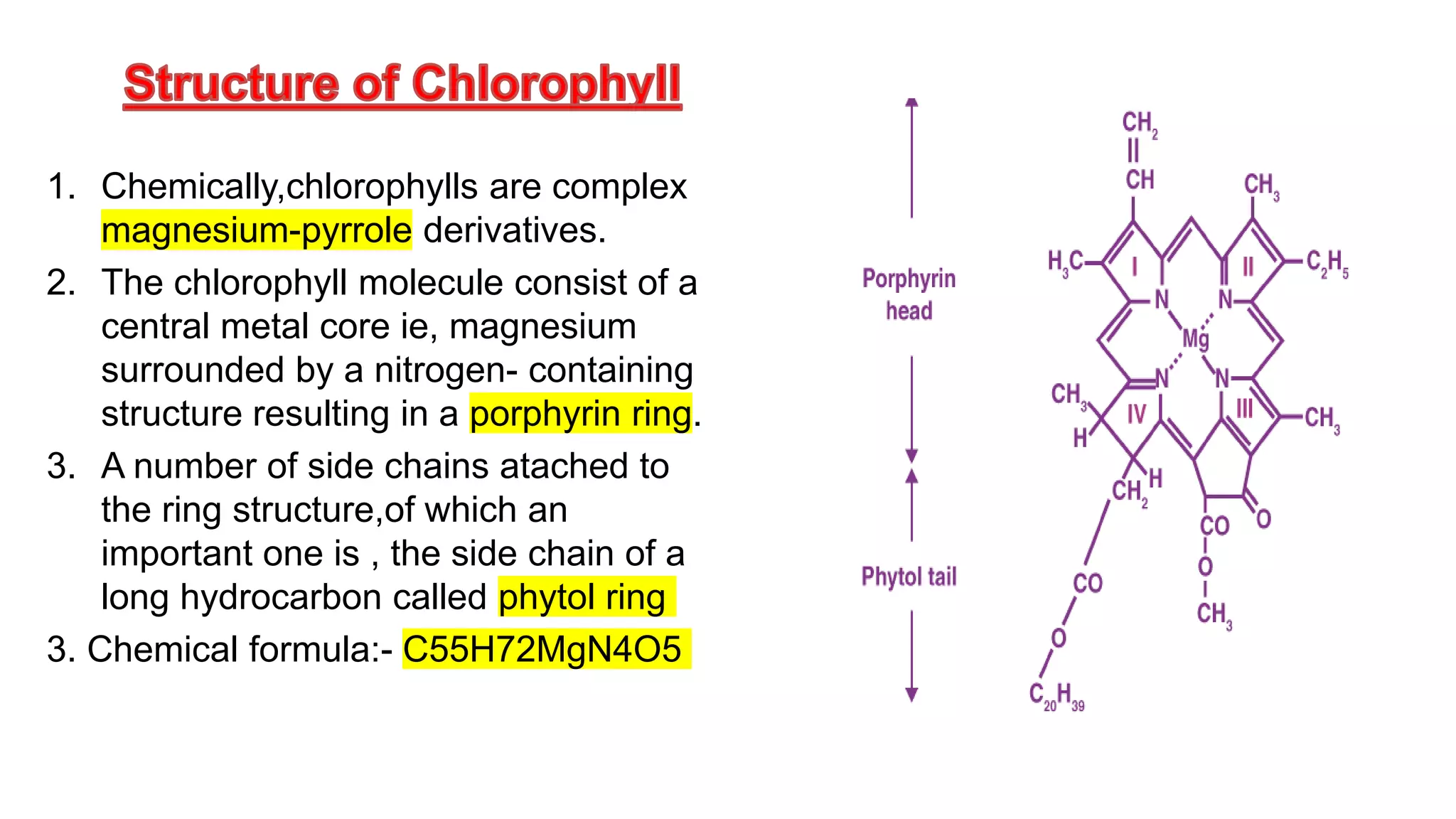
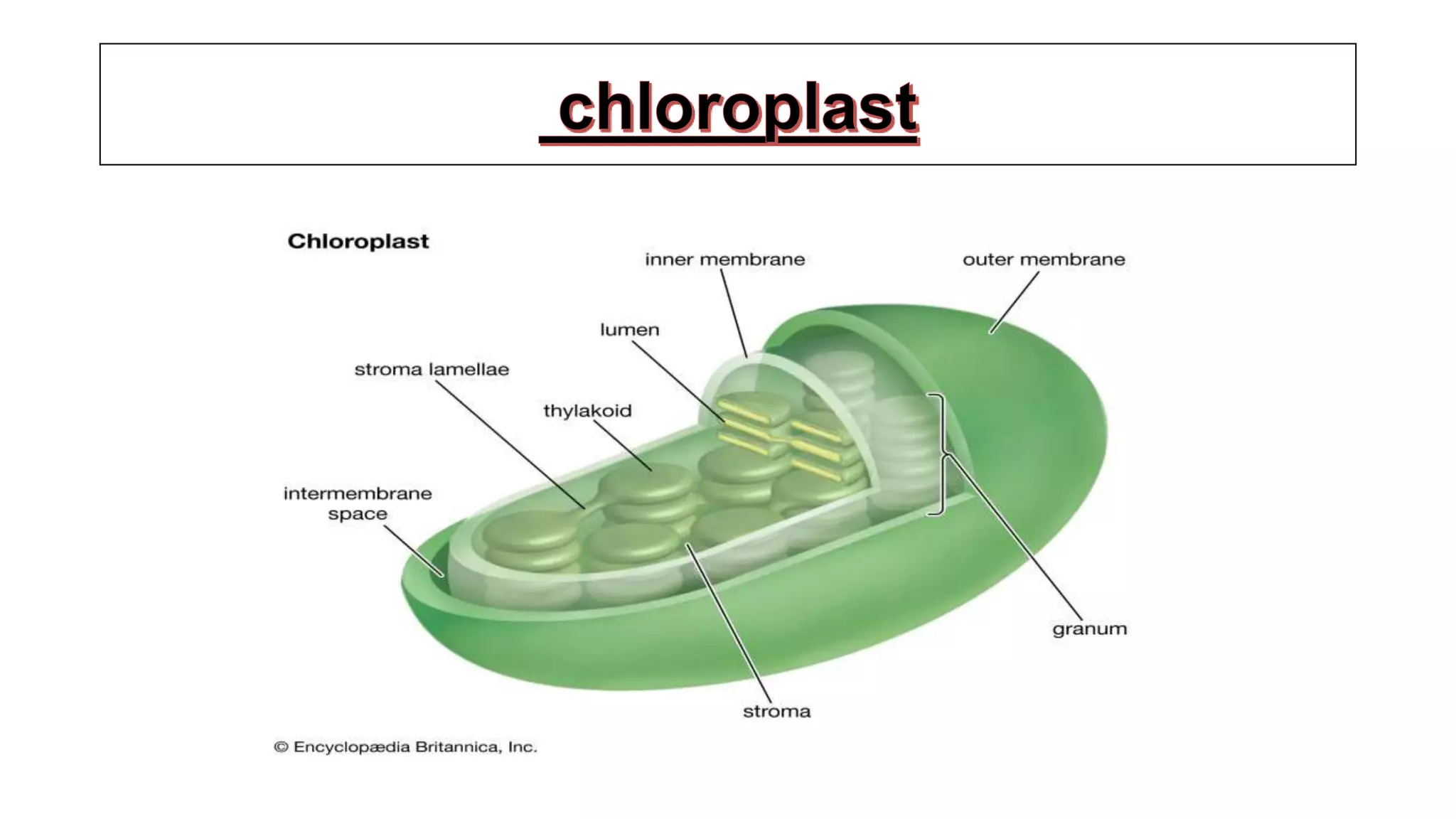
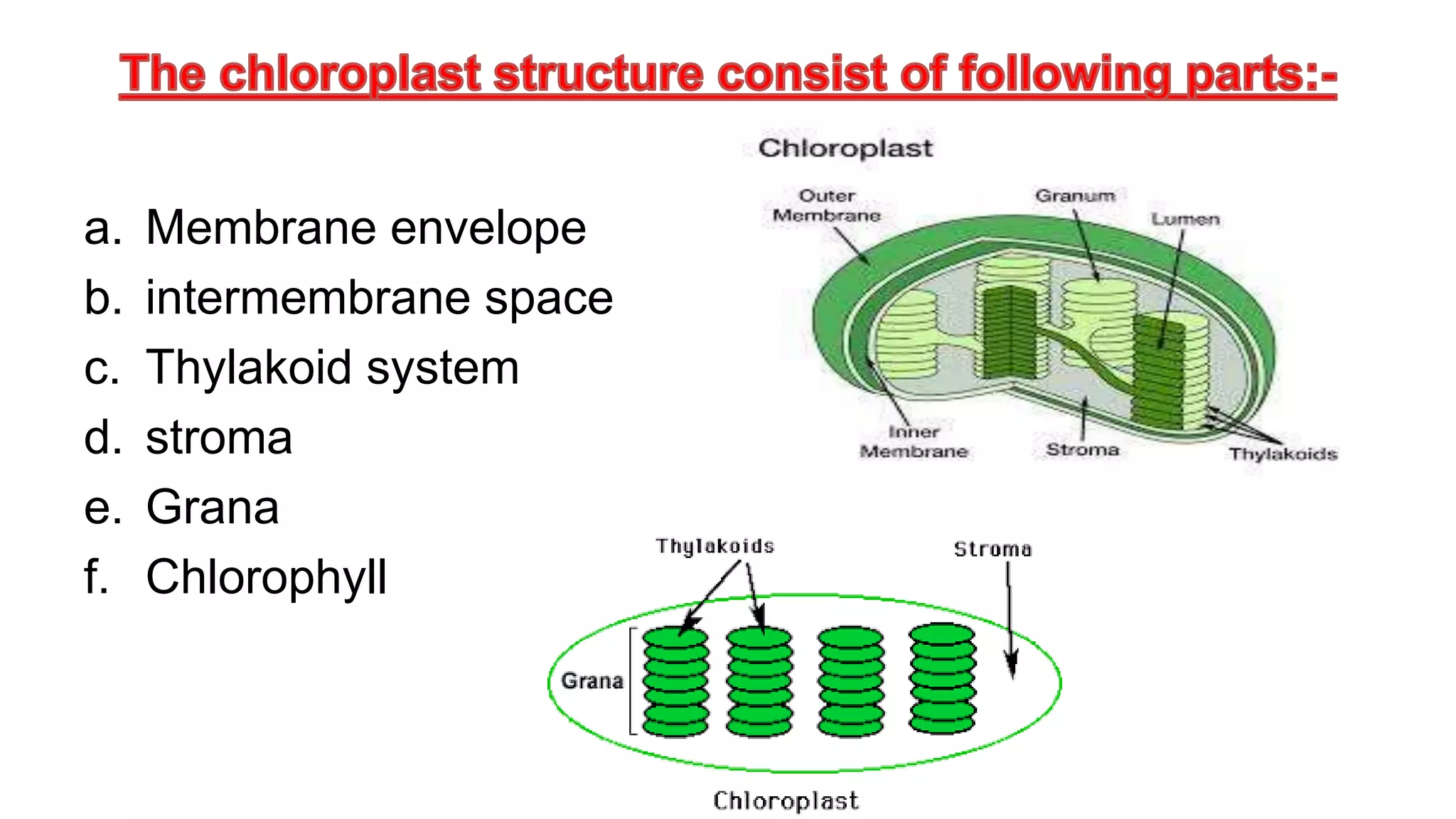
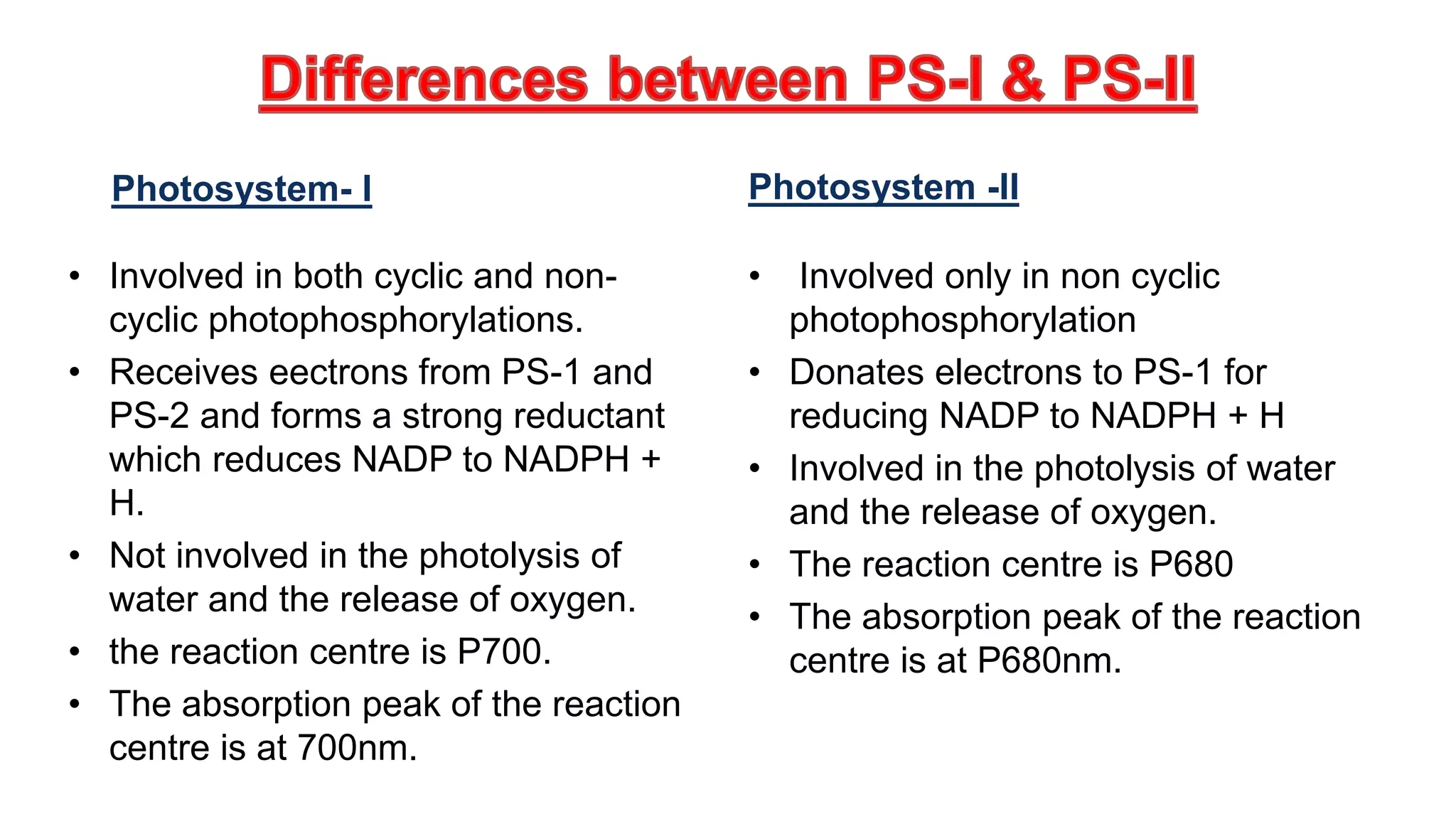
Chlorophyll is found in chloroplasts and is essential for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy which is then used to convert carbon dioxide to carbohydrates via photosystems I and II. Chloroplasts contain a double membrane and thylakoid system. The thylakoids contain pigment systems called photosystem I and photosystem II which drive photophosphorylation and the photolysis of water. Photosystem I receives electrons and reduces NADP while photosystem II donates electrons, is involved in water photolysis, and has a reaction center absorbing at 680nm.