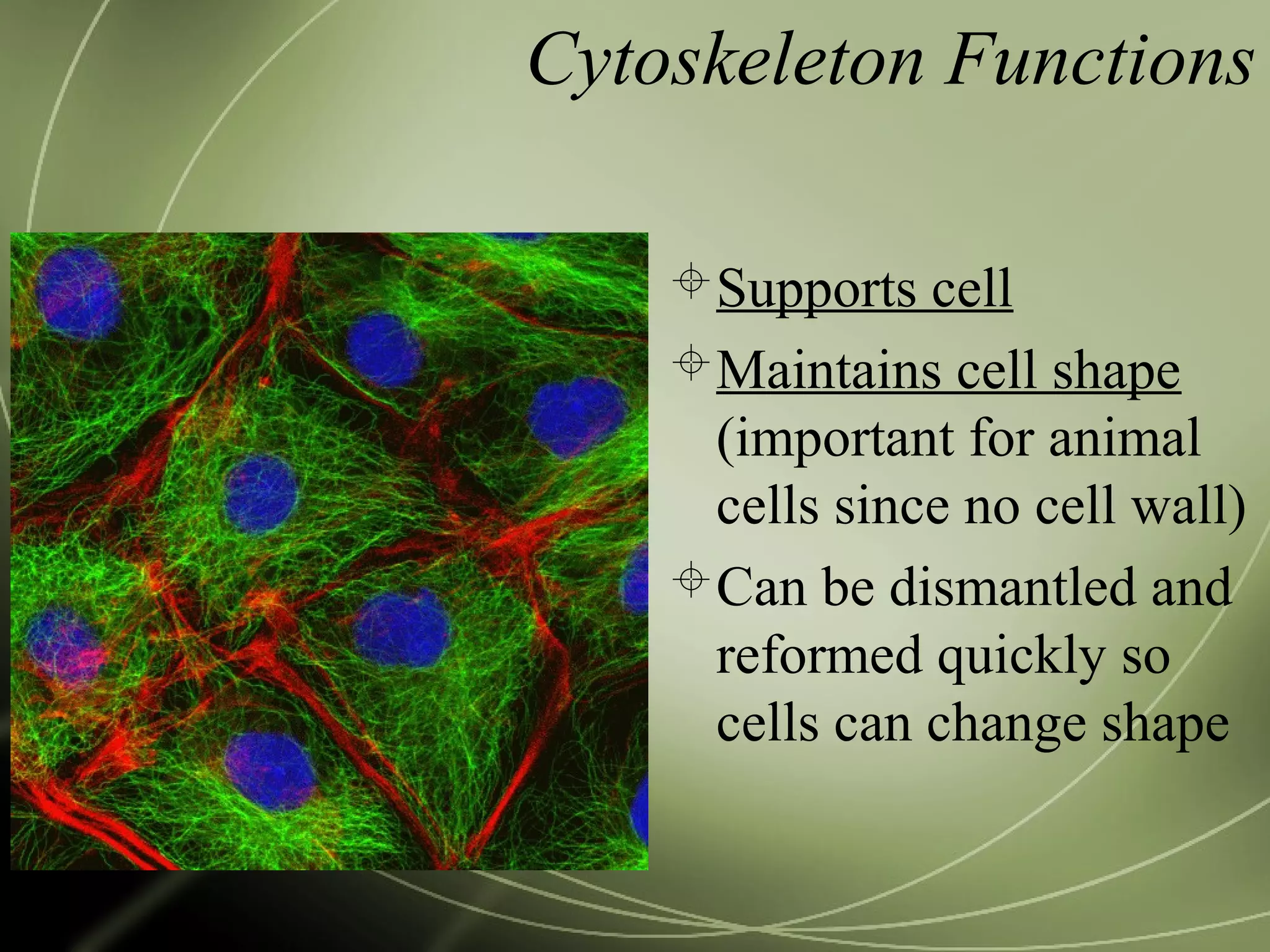
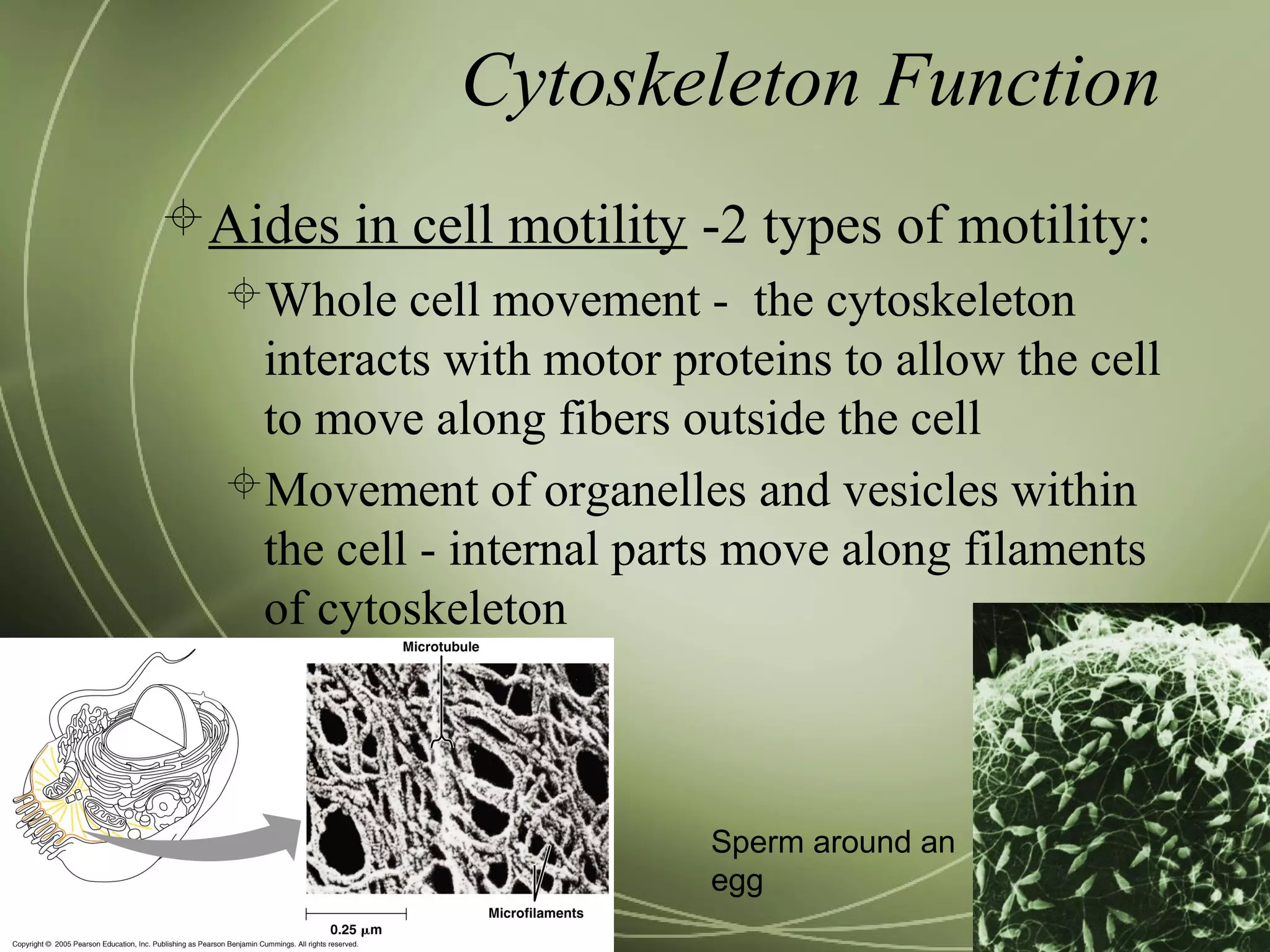
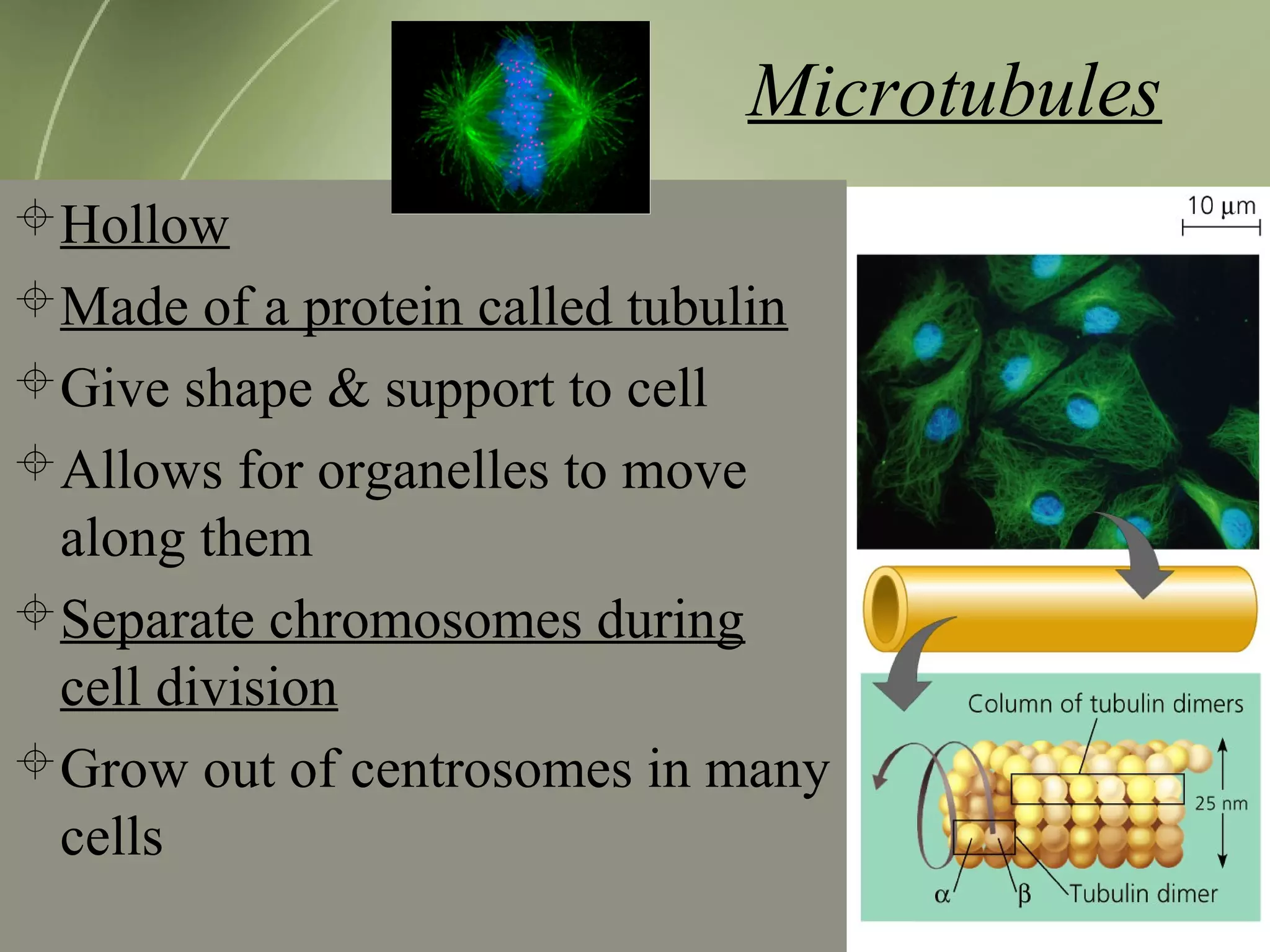
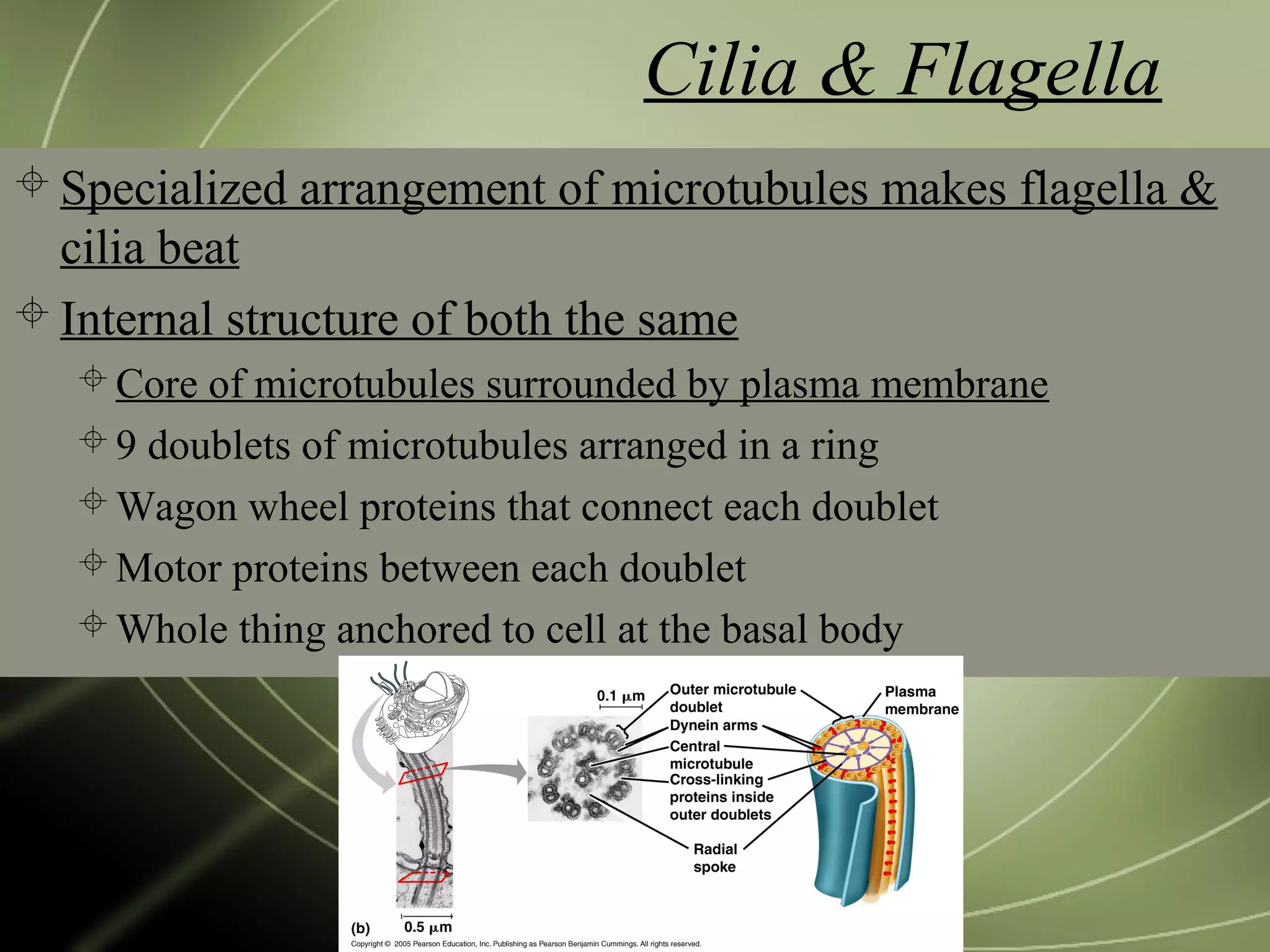
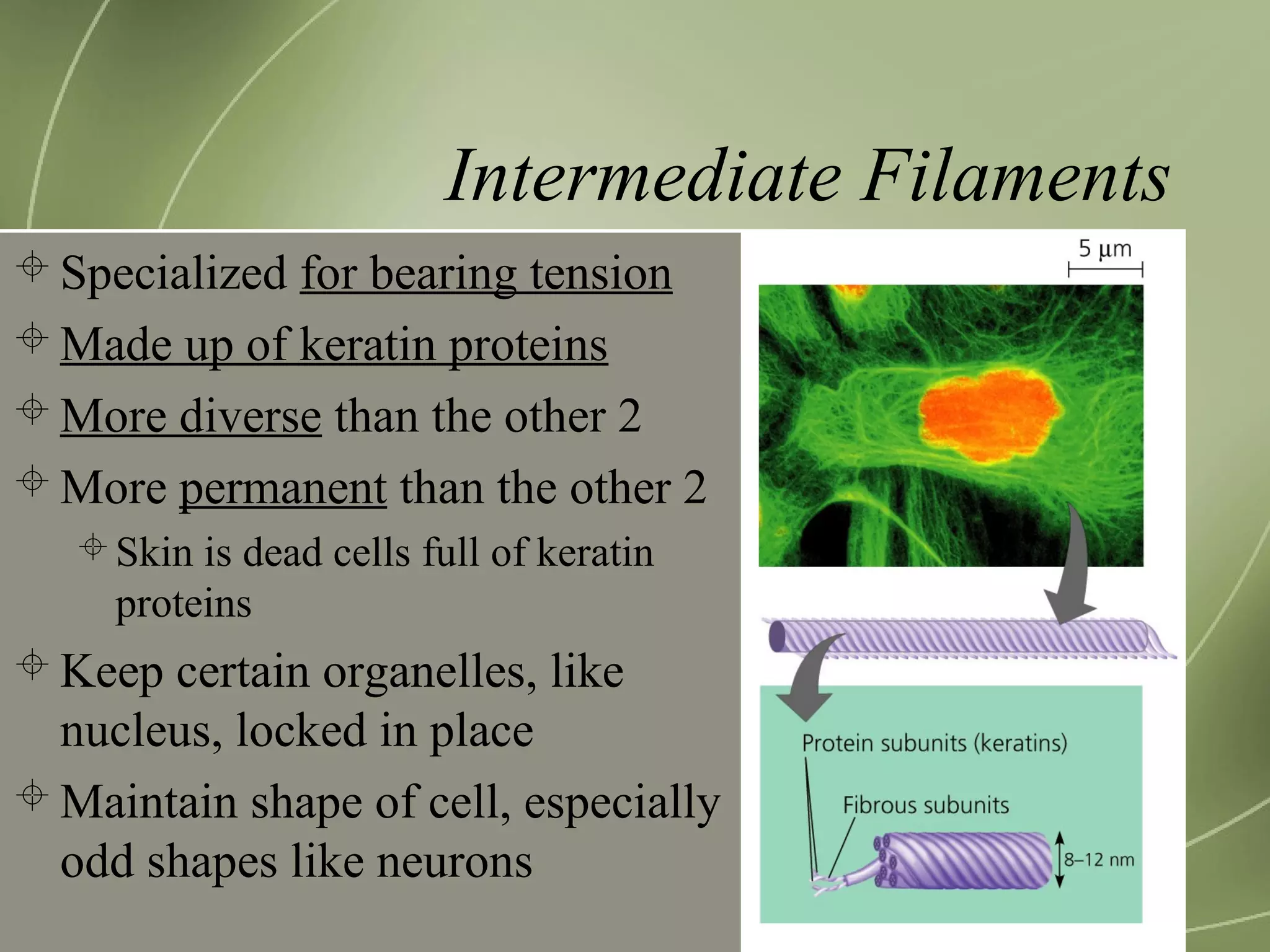
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have two defining features in common: they both have two membranes separating their interior from the cytosol, and they contain their own DNA and ribosomes. They are not part of the endomembrane system because they predate its evolution and were originally independent prokaryotic cells that became incorporated into eukaryotic cells via endosymbiosis. Mitochondria provide energy for the cell through respiration while chloroplasts perform photosynthesis.