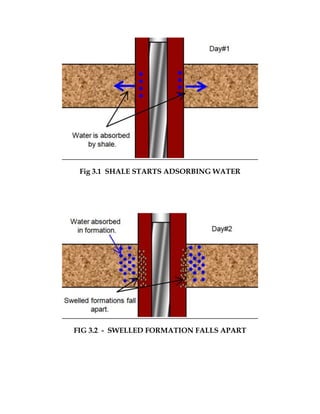
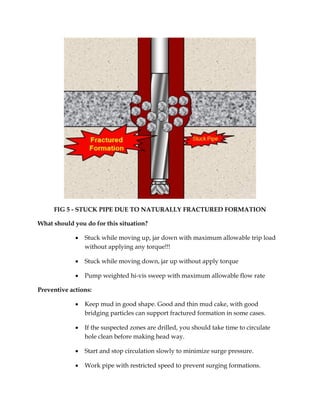
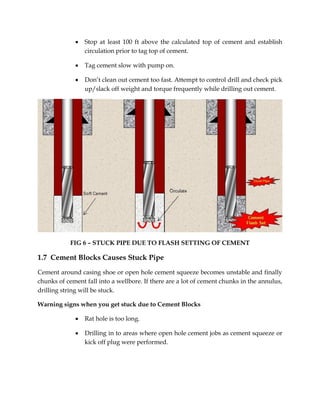
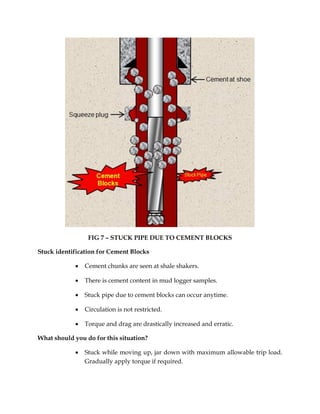
The document discusses various causes of stuck pipe that fall under three main categories: 1) packing off and bridging, 2) differential sticking, and 3) wellbore geometry issues. Under the first category of packing off and bridging, the document describes seven specific cases that can lead to stuck pipe, such as cutting settling in vertical or deviated wells, shale instability, unconsolidated formations, and cement blocks. Preventive actions and procedures for addressing each stuck pipe scenario are provided.